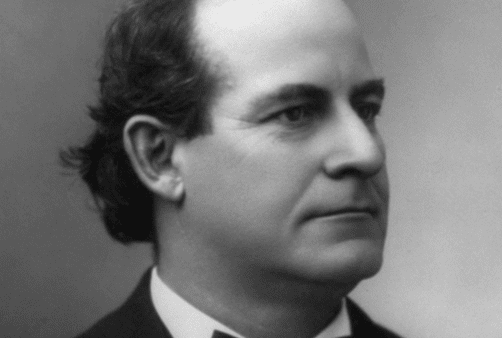Introduction
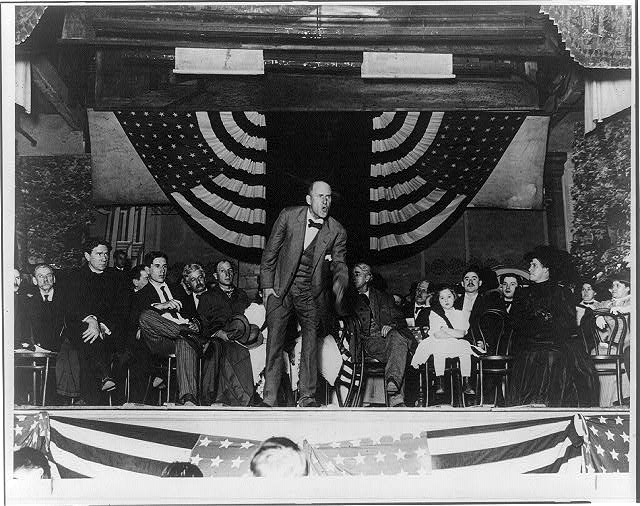
William Jennings Bryan (1860–1925) was an American lawyer, orator, and politician who ran unsuccessfully for the U.S. Presidency in 1896, 1900, and 1908. A member of the Democratic Party, he represented Nebraska in the U.S House of Representatives (1891–95) and served as secretary of state under Woodrow Wilson (1913–15). Widely known for his populist rhetoric, Bryan professed to argue on behalf of the interest of the common man, often the western farmer, against the interests of the eastern financial elite.
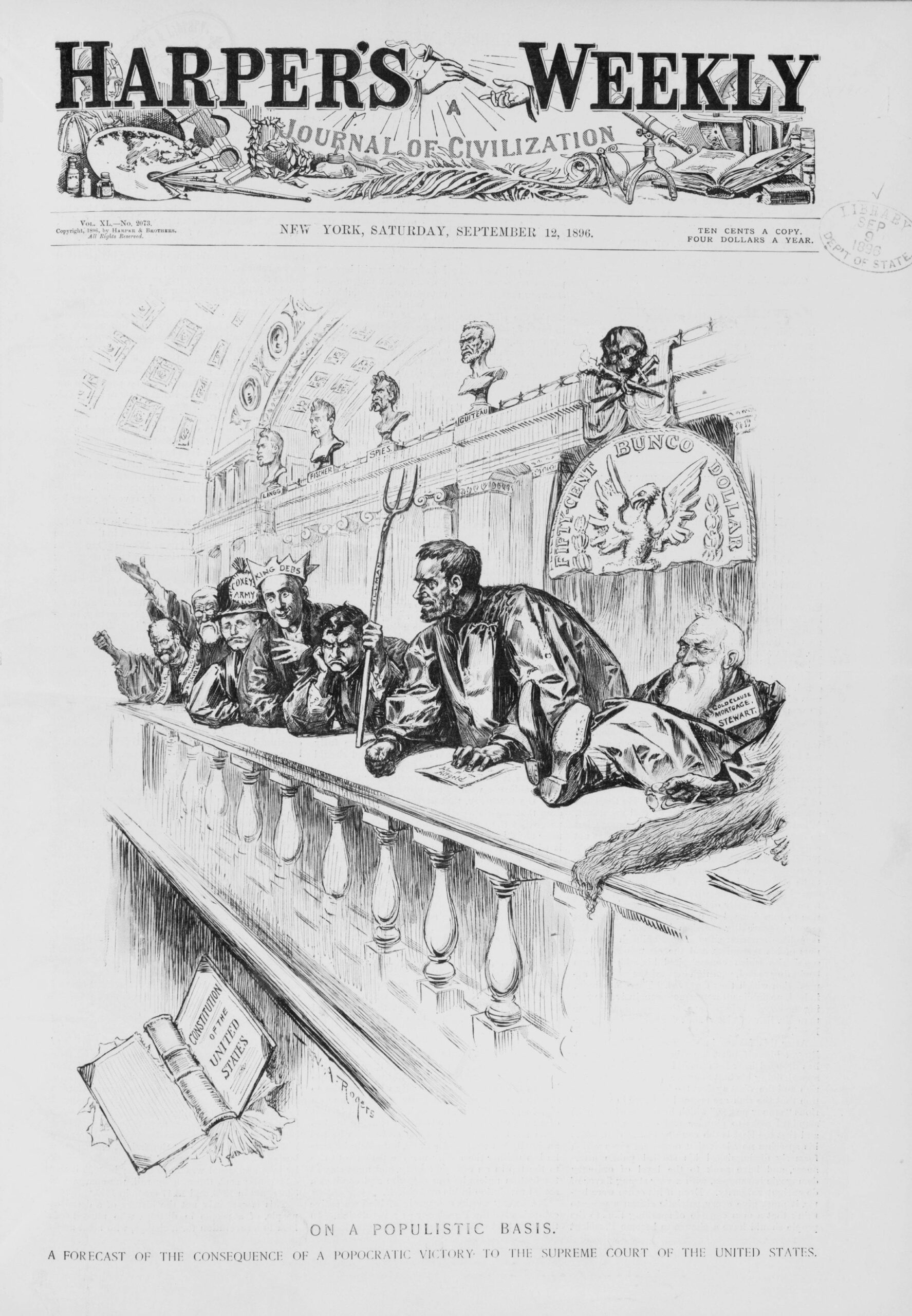
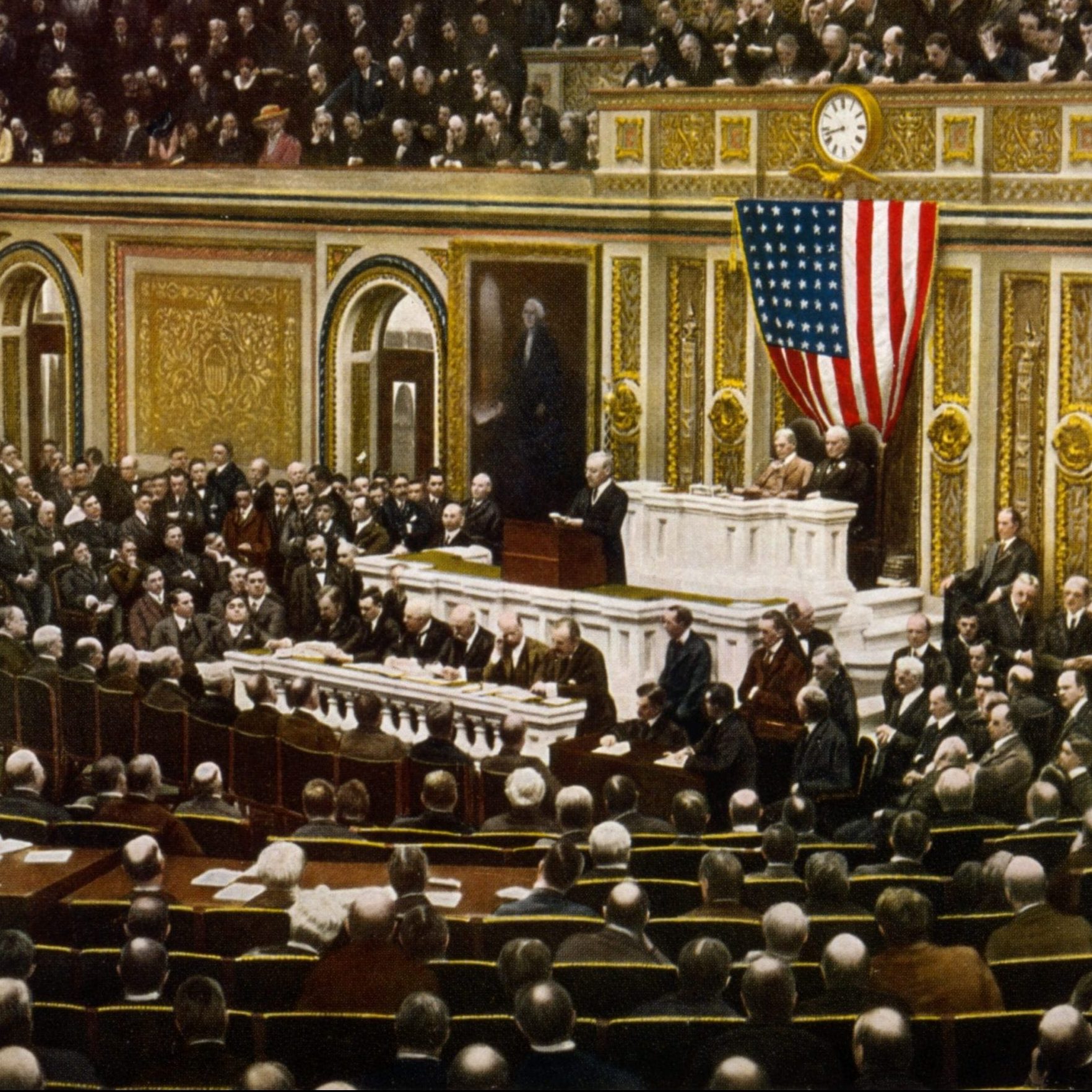
As part of the free silver movement, Bryan and his supporters challenged Grover Cleveland and the other Democrats who supported the gold standard, upon which the U.S. had essentially operated since the Coinage Act of 1873. Prior to this legislation, under the Constitution, the country had operated on a policy of bimetallism; that is, a currency backed by gold and silver. Bryan argued that the supply of paper money in the United States need not be backed by gold alone. Money should also be backed by silver, a metal in more plentiful supply, especially in the West, where silver was mined. Allowing silver to be coined on demand, and in unlimited supply, would increase the money supply and lead to inflation. To the chagrin of creditors, many populist farmers supported this monetary policy because they could pay land mortgages with cheaper dollars and increase the prices of their crops (see The Populist Party Platform and Expression of Sentiments). The populist era of American politics was dominated by such debates over U.S. monetary policy. At the 1896 Democratic National Convention in Chicago, Bryan offered his famed “Cross of Gold” address, in which he made the case for bimetallism and free silver. Bryan secured not only the Democratic and Populist nominations for the presidency, but also the nomination of the short-lived, Nevada-based Silver Party.
Source: William Jennings Bryan, The First Battle: A Story of the Campaign of 1896 (Chicago: W. B. Conkey, 1896), 199–206, available online at the Hathi Trust Digital Library: https://babel.hathitrust.org/cgi/pt?id=uc2.ark:/13960/t93778b3h&view=1up&seq=203.
Mr. Chairman and Gentlemen of the Convention:
. . . On the fourth of March, 1895, a few Democrats, most of them members of Congress, issued an address to the Democrats of the nation, asserting that the money question was the paramount issue of the hour; declaring that a majority of the Democratic Party had the right to control the position of the party on this paramount issue; and concluding with the request that the believers in the free coinage of silver in the Democratic Party should organize, take charge of, and control the policy of the Democratic Party. Three months later, at Memphis, an organization was perfected, and the silver Democrats went forth openly and courageously proclaiming their belief, and declaring that, if successful, they would crystallize in a platform the declaration which they had made. Then began the conflict. . . .
We do not come as individuals. As individuals we might have been glad to compliment the gentleman from New York (Senator Hill), but we know that the people for whom we speak would never be willing to put him in a position where he could thwart the will of the Democratic Party.[1] I say it was not a question of persons; it was a question of principle, and it is not with gladness, my friends, that we find ourselves brought into conflict with those who are now arrayed on the other side.
The gentleman who just preceded me (ex-governor Russell) spoke of the state of Massachusetts; let me assure him that not one person in all this convention entertains the least hostility to the people of the state of Massachusetts, but we stand here representing people who are the equals, before the law, of the greatest citizens in the state of Massachusetts.[2] When you (turning to gold delegates) come before us and tell us that we are about to disturb your business interests, we reply that you have disturbed our business interests by your course.
We say to you that you have made the definition of a businessman too limited in its application. The man who is employed for wages is as much a businessman as his employer; the attorney in a country town is as much a businessman as the corporation counsel in a great metropolis; the merchant at the crossroads store is as much a businessman as the merchant of New York; the farmer who goes forth in the morning and toils all day—who begins in the spring and toils all summer—and who by the application of brain and muscle to the natural resources of this country creates wealth, is as much a businessman as the man who goes upon the board of trade and bets upon the price of grain; the miners who go down a thousand feet into the earth, or climb two thousand feet upon the cliffs, and bring forth from their hiding places the precious metals to be poured in the channels of trade are as much businessmen as the few financial magnates who, in a back room, corner the money of the world. We come to speak for this broader class of businessmen.
Ah, my friends, we say not one word against those who live upon the Atlantic Coast; but those hardy pioneers who have braved all the dangers of the wilderness, who have made the desert to blossom as the rose—the pioneers away out there (pointing to the west), rearing their children near to Nature’s heart, where they can mingle their voices with the voices of the birds—out there where they have erected schoolhouses for the education of their young, churches where they praise their Creator, and cemeteries where rest the ashes of their dead—these people, we say, are as deserving of the consideration of our party as any people in this country. It is for these that we speak. We do not come as aggressors. Our war is not a war of conquest; we are fighting in the defense of our homes, our families, and posterity. We have petitioned, and our petitions have been scorned; we have entreated, and our entreaties have been disregarded; we have begged, and they have mocked when our calamity came. We beg no longer; we entreat no more; we petition no more. We defy them.
The gentleman from Wisconsin has said he fears a Robespierre.[3] My friend, in this land of the free you need not fear that the tyrant will spring up from among the people. What we need is an Andrew Jackson to stand, as Jackson stood, against the encroachments of organized wealth.
They tell us that this platform was made to catch votes. We reply to them that changing conditions make new issues; that the principles upon which democracy rests are as everlasting as the hills, but that they must be applied to new conditions as they arise. Conditions have arisen, and we are here to meet those conditions. They tell us that the income tax ought not to be brought in here; that it is a new idea. They criticize us for our criticism of the Supreme Court of the United States. My friends, we have not criticized; we have simply called attention to what you already know. If you want criticisms, read the dissenting opinions of the Court. There you will find criticisms.[4] They say that we passed an unconstitutional law; we deny it. The income tax law was not unconstitutional when it was passed; it was not unconstitutional when it went before the Supreme Court for the first time; it did not become unconstitutional until one of the judges changed his mind, and we cannot be expected to know when a judge will change his mind. The income tax is just. It simply intends to put the burdens of government justly upon the backs of the people. I am in favor of an income tax. When I find a man who is not willing to bear his share of the burdens of the government which protects him, I find a man who is unworthy to enjoy the blessings of a government like ours.
They say we are opposing national bank currency; it is true. . . . We say in our platform that we believe that the right to coin and issue money is a function of government. We believe it. We believe that it is a part of sovereignty, and can no more with safety be delegated to private individuals than we could afford to delegate to private individuals the power to make penal statutes or levy taxes. Mr. Jefferson, who was once regarded as good Democratic authority, seems to have differed in opinion from the gentleman who has addressed us on the part of the minority. Those who are opposed to this proposition tell us that the issue of paper money is a function of the bank, and that the government ought to go out of the banking business. I stand with Jefferson rather than with them, and tell them, as he did, that the issue of money is a function of government, and that the banks ought to go out of the governing business. . . .
Let me call your attention to two or three important things. The gentleman from New York says that he will propose an amendment to the platform providing that the proposed change in our monetary system shall not affect contracts already made. Let me remind you that there is no intention of affecting those contracts which according to present laws are made payable in gold; but if he means to say that we cannot change our monetary system without protecting those who have loaned money before the change was made, I desire to ask him where, in law or in morals, he can find justification for not protecting the debtors when the act of 1873 was passed, if he now insists that we must protect the creditors.[5]
He says he will also propose an amendment that provides for the suspension of free coinage if we fail to maintain the parity within a year. We reply that when we advocate a policy which we believe will be successful, we are not compelled to raise a doubt as to our own sincerity by trying to show what we shall do if we fail. I ask him, if he would apply his logic to us, why he does not apply it to himself. He says that he wants this country to try to secure an international agreement [on bimetallism].[6] Why does he not tell us what he is going to do if he fails to secure an international agreement? There is more reason for him to do that than there is for us to provide against the failure to maintain the parity. Our opponents have tried for twenty years to secure an international agreement, and those are waiting for it most patiently who do not want it at all.
And now, my friends, let me come to the paramount issue. If they ask us why it is that we say more on the money question than we say upon the tariff question, I reply that, if protection has slain its thousands, the gold standard has slain its tens of thousands. If they ask us why we do not embody in our platform all the things that we believe in, we reply that when we have restored the money of the Constitution all other necessary reforms will be possible; but that until this is done there is no reform that can be accomplished.
Why is it that within three months such a change has come over the country? Three months ago, when it was confidently asserted that those who believe in the gold standard would frame our platform and nominate our candidates, even the advocates of the gold standard did not think that we could elect a president. And they had good reasons for their doubt, because there is scarcely a state here today asking for the gold standard that is not within the absolute control of the Republican Party. But note the change. Mr. [William] McKinley was nominated at St. Louis upon a platform that declared for the maintenance of the gold standard until it can be changed into bimetallism by international agreement.[7] Mr. McKinley was the most popular man among the Republicans, and three months ago everybody in the Republican Party prophesied his election. How is it today? Why, the man who was once pleased to think that he looked like Napoleon—that man shudders today when he thinks that he was nominated on the anniversary of the battle of Waterloo. Not only that, but as he listens he can hear with ever-increasing distinctness the sound of the waves as they beat upon the lonely shores of St. Helena.[8]
Why this change? Ah, my friends, is not the change evident to anyone who will look at the matter? No private character, however pure, no personal popularity, however great, can protect from the avenging wrath of an indignant people the man who will either declare that he is in favor of fastening the gold standard upon this country, or who is willing to surrender the right of self-government and place the legislative control of our affairs in the hands of foreign potentates and powers.
We go forth confident that we shall win. Why? Because upon the paramount issue in this campaign there is not a spot of ground upon which the enemy will dare to challenge battle. If they tell us that the gold standard is a good thing, we shall point to their platform and tell them that their platform pledges the party to get rid of a gold standard and substitute bimetallism. If the gold standard is a good thing, why try to get rid of it? I call your attention to the fact that some of the very people who are in this convention today and who tell you that we ought to declare in favor of international bimetallism—thereby declaring that the gold standard is wrong and that the principle of bimetallism is better—these very people four months ago were open and avowed advocates of the gold standard, and were then telling us that we could not legislate two metals together, even with the aid of all the world. If the gold standard is a good thing, we ought to declare in favor of its retention and not in favor of abandoning it; and if the gold standard is a bad thing why should we wait until other nations are willing to help us to let go? Here is the line of battle, and we care not upon which issue they force the fight; we are prepared to meet them on either issue or on both. If they tell us that the gold standard is the standard of civilization, we reply to them that this, the most enlightened of all the nations of the earth, has never declared for a gold standard, and that both the great parties this year are declaring against it. If the gold standard is the standard of civilization, why, my friends, should we not have it? If they come to meet us on that issue we can present the history of our nation. More than that; we can tell them that they will search the pages of history in vain to find a single instance in which the common people of any land have ever declared themselves in favor of the gold standard. They can find where the holders of fixed investments have declared for a gold standard, but not where the masses have.
Mr. Carlisle said in 1878 that this was a struggle between “the idle holders of idle capital” and “the struggling masses who produce the wealth and pay the taxes of the country”; and, my friends, the question we are to decide is: Upon which side will the Democratic Party fight; upon the side of the “idle holders of idle capital” or upon the side of “the struggling masses?”[9] That is the question which the party must answer first, and then it must be answered by each individual hereafter. The sympathies of the Democratic Party, as shown by the platform, are on the side of the struggling masses who have ever been the foundation of the Democratic Party. There are two ideas of government. There are those who believe that, if you will only legislate to make the well-to-do prosperous, their prosperity will leak through on those below. The Democratic idea, however, has been that if you legislate to make the masses prosperous, their prosperity will find its way up through every class which rests upon them.
You come to us and tell us that the great cities are in favor of the gold standard; we reply that the great cities rest upon our broad and fertile prairies. Burn down your cities and leave our farms, and your cities will spring up again as if by magic; but destroy our farms and the grass will grow in the streets of every city in the country.
My friends, we declare that this nation is able to legislate for its own people on every question, without waiting for the aid or consent of any other nation on earth; and upon that issue we expect to carry every state in the Union. I shall not slander the inhabitants of the fair state of Massachusetts nor the inhabitants of the state of New York by saying that, when they are confronted with the proposition, they will declare that this nation is not able to attend to its own business. It is the issue of 1776 over again. Our ancestors, when but three millions in number, had the courage to declare their political independence of every other nation; shall we, their descendants, when we have grown to seventy millions, declare that we are less independent than our forefathers? No, my friends, that will never be the verdict of our people. Therefore, we care not upon what lines the battle is fought. If they say bimetallism is good, but that we cannot have it until some other nations help us, we reply that, instead of having a gold standard because England has, we will restore bimetallism, and then let England have bimetallism because the United States has it. If they dare to come out in the open field and defend the gold standard as a good thing, we will fight them to the uttermost. Having behind us the producing masses of this nation and the world, supported by the commercial interests, the laboring interests, and the toilers everywhere, we will answer their demand for a gold standard by saying to them: You shall not press down upon the brow of labor this crown of thorns, you shall not crucify mankind upon a cross of gold.
- 1. David Bennett Hill (1843–1910) was a Democratic senator from New York. He opposed Bryan’s 1896 nomination for the presidency but supported him during the general election.
- 2. William Eustis Russell (1857–1896) was a former governor of Massachusetts who vehemently opposed the free silver movement. Himself a possible candidate for the Democratic nomination in 1896, Russell had delivered a speech in favor of the gold standard just before Bryan’s “Cross of Gold” speech.
- 3. Senator William Freeman Vilas of Wisconsin (1840–1908). Maximilien Robespierre (1758–1794) was a French politician closely associated with the Reign of Terror in 1793–94, which resulted in the execution of many thousands of suspected enemies of the French Revolution.
- 4. Bryan here refers to the recent U.S. Supreme Court decision Pollock v. Farmers’ Loan and Trust Company, 157 U.S. 429 (1895). In a narrow 5-4 decision, the Court struck down an income tax established by the Revenue Act of 1894. The Court reasoned that the provision was an unapportioned direct tax and that the U.S. Constitution required direct taxes to be apportioned according to population. The ruling would later be rendered moot by the passage of the Sixteenth Amendment in 1913.
- 5. Provisions of the Coinage Act of 1873 effectively abandoned bimetallism and embraced the gold standard. The act demonetized silver, abolishing the standard silver dollar. Proponents of free silver referred to the act as the “Crime of ’73.” The inability to turn silver into cash was contrary to the immediate economic interests of many western farmers and miners.
- 6. Some proposed that bimetallism ought to be adopted only if the United States could negotiate an international agreement to recognize silver, along with gold, as backing for key European currencies.
- 7. William McKinley (1843–1901), then governor of Ohio, was the nominee of the Democratic Party for president in 1896.
- 8. St. Helena is a remote island in the south Atlantic to which Napoleon was exiled after his defeat at Waterloo in 1815.
- 9. A Bourbon Democrat—a Democrat who supported free markets and the gold standard—John G. Carlisle (1834–1910) represented Kentucky as a U.S. congressman (1877–90) and a U.S. senator (1890–93). During his national political career, he served as Speaker of the House as well as secretary of the Treasury.

Conversation-based seminars for collegial PD, one-day and multi-day seminars, graduate credit seminars (MA degree), online and in-person.