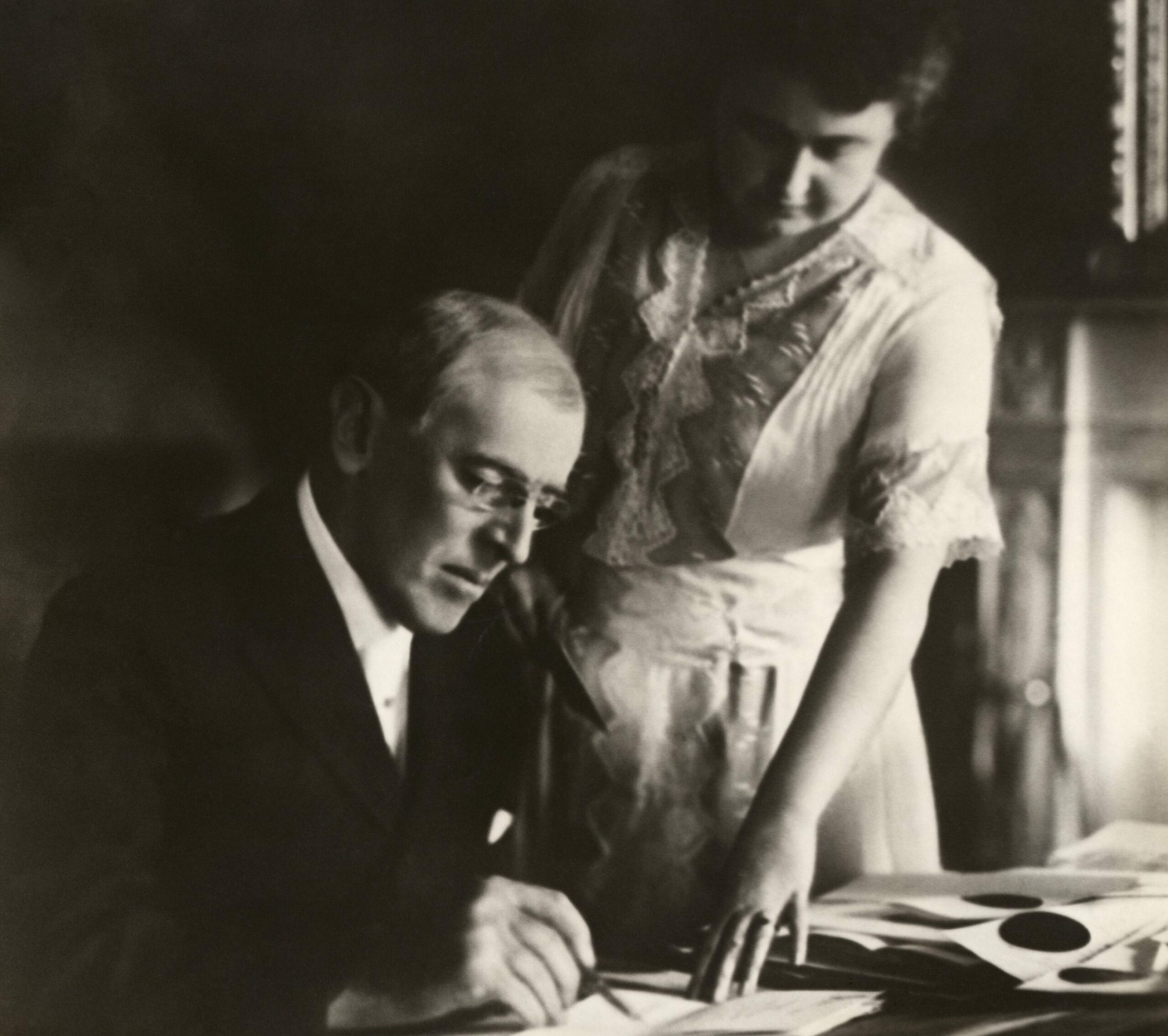
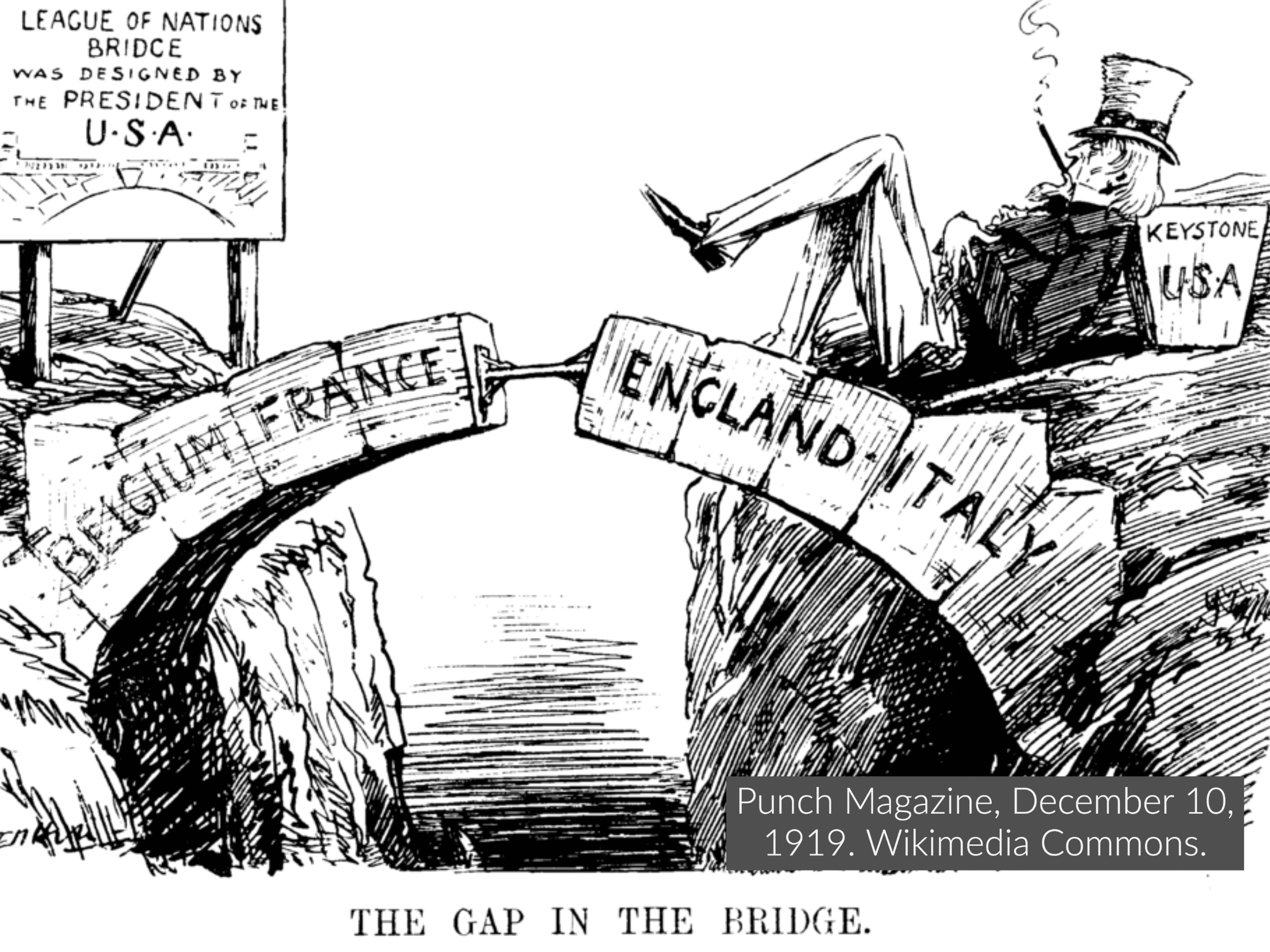
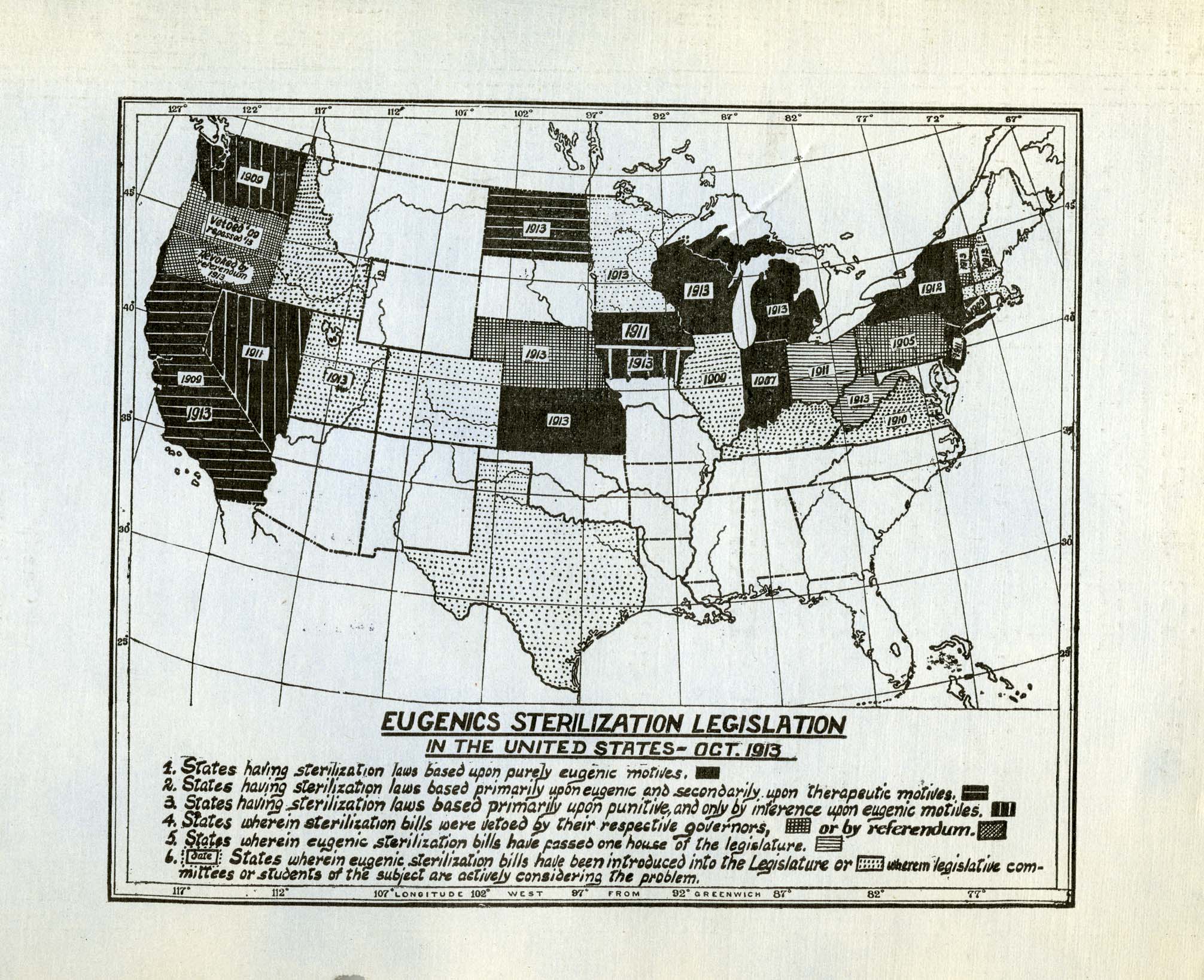
No study questions
No related resources
Introduction
President's Annual Message, 59th Cong., 2nd sess., Congressional Record 41, p 1 S22. https://www.congress.gov/bound-congressional-record/1906/12/04.
To the Senate and House of Representatives:
As a nation we still continue to enjoy a literally unprecedented prosperity; and it is probable that only reckless speculation and disregard of legitimate business methods on the part of the business world can materially mar this prosperity.
No Congress in our time has done more good work of importance than the present Congress. There were several matters left unfinished at your last session, however, which I most earnestly hope you will complete before your adjournment.
I again recommend a law prohibiting all corporations from contributing to the campaign expenses of any party. Such a bill has already past one House of Congress. Let individuals contribute as they desire; but let us prohibit in effective fashion all corporations from making contributions for any political purpose, directly or indirectly. Another bill which has just past one House of the Congress and which it is urgently necessary should be enacted into law is that conferring upon the Government the right of appeal in criminal cases on questions of law. This right exists in many of the States; it exists in the District of Columbia by act of the Congress. It is of course not proposed that in any case a verdict for the defendant on the merits should be set aside. Recently in one district where the Government had indicted certain persons for conspiracy in connection with rebates, the court sustained the defendant’s demurrer; while in another jurisdiction an indictment for conspiracy to obtain rebates has been sustained by the court, convictions obtained under it, and two defendants sentenced to imprisonment. The two cases referred to may not be in real conflict with each other, but it is unfortunate that there should even be an apparent conflict. At present there is no way by which the Government can cause such a conflict, when it occurs, to be solved by an appeal to a higher court; and the wheels of justice are blocked without any real decision of the question. I can not too strongly urge the passage of the bill in question. A failure to pass it will result in seriously hampering the Government in its effort to obtain justice, especially against wealthy individuals or corporations who do wrong; and may also prevent the Government from obtaining justice for wage-workers who are not themselves able effectively to contest a case where the judgment of an inferior court has been against them. I have specifically in view a recent decision by a district judge leaving railway employees without remedy for violation of a certain so-called labor statute. It seems an absurdity to permit a single district judge, against what may be the judgment of the immense majority of his colleagues on the bench, to declare a law solemnly enacted by the Congress to be "unconstitutional," and then to deny to the Government the right to have the Supreme Court definitely decide the question.
It is well to recollect that the real efficiency of the law often depends not upon the passage of acts as to which there is great public excitement, but upon the passage of acts of this nature as to which there is not much public excitement, because there is little public understanding of their importance, while the interested parties are keenly alive to the desirability of defeating them. The importance of enacting into law the particular bill in question is further increased by the fact that the Government has now definitely begun a policy of resorting to the criminal law in those trust and interstate commerce cases where such a course offers a reasonable chance of success. At first, as was proper, every effort was made to enforce these laws by civil proceedings; but it has become increasingly evident that the action of the Government in finally deciding, in certain cases, to undertake criminal proceedings was justifiable; and though there have been some conspicuous failures in these cases, we have had many successes, which have undoubtedly had a deterrent effect upon evil-doers, whether the penalty inflicted was in the shape of fine or imprisonment—and penalties of both kinds have already been inflicted by the courts. Of course, where the judge can see his way to inflict the penalty of imprisonment the deterrent effect of the punishment on other offenders is increased; but sufficiently heavy fines accomplish much. Judge Holt, of the New York district court, in a recent decision admirably stated the need for treating with just severity offenders of this kind. His opinion runs in part as follows:
’The Government’s evidence to establish the defendant’s guilt was clear, conclusive, and undisputed. The case was a flagrant one. The transactions which took place under this illegal contract were very large; the amounts of rebates returned were considerable; and the amount of the rebate itself was large, amounting to more than one-fifth of the entire tariff charge for the transportation of merchandise from this city to Detroit. It is not too much to say, in my opinion, that if this business was carried on for a considerable time on that basis—that is, if this discrimination in favor of this particular shipper was made with an 18 instead of a 23 cent rate and the tariff rate was maintained as against their competitors—the result might be and not improbably would be that their competitors would be driven out of business. This crime is one which in its nature is deliberate and premeditated. I think over a fortnight elapsed between the date of Palmer’s letter requesting the reduced rate and the answer of the railroad company deciding to grant it, and then for months afterwards this business was carried on and these claims for rebates submitted month after month and checks in payment of them drawn month after month. Such a violation of the law, in my opinion, in its essential nature, is a very much more heinous act than the ordinary common, vulgar crimes which come before criminal courts constantly for punishment and which arise from sudden passion or temptation. This crime in this case was committed by men of education and of large business experience, whose standing in the community was such that they might have been expected to set an example of obedience to law upon the maintenance of which alone in this country the security of their property depends. It was committed on behalf of a great railroad corporation, which, like other railroad corporations, has received gratuitously from the State large and valuable privileges for the public’s convenience and its own, which performs quasi public functions and which is charged with the highest obligation in the transaction of its business to treat the citizens of this country alike, and not to carry on its business with unjust discriminations between different citizens or different classes of citizens. This crime in its nature is one usually done with secrecy, and proof of which it is very difficult to obtain. The interstate commerce act was past in 1887, nearly twenty years ago. Ever since that time complaints of the granting of rebates by railroads have been common, urgent, and insistent, and although the Congress has repeatedly past legislation endeavoring to put a stop to this evil, the difficulty of obtaining proof upon which to bring prosecution in these cases is so great that this is the first case that has ever been brought in this court, and, as I am formed, this case and one recently brought in Philadelphia are the only cases that have ever been brought in the eastern part of this country. In fact, but few cases of this kind have ever been brought in this country, East or West. Now, under these circumstances, I am forced to the conclusion, in a case in which the proof is so clear and the facts are so flagrant, it is the duty of the court to fix a penalty which shall in some degree be commensurate with the gravity of the offense. As between the two defendants, in my opinion, the principal penalty should be imposed on the corporation. The traffic manager in this case, presumably, acted without any advantage to himself and without any interest in the transaction, either by the direct authority or in accordance with what he understood to be the policy or the wishes of his employer.
"The sentence of this court in this case is, that the defendant Pomeroy, for each of the six offenses upon which he has been convicted, be fined the sum of $1,000, making six fines, amounting in all to the sum of $6,000; and the defendant, The New York Central and Hudson River Railroad Company, for each of the six crimes of which it has been convicted, be fined the sum of $18,000, making six fines amounting in the aggregate to the sum of $108,000, and judgment to that effect will be entered in this case."
In connection with this matter, I would like to call attention to the very unsatisfactory state of our criminal law, resulting in large part from the habit of setting aside the judgments of inferior courts on technicalities absolutely unconnected with the merits of the case, and where there is no attempt to show that there has been any failure of substantial justice. It would be well to enact a law providing something to the effect that:
No judgment shall be set aside or new trial granted in any cause, civil or criminal, on the ground of misdirection of the jury or the improper admission or rejection of evidence, or for error as to any matter of pleading or procedure unless, in the opinion of the court to which the application is made, after an examination of the entire cause, it shall affirmatively appear that the error complained of has resulted in a miscarriage of justice.
In my last message I suggested the enactment of a law in connection with the issuance of injunctions, attention having been sharply drawn to the matter by the demand that the right of applying injunctions in labor cases should be wholly abolished. It is at least doubtful whether a law abolishing altogether the use of injunctions in such cases would stand the test of the courts; in which case of course the legislation would be ineffective. Moreover, I believe it would be wrong altogether to prohibit the use of injunctions. It is criminal to permit sympathy for criminals to weaken our hands in upholding the law; and if men seek to destroy life or property by mob violence there should be no impairment of the power of the courts to deal with them in the most summary and effective way possible. But so far as possible the abuse of the power should be provided against by some such law as I advocated last year.
In this matter of injunctions there is lodged in the hands of the judiciary a necessary power which is nevertheless subject to the possibility of grave abuse. It is a power that should be exercised with extreme care and should be subject to the jealous scrutiny of all men, and condemnation should be meted out as much to the judge who fails to use it boldly when necessary as to the judge who uses it wantonly or oppressively. Of course a judge strong enough to be fit for his office will enjoin any resort to violence or intimidation, especially by conspiracy, no matter what his opinion may be of the rights of the original quarrel. There must be no hesitation in dealing with disorder. But there must likewise be no such abuse of the injunctive power as is implied in forbidding laboring men to strive for their own betterment in peaceful and lawful ways; nor must the injunction be used merely to aid some big corporation in carrying out schemes for its own aggrandizement. It must be remembered that a preliminary injunction in a labor case, if granted without adequate proof (even when authority can be found to support the conclusions of law on which it is founded), may often settle the dispute between the parties; and therefore if improperly granted may do irreparable wrong. Yet there are many judges who assume a matter-of-course granting of a preliminary injunction to be the ordinary and proper judicial disposition of such cases; and there have undoubtedly been flagrant wrongs committed by judges in connection with labor disputes even within the last few years, although I think much less often than in former years. Such judges by their unwise action immensely strengthen the hands of those who are striving entirely to do away with the power of injunction; and therefore such careless use of the injunctive process tends to threaten its very existence, for if the American people ever become convinced that this process is habitually abused, whether in matters affecting labor or in matters affecting corporations, it will be well-nigh impossible to prevent its abolition.
It may be the highest duty of a judge at any given moment to disregard, not merely the wishes of individuals of great political or financial power, but the overwhelming tide of public sentiment; and the judge who does thus disregard public sentiment when it is wrong, who brushes aside the plea of any special interest when the pleading is not rounded on righteousness, performs the highest service to the country. Such a judge is deserving of all honor; and all honor can not be paid to this wise and fearless judge if we permit the growth of an absurd convention which would forbid any criticism of the judge of another type, who shows himself timid in the presence of arrogant disorder, or who on insufficient grounds grants an injunction that does grave injustice, or who in his capacity as a construer, and therefore in part a maker, of the law, in flagrant fashion thwarts the cause of decent government. The judge has a power over which no review can be exercised; he himself sits in review upon the acts of both the executive and legislative branches of the Government; save in the most extraordinary cases he is amenable only at the bar of public opinion; and it is unwise to maintain that public opinion in reference to a man with such power shall neither be exprest nor led.
The best judges have ever been foremost to disclaim any immunity from criticism. This has been true since the days of the great English Lord Chancellor Parker, who said: "Let all people be at liberty to know what I found my judgment upon; that, so when I have given it in any cause, others may be at liberty to judge of me." The proprieties of the case were set forth with singular clearness and good temper by Judge W. H. Taft, when a United States circuit judge, eleven years ago, in 1895:
"The opportunity freely and publicly to criticize judicial action is of vastly more importance to the body politic than the immunity of courts and judges from unjust aspersions and attack. Nothing tends more to render judges careful in their decisions and anxiously solicitous to do exact justice than the consciousness that every act of theirs is to be subjected to the intelligent scrutiny and candid criticism of their fellow-men. Such criticism is beneficial in proportion as it is fair, dispassionate, discriminating, and based on a knowledge of sound legal principles. The comments made by learned text writers and by the acute editors of the various law reviews upon judicial decisions are therefore highly useful. Such critics constitute more or less impartial tribunals of professional opinion before which each judgment is made to stand or fall on its merits, and thus exert a strong influence to secure uniformity of decision. But non-professional criticism also is by no means without its uses, even if accompanied, as it often is, by a direct attack upon the judicial fairness and motives of the occupants of the bench; for if the law is but the essence of common sense, the protest of many average men may evidence a defect in a judicial conclusion, though based on the nicest legal reasoning and profoundest learning. The two important elements of moral character in a judge are an earnest desire to reach a just conclusion and courage to enforce it. In so far as fear of public comment does not affect the courage of a judge, but only spurs him on to search his conscience and to reach the result which approves itself to his inmost heart such comment serves a useful purpose. There are few men, whether they are judges for life or for a shorter term, who do not prefer to earn and hold the respect of all, and who can not be reached and made to pause and deliberate by hostile public criticism. In the case of judges having a life tenure, indeed their very independence makes the right freely to comment on their decisions of greater importance, because it is the only practical and available instrument in the hands of a free people to keep such judges alive to the reasonable demands of those they serve.
"On the other hand, the danger of destroying the proper influence of judicial decisions by creating unfounded prejudices against the courts justifies and requires that unjust attacks shall be met and answered. Courts must ultimately rest their defense upon the inherent strength of the opinions they deliver as the ground for their conclusions and must trust to the calm and deliberate judgment of all the people as their best vindication."
There is one consideration which should be taken into account by the good people who carry a sound proposition to an excess in objecting to any criticism of a judge’s decision. The instinct of the American people as a whole is sound in this matter. They will not subscribe to the doctrine that any public servant is to be above all criticism. If the best citizens, those most competent to express their judgment in such matters, and above all those belonging to the great and honorable profession of the bar, so profoundly influential in American life, take the position that there shall be no criticism of a judge under any circumstances, their view will not be accepted by the American people as a whole. In such event the people will turn to, and tend to accept as justifiable, the intemperate and improper criticism uttered by unworthy agitators. Surely it is a misfortune to leave to such critics a function, right, in itself, which they are certain to abuse. Just and temperate criticism, when necessary, is a safeguard against the acceptance by the people as a whole of that intemperate antagonism towards the judiciary which must be combated by every right-thinking man, and which, if it became widespread among the people at large, would constitute a dire menace to the Republic.
In connection with the delays of the law, I call your attention and the attention of the Nation to the prevalence of crime among us, and above all to the epidemic of lynching and mob violence that springs up, now in one part of our country, now in another. Each section, North, South, East, or West, has its own faults; no section can with wisdom spend its time jeering at the faults of another section; it should be busy trying to amend its own shortcomings. To deal with the crime of corruption it is necessary to have an awakened public conscience, and to supplement this by whatever legislation will add speed and certainty in the execution of the law. When we deal with lynching even mote is necessary. A great many white men are lynched, but the crime is peculiarly frequent in respect to black men. The greatest existing cause of lynching is the perpetration, especially by black men, of the hideous crime of rape—the most abominable in all the category of crimes, even worse than murder. Mobs frequently avenge the commission of this crime by themselves torturing to death the man committing it; thus avenging in bestial fashion a bestial deed, and reducing themselves to a level with the criminal.
Lawlessness grows by what it feeds upon; and when mobs begin to lynch for rape they speedily extend the sphere of their operations and lynch for many other kinds of crimes, so that two-thirds of the lynchings are not for rape at all; while a considerable proportion of the individuals lynched are innocent of all crime. Governor Candler, of Georgia, stated on one occasion some years ago: "I can say of a verity that I have, within the last month, saved the lives of half a dozen innocent Negroes who were pursued by the mob, and brought them to trial in a court of law in which they were acquitted." As Bishop Galloway, of Mississippi, has finely said: "When the rule of a mob obtains, that which distinguishes a high civilization is surrendered. The mob which lynches a negro charged with rape will in a little while lynch a white man suspected of crime. Every Christian patriot in America needs to lift up his voice in loud and eternal protest against the mob spirit that is threatening the integrity of this Republic." Governor Jelks, of Alabama, has recently spoken as follows: "The lynching of any person for whatever crime is inexcusable anywhere—it is a defiance of orderly government; but the killing of innocent people under any provocation is infinitely more horrible; and yet innocent people are likely to die when a mob’s terrible lust is once aroused. The lesson is this: No good citizen can afford to countenance a defiance of the statutes, no matter what the provocation. The innocent frequently suffer, and, it is my observation, more usually suffer than the guilty. The white people of the South indict the whole colored race on the ground that even the better elements lend no assistance whatever in ferreting out criminals of their own color. The respectable colored people must learn not to harbor their criminals, but to assist the officers in bringing them to justice. This is the larger crime, and it provokes such atrocious offenses as the one at Atlanta. The two races can never get on until there is an understanding on the part of both to make common cause with the law-abiding against criminals of any color."
Moreover, where any crime committed by a member of one race against a member of another race is avenged in such fashion that it seems as if not the individual criminal, but the whole race, is attacked, the result is to exasperate to the highest degree race feeling. There is but one safe rule in dealing with black men as with white men; it is the same rule that must be applied in dealing with rich men and poor men; that is, to treat each man, whatever his color, his creed, or his social position, with even-handed justice on his real worth as a man. White people owe it quite as much to themselves as to the colored race to treat well the colored man who shows by his life that he deserves such treatment; for it is surely the highest wisdom to encourage in the colored race all those individuals who are honest, industrious, law-abiding, and who therefore make good and safe neighbors and citizens. Reward or punish the individual on his merits as an individual. Evil will surely come in the end to both races if we substitute for this just rule the habit of treating all the members of the race, good and bad, alike. There is no question of "social equality" or "negro domination" involved; only the question of relentlessly punishing bad men, and of securing to the good man the right to his life, his liberty, and the pursuit of his happiness as his own qualities of heart, head, and hand enable him to achieve it.
Every colored man should realize that the worst enemy of his race is the negro criminal, and above all the negro criminal who commits the dreadful crime of rape; and it should be felt as in the highest degree an offense against the whole country, and against the colored race in particular, for a colored man to fail to help the officers of the law in hunting down with all possible earnestness and zeal every such infamous offender. Moreover, in my judgment, the crime of rape should always be punished with death, as is the case with murder; assault with intent to commit rape should be made a capital crime, at least in the discretion of the court; and provision should be made by which the punishment may follow immediately upon the heels of the offense; while the trial should be so conducted that the victim need not be wantonly shamed while giving testimony, and that the least possible publicity shall be given to the details.
The members of the white race on the other hand should understand that every lynching represents by just so much a loosening of the bands of civilization; that the spirit of lynching inevitably throws into prominence in the community all the foul and evil creatures who dwell therein. No man can take part in the torture of a human being without having his own moral nature permanently lowered. Every lynching means just so much moral deterioration in all the children who have any knowledge of it, and therefore just so much additional trouble for the next generation of Americans.
Let justice be both sure and swift; but let it be justice under the law, and not the wild and crooked savagery of a mob.
There is another matter which has a direct bearing upon this matter of lynching and of the brutal crime which sometimes calls it forth and at other times merely furnishes the excuse for its existence. It is out of the question for our people as a whole permanently to rise by treading down any of their own number. Even those who themselves for the moment profit by such maltreatment of their fellows will in the long run also suffer. No more shortsighted policy can be imagined than, in the fancied interest of one class, to prevent the education of another class. The free public school, the chance for each boy or girl to get a good elementary education, lies at the foundation of our whole political situation. In every community the poorest citizens, those who need the schools most, would be deprived of them if they only received school facilities proportioned to the taxes they paid. This is as true of one portion of our country as of another. It is as true for the negro as for the white man. The white man, if he is wise, will decline to allow the Negroes in a mass to grow to manhood and womanhood without education. Unquestionably education such as is obtained in our public schools does not do everything towards making a man a good citizen; but it does much. The lowest and most brutal criminals, those for instance who commit the crime of rape, are in the great majority men who have had either no education or very little; just as they are almost invariably men who own no property; for the man who puts money by out of his earnings, like the man who acquires education, is usually lifted above mere brutal criminality. Of course the best type of education for the colored man, taken as a whole, is such education as is conferred in schools like Hampton and Tuskegee; where the boys and girls, the young men and young women, are trained industrially as well as in the ordinary public school branches. The graduates of these schools turn out well in the great majority of cases, and hardly any of them become criminals, while what little criminality there is never takes the form of that brutal violence which invites lynch law. Every graduate of these schools—and for the matter of that every other colored man or woman—who leads a life so useful and honorable as to win the good will and respect of those whites whose neighbor he or she is, thereby helps the whole colored race as it can be helped in no other way; for next to the negro himself, the man who can do most to help the negro is his white neighbor who lives near him; and our steady effort should be to better the relations between the two. Great though the benefit of these schools has been to their colored pupils and to the colored people, it may well be questioned whether the benefit, has not been at least as great to the white people among whom these colored pupils live after they graduate.
Be it remembered, furthermore, that the individuals who, whether from folly, from evil temper, from greed for office, or in a spirit of mere base demagogy, indulge in the inflammatory and incendiary speeches and writings which tend to arouse mobs and to bring about lynching, not only thus excite the mob, but also tend by what criminologists call "suggestion," greatly to increase the likelihood of a repetition of the very crime against which they are inveighing. When the mob is composed of the people of one race and the man lynched is of another race, the men who in their speeches and writings either excite or justify the action tend, of course, to excite a bitter race feeling and to cause the people of the opposite race to lose sight of the abominable act of the criminal himself; and in addition, by the prominence they give to the hideous deed they undoubtedly tend to excite in other brutal and depraved natures thoughts of committing it. Swift, relentless, and orderly punishment under the law is the only way by which criminality of this type can permanently be supprest.
In dealing with both labor and capital, with the questions affecting both corporations and trades unions, there is one matter more important to remember than aught else, and that is the infinite harm done by preachers of mere discontent. These are the men who seek to excite a violent class hatred against all men of wealth. They seek to turn wise and proper movements for the better control of corporations and for doing away with the abuses connected with wealth, into a campaign of hysterical excitement and falsehood in which the aim is to inflame to madness the brutal passions of mankind. The sinister demagogs and foolish visionaries who are always eager to undertake such a campaign of destruction sometimes seek to associate themselves with those working for a genuine reform in governmental and social methods, and sometimes masquerade as such reformers. In reality they are the worst enemies of the cause they profess to advocate, just as the purveyors of sensational slander in newspaper or magazine are the worst enemies of all men who are engaged in an honest effort to better what is bad in our social and governmental conditions. To preach hatred of the rich man as such, to carry on a campaign of slander and invective against him, to seek to mislead and inflame to madness honest men whose lives are hard and who have not the kind of mental training which will permit them to appreciate the danger in the doctrines preached—all this is to commit a crime against the body politic and to be false to every worthy principle and tradition of American national life. Moreover, while such preaching and such agitation may give a livelihood and a certain notoriety to some of those who take part in it, and may result in the temporary political success of others, in the long run every such movement will either fail or else will provoke a violent reaction, which will itself result not merely in undoing the mischief wrought by the demagog and the agitator, but also in undoing the good that the honest reformer, the true upholder of popular rights, has painfully and laboriously achieved. Corruption is never so rife as in communities where the demagog and the agitator bear full sway, because in such communities all moral bands become loosened, and hysteria and sensationalism replace the spirit of sound judgment and fair dealing as between man and man. In sheer revolt against the squalid anarchy thus produced men are sure in the end to turn toward any leader who can restore order, and then their relief at being free from the intolerable burdens of class hatred, violence, and demagogy is such that they can not for some time be aroused to indignation against misdeeds by men of wealth; so that they permit a new growth of the very abuses which were in part responsible for the original outbreak. The one hope for success for our people lies in a resolute and fearless, but sane and cool-headed, advance along the path marked out last year by this very Congress. There must be a stern refusal to be misled into following either that base creature who appeals and panders to the lowest instincts and passions in order to arouse one set of Americans against their fellows, or that other creature, equally base but no baser, who in a spirit of greed, or to accumulate or add to an already huge fortune, seeks to exploit his fellow Americans with callous disregard to their welfare of soul and body. The man who debauches others in order to obtain a high office stands on an evil equality of corruption with the man who debauches others for financial profit; and when hatred is sown the crop which springs up can only be evil.
The plain people who think—the mechanics, farmers, merchants, workers with head or hand, the men to whom American traditions are dear, who love their country and try to act decently by their neighbors, owe it to themselves to remember that the most damaging blow that can be given popular government is to elect an unworthy and sinister agitator on a platform of violence and hypocrisy. Whenever such an issue is raised in this country nothing can be gained by flinching from it, for in such case democracy is itself on trial, popular self-government under republican forms is itself on trial. The triumph of the mob is just as evil a thing as the triumph of the plutocracy, and to have escaped one danger avails nothing whatever if we succumb to the other. In the end the honest man, whether rich or poor, who earns his own living and tries to deal justly by his fellows, has as much to fear from the insincere and unworthy demagog, promising much and performing nothing, or else performing nothing but evil, who would set on the mob to plunder the rich, as from the crafty corruptionist, who, for his own ends, would permit the common people to be exploited by the very wealthy. If we ever let this Government fall into the hands of men of either of these two classes, we shall show ourselves false to America’s past. Moreover, the demagog and the corruptionist often work hand in hand. There are at this moment wealthy reactionaries of such obtuse morality that they regard the public servant who prosecutes them when they violate the law, or who seeks to make them bear their proper share of the public burdens, as being even more objectionable than the violent agitator who hounds on the mob to plunder the rich. There is nothing to choose between such a reactionary and such an agitator; fundamentally they are alike in their selfish disregard of the rights of others; and it is natural that they should join in opposition to any movement of which the aim is fearlessly to do exact and even justice to all.
I call your attention to the need of passing the bill limiting the number of hours of employment of railroad employees. The measure is a very moderate one and I can conceive of no serious objection to it. Indeed, so far as it is in our power, it should be our aim steadily to reduce the number of hours of labor, with as a goal the general introduction of an eight-hour day. There are industries in which it is not possible that the hours of labor should be reduced; just as there are communities not far enough advanced for such a movement to be for their good, or, if in the Tropics, so situated that there is no analogy between their needs and ours in this matter. On the Isthmus of Panama, for instance, the conditions are in every way so different from what they are here that an eight-hour day would be absurd; just as it is absurd, so far as the Isthmus is concerned, where white labor can not be employed, to bother as to whether the necessary work is done by alien black men or by alien yellow men. But the wageworkers of the United States are of so high a grade that alike from the merely industrial standpoint and from the civic standpoint it should be our object to do what we can in the direction of securing the general observance of an eight-hour day. Until recently the eight-hour law on our Federal statute books has been very scantily observed. Now, however, largely through the instrumentality of the Bureau of Labor, it is being rigidly enforced, and I shall speedily be able to say whether or not there is need of further legislation in reference thereto; .for our purpose is to see it obeyed in spirit no less than in letter. Half holidays during summer should be established for Government employees; it is as desirable for wageworkers who toil with their hands as for salaried officials whose labor is mental that there should be a reasonable amount of holiday.
The Congress at its last session wisely provided for a truant court for the District of Columbia; a marked step in advance on the path of properly caring for the children. Let me again urge that the Congress provide for a thorough investigation of the conditions of child labor and of the labor of women in the United States. More and more our people are growing to recognize the fact that the questions which are not merely of industrial but of social importance outweigh all others; and these two questions most emphatically come in the category of those which affect in the most far-reaching way the home life of the Nation. The horrors incident to the employment of young children in factories or at work anywhere are a blot on our civilization. It is true that each. State must ultimately settle the question in its own way; but a thorough official investigation of the matter, with the results published broadcast, would greatly help toward arousing the public conscience and securing unity of State action in the matter. There is, however, one law on the subject which should be enacted immediately, because there is no need for an investigation in reference thereto, and the failure to enact it is discreditable to the National Government. A drastic and thoroughgoing child-labor law should be enacted for the District of Columbia and the Territories.
Among the excellent laws which the Congress past at the last session was an employers’ liability law. It was a marked step in advance to get the recognition of employers’ liability on the statute books; but the law did not go far enough. In spite of all precautions exercised by employers there are unavoidable accidents and even deaths involved in nearly every line of business connected with the mechanic arts. This inevitable sacrifice of life may be reduced to a minimum, but it can not be completely eliminated. It is a great social injustice to compel the employee, or rather the family of the killed or disabled victim, to bear the entire burden of such an inevitable sacrifice. In other words, society shirks its duty by laying the whole cost on the victim, whereas the injury comes from what may be called the legitimate risks of the trade. Compensation for accidents or deaths due in any line of industry to the actual conditions under which that industry is carried on, should be paid by that portion of the community for the benefit of which the industry is carried on—that is, by those who profit by the industry. If the entire trade risk is placed upon the employer he will promptly and properly add it to the legitimate cost of production and assess it proportionately upon the consumers of his commodity. It is therefore clear to my mind that the law should place this entire "risk of a trade" upon the employer. Neither the Federal law, nor, as far as I am informed, the State laws dealing with the question of employers’ liability are sufficiently thoroughgoing. The Federal law should of course include employees in navy-yards, arsenals, and the like.
The commission appointed by the President October 16, 1902, at the request of both the anthracite coal operators and miners, to inquire into, consider, and pass upon the questions in controversy in connection with the strike in the anthracite regions of Pennsylvania and the causes out of which the controversy arose, in their report, findings, and award exprest the belief "that the State and Federal governments should provide the machinery for what may be called the compulsory investigation of controversies between employers and employees when they arise." This expression of belief is deserving of the favorable consideration of the Congress and the enactment of its provisions into law. A bill has already been introduced to this end.
Records show that during the twenty years from January 1, 1881, to, December 31, 1900, there were strikes affecting 117,509 establishments, and 6,105,694 employees were thrown out of employment. During the same period there were 1,005 lockouts, involving nearly 10,000 establishments, throwing over one million people out of employment. These strikes and lockouts involved an estimated loss to employees of $307,000,000 and to employers of $143,000,000, a total of $450,000,000. The public suffered directly and indirectly probably as great additional loss. But the money loss, great as it was, did not measure the anguish and suffering endured by the wives and children of employees whose pay stopt when their work stopt, or the disastrous effect of the strike or lockout upon the business of employers, or the increase in the cost of products and the inconvenience and loss to the public.
Many of these strikes and lockouts would not have occurred had the parties to the dispute been required to appear before an unprejudiced body representing the nation and, face to face, state the reasons for their contention. In most instances the dispute would doubtless be found to be due to a misunderstanding by each of the other’s rights, aggravated by an unwillingness of either party to accept as true the statements of the other as to the justice or injustice of the matters in dispute. The exercise of a judicial spirit by a disinterested body representing the Federal Government, such as would be provided by a commission on conciliation and arbitration, would tend to create an atmosphere of friendliness and conciliation between contending parties; and the giving each side an equal opportunity to present fully its case in the presence of the other would prevent many disputes from developing into serious strikes or lockouts, and, in other cases, would enable the commission to persuade the opposing parties to come to terms.
In this age of great corporate and labor combinations, neither employers nor employees should be left completely at the mercy of the stronger party to a dispute, regardless of the righteousness of their respective claims. The proposed measure would be in the line of securing recognition of the fact that in many strikes the public has itself an interest which can not wisely be disregarded; an interest not merely of general convenience, for the question of a just and proper public policy must also be considered. In all legislation of this kind it is well to advance cautiously, testing each step by the actual results; the step proposed can surely be safely taken, for the decisions of the commission would not bind the parties in legal fashion, and yet would give a chance for public opinion to crystallize and thus to exert its full force for the right.
It is not wise that the Nation should alienate its remaining coal lands. I have temporarily withdrawn from settlement all the lands which the Geological Survey has indicated as containing, or in all probability containing, coal. The question, however, can be properly settled only by legislation, which in my judgment should provide for the withdrawal of these lands from sale or from entry, save in certain especial circumstances. The ownership would then remain in the United States, which should not, however, attempt to work them, but permit them to be worked by private individuals under a royalty system, the Government keeping such control as to permit it to see that no excessive price was charged consumers. It would, of course, be as necessary to supervise the rates charged by the common carriers to transport the product as the rates charged by those who mine it; and the supervision must extend to the conduct of the common carriers, so that they shall in no way favor one competitor at the expense of another. The withdrawal of these coal lands would constitute a policy analogous to that which has been followed in withdrawing the forest lands from ordinary settlement. The coal, like the forests, should be treated as the property of the public and its disposal should be under conditions which would inure to the benefit of the public as a whole.
The present Congress has taken long strides in the direction of securing proper supervision and control by the National Government over corporations engaged in interstate business and the enormous majority of corporations of any size are engaged in interstate business. The passage of the railway rate bill, and only to a less degree the passage of the pure food bill, and the provision for increasing and rendering more effective national control over the beef-packing industry, mark an important advance in the proper direction. In the short session it will perhaps be difficult to do much further along this line; and it may be best to wait until the laws have been in operation for a number of months before endeavoring to increase their scope, because only operation will show with exactness their merits and their shortcomings and thus give opportunity to define what further remedial legislation is needed. Yet in my judgment it will in the end be advisable in connection with the packing house inspection law to provide for putting a date on the label and for charging the cost of inspection to the packers. All these laws have already justified their enactment. The interstate commerce law, for instance, has rather amusingly falsified the predictions, both of those who asserted that it would ruin the railroads and of those who asserted that it did not go far enough and would accomplish nothing. During the last five months the railroads have shown increased earnings and some of them unusual dividends; while during the same period the mere taking effect of the law has produced an unprecedented, a hitherto unheard of, number of voluntary reductions in freights and fares by the railroads. Since the founding of the Commission there has never been a time of equal length in which anything like so many reduced tariffs have been put into effect. On August 27, for instance, two days before the new law went into effect, the Commission received notices of over five thousand separate tariffs which represented reductions from previous rates.
It must not be supposed, however, that with the passage of these laws it will be possible to stop progress along the line of increasing the power of the National Government over the use of capital interstate commerce. For example, there will ultimately be need of enlarging the powers of the Interstate Commerce Commission along several different lines, so as to give it a larger and more efficient control over the railroads.
It can not too often be repeated that experience has conclusively shown the impossibility of securing by the actions of nearly half a hundred different State legislatures anything but ineffective chaos in the way of dealing with the great corporations which do not operate exclusively within the limits of any one State. In some method, whether by a national license law or in other fashion, we must exercise, and that at an early date, a far more complete control than at present over these great corporations—a control that will among other things prevent the evils of excessive overcapitalization, and that will compel the disclosure by each big corporation of its stockholders and of its properties and business, whether owned directly or through subsidiary or affiliated corporations. This will tend to put a stop to the securing of inordinate profits by favored individuals at the expense whether of the general public, the stockholders, or the wageworkers. Our effort should be not so much to prevent consolidation as such, but so to supervise and control it as to see that it results in no harm to the people. The reactionary or ultraconservative apologists for the misuse of wealth assail the effort to secure such control as a step toward socialism. As a matter of fact it is these reactionaries and ultraconservatives who are themselves most potent in increasing socialistic feeling. One of the most efficient methods of averting the consequences of a dangerous agitation, which is 80 per cent wrong, is to remedy the 20 per cent of evil as to which the agitation is well rounded. The best way to avert the very undesirable move for the government ownership of railways is to secure by the Government on behalf of the people as a whole such adequate control and regulation of the great interstate common carriers as will do away with the evils which give rise to the agitation against them. So the proper antidote to the dangerous and wicked agitation against the men of wealth as such is to secure by proper legislation and executive action the abolition of the grave abuses which actually do obtain in connection with the business use of wealth under our present system—or rather no system—of failure to exercise any adequate control at all. Some persons speak as if the exercise of such governmental control would do away with the freedom of individual initiative and dwarf individual effort. This is not a fact. It would be a veritable calamity to fail to put a premium upon individual initiative, individual capacity and effort; upon the energy, character, and foresight which it is so important to encourage in the individual. But as a matter of fact the deadening and degrading effect of pure socialism, and especially of its extreme form communism, and the destruction of individual character which they would bring about, are in part achieved by the wholly unregulated competition which results in a single individual or corporation rising at the expense of all others until his or its rise effectually checks all competition and reduces former competitors to a position of utter inferiority and subordination.
In enacting and enforcing such legislation as this Congress already has to its credit, we are working on a coherent plan, with the steady endeavor to secure the needed reform by the joint action of the moderate men, the plain men who do not wish anything hysterical or dangerous, but who do intend to deal in resolute common-sense fashion with the real and great evils of the present system. The reactionaries and the violent extremists show symptoms of joining hands against us. Both assert, for instance, that, if logical, we should go to government ownership of railroads and the like; the reactionaries, because on such an issue they think the people would stand with them, while the extremists care rather to preach discontent and agitation than to achieve solid results. As a matter of fact, our position is as remote from that of the Bourbon reactionary as from that of the impracticable or sinister visionary. We hold that the Government should not conduct the business of the nation, but that it should exercise such supervision as will insure its being conducted in the interest of the nation. Our aim is, so far as may be, to secure, for all decent, hard working men, equality of opportunity and equality of burden.
The actual working of our laws has shown that the effort to prohibit all combination, good or bad, is noxious where it is not ineffective. Combination of capital like combination of labor is a necessary element of our present industrial system. It is not possible completely to prevent it; and if it were possible, such complete prevention would do damage to the body politic. What we need is not vainly to try to prevent all combination, but to secure such rigorous and adequate control and supervision of the combinations as to prevent their injuring the public, or existing in such form as inevitably to threaten injury—for the mere fact that a combination has secured practically complete control of a necessary of life would under any circumstances show that such combination was to be presumed to be adverse to the public interest. It is unfortunate that our present laws should forbid all combinations, instead of sharply discriminating between those combinations which do good and those combinations which do evil. Rebates, for instance, are as often due to the pressure of big shippers (as was shown in the investigation of the Standard Oil Company and as has been shown since by the investigation of the tobacco and sugar trusts) as to the initiative of big railroads. Often railroads would like to combine for the purpose of preventing a big shipper from maintaining improper advantages at the expense of small shippers and of the general public. Such a combination, instead of being forbidden by law, should be favored. In other words, it should be permitted to railroads to make agreements, provided these agreements were sanctioned by the Interstate Commerce Commission and were published. With these two conditions complied with it is impossible to see what harm such a combination could do to the public at large. It is a public evil to have on the statute books a law incapable of full enforcement because both judges and juries realize that its full enforcement would destroy the business of the country; for the result is to make decent railroad men violators of the law against their will, and to put a premium on the behavior of the wilful wrongdoers. Such a result in turn tends to throw the decent man and the wilful wrongdoer into close association, and in the end to drag down the former to the latter’s level; for the man who becomes a lawbreaker in one way unhappily tends to lose all respect for law and to be willing to break it in many ways. No more scathing condemnation could be visited upon a law than is contained in the words of the Interstate Commerce Commission when, in commenting upon the fact that the numerous joint traffic associations do technically violate the law, they say: "The decision of the United States Supreme Court in the Trans-Missouri case and the Joint Traffic Association case has produced no practical effect upon the railway operations of the country. Such associations, in fact, exist now as they did before these decisions, and with the same general effect. In justice to all parties, we ought probably to add that it is difficult to see how our interstate railways could be operated with due regard to the interest of the shipper and the railway without concerted action of the kind afforded through these associations."
This means that the law as construed by the Supreme Court is such that the business of the country can not be conducted without breaking it. I recommend that you give careful and early consideration to this subject, and if you find the opinion of the Interstate Commerce Commission justified, that you amend the law so as to obviate the evil disclosed.
The question of taxation is difficult in any country, but it is especially difficult in ours with its Federal system of government. Some taxes should on every ground be levied in a small district for use in that district. Thus the taxation of real estate is peculiarly one for the immediate locality in which the real estate is found. Again, there is no more legitimate tax for any State than a tax on the franchises conferred by that State upon street railroads and similar corporations which operate wholly within the State boundaries, sometimes in one and sometimes in several municipalities or other minor divisions of the State. But there are many kinds of taxes which can only be levied by the General Government so as to produce the best results, because, among other reasons, the attempt to impose them in one particular State too often results merely in driving the corporation or individual affected to some other locality or other State. The National Government has long derived its chief revenue from a tariff on imports and from an internal or excise tax. In addition to these there is every reason why, when next our system of taxation is revised, the National Government should impose a graduated inheritance tax, and, if possible, a graduated income tax. The man of great wealth owes a peculiar obligation to the State, because he derives special advantages from the mere existence of government. Not only should he recognize this obligation in the way he leads his daily life and in the way he earns and spends his money, but it should also be recognized by the way in which he pays for the protection the State gives him. On the one hand, it is desirable that he should assume his full and proper share of the burden of taxation; on the other hand, it is quite as necessary that in this kind of taxation, where the men who vote the tax pay but little of it, there should be clear recognition of the danger of inaugurating any such system save in a spirit of entire justice and moderation. Whenever we, as a people, undertake to remodel our taxation system along the lines suggested, we must make it clear beyond peradventure that our aim is to distribute the burden of supporting the Government more equitably than at present; that we intend to treat rich man and poor man on a basis of absolute equality, and that we regard it as equally fatal to true democracy to do or permit injustice to the one as to do or permit injustice to the other.
I am well aware that such a subject as this needs long and careful study in order that the people may become familiar with what is proposed to be done, may clearly see the necessity of proceeding with wisdom and self-restraint, and may make up their minds just how far they are willing to go in the matter; while only trained legislators can work out the project in necessary detail. But I feel that in the near future our national legislators should enact a law providing for a graduated inheritance tax by which a steadily increasing rate of duty should be put upon all moneys or other valuables coming by gift, bequest, or devise to any individual or corporation. It may be well to make the tax heavy in proportion as the individual benefited is remote of kin. In any event, in my judgment the pro rata of the tax should increase very heavily with the increase of the amount left to any one individual after a certain point has been reached. It is most desirable to encourage thrift and ambition, and a potent source of thrift and ambition is the desire on the part of the breadwinner to leave his children well off. This object can be attained by making the tax very small on moderate amounts of property left; because the prime object should be to put a constantly increasing burden on the inheritance of those swollen fortunes which it is certainly of no benefit to this country to perpetuate.
There can be no question of the ethical propriety of the Government thus determining the conditions upon which any gift or inheritance should be received. Exactly how far the inheritance tax would, as an incident, have the effect of limiting the transmission by devise or gift of the enormous fortunes in question it is not necessary at present to discuss. It is wise that progress in this direction should be gradual. At first a permanent national inheritance tax, while it might be more substantial than any such tax has hitherto been, need not approximate, either in amount or in the extent of the increase by graduation, to what such a tax should ultimately be.
This species of tax has again and again been imposed, although only temporarily, by the National Government. It was first imposed by the act of July 6, 1797, when the makers of the Constitution were alive and at the head of affairs. It was a graduated tax; though small in amount, the rate was increased with the amount left to any individual, exceptions being made in the case of certain close kin. A similar tax was again imposed by the act of July 1, 1862; a minimum sum of one thousand dollars in personal property being excepted from taxation, the tax then becoming progressive according to the remoteness of kin. The war-revenue act of June 13, 1898, provided for an inheritance tax on any sum exceeding the value of ten thousand dollars, the rate of the tax increasing both in accordance with the amounts left and in accordance with the legatee’s remoteness of kin. The Supreme Court has held that the succession tax imposed at the time of the Civil War was not a direct tax but an impost or excise which was both constitutional and valid. More recently the Court, in an opinion delivered by Mr. Justice White, which contained an exceedingly able and elaborate discussion of the powers of the Congress to impose death duties, sustained the constitutionality of the inheritance-tax feature of the war-revenue act of 1898.
In its incidents, and apart from the main purpose of raising revenue, an income tax stands on an entirely different footing from an inheritance tax; because it involves no question of the perpetuation of fortunes swollen to an unhealthy size. The question is in its essence a question of the proper adjustment of burdens to benefits. As the law now stands it is undoubtedly difficult to devise a national income tax which shall be constitutional. But whether it is absolutely impossible is another question; and if possible it is most certainly desirable. The first purely income-tax law was past by the Congress in 1861, but the most important law dealing with the subject was that of 1894. This the court held to be unconstitutional.
The question is undoubtedly very intricate, delicate, and troublesome. The decision of the court was only reached by one majority. It is the law of the land, and of course is accepted as such and loyally obeyed by all good citizens. Nevertheless, the hesitation evidently felt by the court as a whole in coming to a conclusion, when considered together with the previous decisions on the subject, may perhaps indicate the possibility of devising a constitutional income-tax law which shall substantially accomplish the results aimed at. The difficulty of amending the Constitution is so great that only real necessity can justify a resort thereto. Every effort should be made in dealing with this subject, as with the subject of the proper control by the National Government over the use of corporate wealth in interstate business, to devise legislation which without such action shall attain the desired end; but if this fails, there will ultimately be no alternative to a constitutional amendment.
It would be impossible to overstate (though it is of course difficult quantitatively to measure) the effect upon a nation’s growth to greatness of what may be called organized patriotism, which necessarily includes the substitution of a national feeling for mere local pride; with as a resultant a high ambition for the whole country. No country can develop its full strength so long as the parts which make up the whole each put a feeling of loyalty to the part above the feeling of loyalty to the whole. This is true of sections and it is just as true of classes. The industrial and agricultural classes must work together, capitalists and wageworkers must work together, if the best work of which the country is capable is to be done. It is probable that a thoroughly efficient system of education comes next to the influence of patriotism in bringing about national success of this kind. Our federal form of government, so fruitful of advantage to our people in certain ways, in other ways undoubtedly limits our national effectiveness. It is not possible, for instance, for the National Government to take the lead in technical industrial education, to see that the public school system of this country develops on all its technical, industrial, scientific, and commercial sides. This must be left primarily to the several States. Nevertheless, the National Government has control of the schools of the District of Columbia, and it should see that these schools promote and encourage the fullest development of the scholars in both commercial and industrial training. The commercial training should in one of its branches deal with foreign trade. The industrial training is even more important. It should be one of our prime objects as a Nation, so far as feasible, constantly to work toward putting the mechanic, the wageworker who works with his hands, on a higher plane of efficiency and reward, so as to increase his effectiveness in the economic world, and the dignity, the remuneration, and the power of his position in the social world. Unfortunately, at present the effect of some of the work in the public schools is in the exactly opposite direction. If boys and girls are trained merely in literary accomplishments, to the total exclusion of industrial, manual, and technical training, the tendency is to unfit them for industrial work and to make them reluctant to go into it, or unfitted to do well if they do go into it. This is a tendency which should be strenuously combated. Our industrial development depends largely upon technical education, including in this term all industrial education, from that which fits a man to be a good mechanic, a good carpenter, or blacksmith, to that which fits a man to do the greatest engineering feat. The skilled mechanic, the skilled workman, can best become such by technical industrial education. The far-reaching usefulness of institutes of technology and schools of mines or of engineering is now universally acknowledged, and no less far—reaching is the effect of a good building or mechanical trades school, a textile, or watch-making, or engraving school. All such training must develop not only manual dexterity but industrial intelligence. In international rivalry this country does not have to fear the competition of pauper labor as much as it has to fear the educated labor of specially trained competitors; and we should have the education of the hand, eye, and brain which will fit us to meet such competition.
In every possible way we should help the wageworker who toils with his hands and who must (we hope in a constantly increasing measure) also toil with his brain. Under the Constitution the National Legislature can do but little of direct importance for his welfare save where he is engaged in work which permits it to act under the interstate commerce clause of the Constitution; and this is one reason why I so earnestly hope that both the legislative and judicial branches of the Government will construe this clause of the Constitution in the broadest possible manner. We can, however, in such a matter as industrial training, in such a matter as child labor and factory laws, set an example to the States by enacting the most advanced legislation that can wisely be enacted for the District of Columbia.
The only other persons whose welfare is as vital to the welfare of the whole country as is the welfare of the wageworkers are the tillers of the soil, the farmers. It is a mere truism to say that no growth of cities, no growth of wealth, no industrial development can atone for any falling off in the character and standing of the farming population. During the last few decades this fact has been recognized with ever-increasing clearness. There is no longer any failure to realize that farming, at least in certain branches, must become a technical and scientific profession. This means that there must be open to farmers the chance for technical and scientific training, not theoretical merely but of the most severely practical type. The farmer represents a peculiarly high type of American citizenship, and he must have the same chance to rise and develop as other American citizens have. Moreover, it is exactly as true of the farmer, as it is of the business man and the wageworker, that the ultimate success of the Nation of which he forms a part must be founded not alone on material prosperity but upon high moral, mental, and physical development. This education of the farmer—self-education by preference but also education from the outside, as with all other men—is peculiarly necessary here in the United States, where the frontier conditions even in the newest States have now nearly vanished, where there must be a substitution of a more intensive system of cultivation for the old wasteful farm management, and where there must be a better business organization among the farmers themselves.
Several factors must cooperate in the improvement of the farmer’s condition. He must have the chance to be educated in the widest possible sense—in the sense which keeps ever in view the intimate relationship between the theory of education and the facts of life. In all education we should widen our aims. It is a good thing to produce a certain number of trained scholars and students; but the education superintended by the State must seek rather to produce a hundred good citizens than merely one scholar, and it must be turned now and then from the class book to the study of the great book of nature itself. This is especially true of the farmer, as has been pointed out again and again by all observers most competent to pass practical judgment on the problems of our country life. All students now realize that education must seek to train the executive powers of young people and to confer more real significance upon the phrase "dignity of labor," and to prepare the pupils so that, in addition to each developing in the highest degree his individual capacity for work, they may together help create a right public opinion, and show in many ways social and cooperative spirit. Organization has become necessary in the business world; and it has accomplished much for good in the world of labor. It is no less necessary for farmers. Such a movement as the grange movement is good in itself and is capable of a well-nigh infinite further extension for good so long as it is kept to its own legitimate business. The benefits to be derived by the association of farmers for mutual advantage are partly economic and partly sociological.
Moreover, while in the long run voluntary efforts will prove more efficacious than government assistance, while the farmers must primarily do most for themselves, yet the Government can also do much. The Department of Agriculture has broken new ground in many directions, and year by year it finds how it can improve its methods and develop fresh usefulness. Its constant effort is to give the governmental assistance in the most effective way; that is, through associations of farmers rather than to or through individual farmers. It is also striving to coordinate its work with the agricultural departments of the several States, and so far as its own work is educational to coordinate it with the work of other educational authorities. Agricultural education is necessarily based upon general education, but our agricultural educational institutions are wisely specializing themselves, making their courses relate to the actual teaching of the agricultural and kindred sciences to young country people or young city people who wish to live in the country.
Great progress has already been made among farmers by the creation of farmers’ institutes, of dairy associations, of breeders’ associations, horticultural associations, and the like. A striking example of how the Government and the farmers can cooperate is shown in connection with the menace offered to the cotton growers of the Southern States by the advance of the boll weevil. The Department is doing all it can to organize the farmers in the threatened districts, just as it has been doing all it can to organize them in aid of its work to eradicate the cattle fever tick in the South. The Department can and will cooperate with all such associations, and it must have their help if its own work is to be done in the most efficient style.
Much is now being done for the States of the Rocky Mountains and Great Plains through the development of the national policy of irrigation and forest preservation; no Government policy for the betterment of our internal conditions has been more fruitful of good than this. The forests of the White Mountains and Southern Appalachian regions should also be preserved; and they can not be unless the people of the States in which they lie, through their representatives in the Congress, secure vigorous action by the National Government.
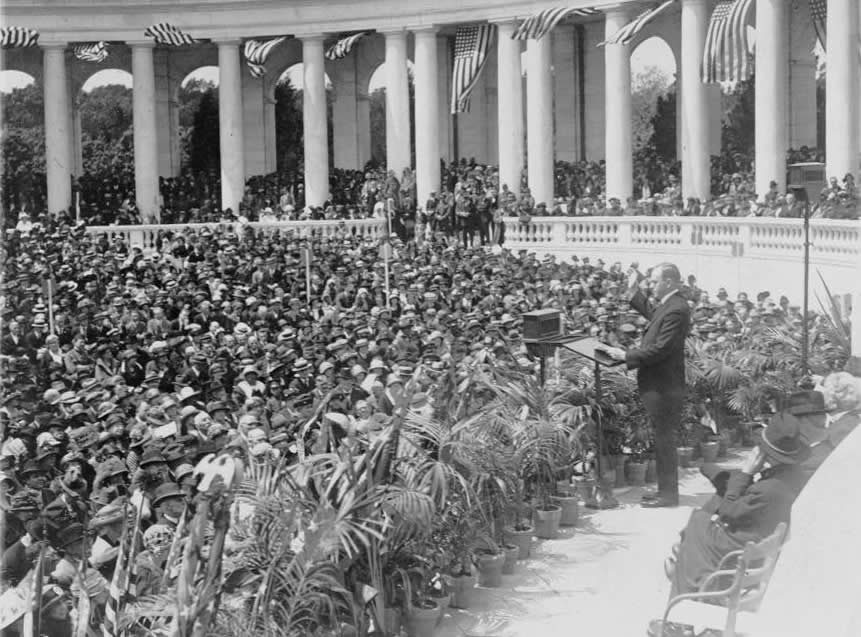
I invite the attention of the Congress to the estimate of the Secretary of War for an appropriation to enable him to begin the preliminary work for the construction of a memorial amphitheater at Arlington. The Grand Army of the Republic in its national encampment has urged the erection of such an amphitheater as necessary for the proper observance Of Memorial Day and as a fitting monument to the soldier and sailor dead buried there. In this I heartily concur and commend the matter to the favorable consideration of the Congress.
I am well aware of how difficult it is to pass a constitutional amendment. Nevertheless in my judgment the whole question of marriage and divorce should be relegated to the authority of the National Congress. At present the wide differences in the laws of the different States on this subject result in scandals and abuses; and surely there is nothing so vitally essential to the welfare of the nation, nothing around which the nation should so bend itself to throw every safeguard, as the home life of the average citizen. The change would be good from every standpoint. In particular it would be good because it would confer on the Congress the power at once to deal radically and efficiently with polygamy; and this should be done whether or not marriage and divorce are dealt with. It is neither safe nor proper to leave the question of polygamy to be dealt with by the several States. Power to deal with it should be conferred on the National Government.
When home ties are loosened; when men and women cease to regard a worthy family life, with all its duties fully performed, and all its responsibilities lived up to, as the life best worth living; then evil days for the commonwealth are at hand. There are regions in our land, and classes of our population, where the birth rate has sunk below the death rate. Surely it should need no demonstration to show that wilful sterility is, from the standpoint of the nation, from the standpoint of the human race, the one sin for which the penalty is national death, race death; a sin for which there is no atonement; a sin which is the more dreadful exactly in proportion as the men and women guilty thereof are in other respects, in character, and bodily and mental powers, those whom for the sake of the state it would be well to see the fathers and mothers of many healthy children, well brought up in homes made happy by their presence. No man, no woman, can shirk the primary duties of life, whether for love of ease and pleasure, or for any other cause, and retain his or her self-respect.
Let me once again call the attention of the Congress to two subjects concerning which I have frequently before communicated with them. One is the question of developing American shipping. I trust that a law embodying in substance the views, or a major part of the views, exprest in the report on this subject laid before the House at its last session will be past. I am well aware that in former years objectionable measures have been proposed in reference to the encouragement of American shipping; but it seems to me that the proposed measure is as nearly unobjectionable as any can be. It will of course benefit primarily our seaboard States, such as Maine, Louisiana, and Washington; but what benefits part of our people in the end benefits all; just as Government aid to irrigation and forestry in the West is really of benefit, not only to the Rocky Mountain States, but to all our country. If it prove impracticable to enact a law for the encouragement of shipping generally, then at least provision should be made for better communication with South America, notably for fast mail lines to the chief South American ports. It is discreditable to us that our business people, for lack of direct communication in the shape of lines of steamers with South America, should in that great sister continent be at a disadvantage compared to the business people of Europe.
I especially call your attention to the second subject, the condition of our currency laws. The national bank act has ably served a great purpose in aiding the enormous business development of the country; and within ten years there has been an increase in circulation per capita from $21.41 to $33.08. For several years evidence has been accumulating that additional legislation is needed. The recurrence of each crop season emphasizes the defects of the present laws. There must soon be a revision of them, because to leave them as they are means to incur liability of business disaster. Since your body adjourned there has been a fluctuation in the interest on call money from 2 per cent to 30 per cent; and the fluctuation was even greater during the preceding six months. The Secretary of the Treasury had to step in and by wise action put a stop to the most violent period of oscillation. Even worse than such fluctuation is the advance in commercial rates and the uncertainty felt in the sufficiency of credit even at high rates. All commercial interests suffer during each crop period. Excessive rates for call money in New York attract money from the interior banks into the speculative field; this depletes the fund that would otherwise be available for commercial uses, and commercial borrowers are forced to pay abnormal rates; so that each fall a tax, in the shape of increased interest charges, is placed on the whole commerce of the country.
The mere statement of these has shows that our present system is seriously defective. There is need of a change. Unfortunately, however, many of the proposed changes must be ruled from consideration because they are complicated, are not easy of comprehension, and tend to, disturb existing rights and interests. We must also rule out any plan which would materially impair the value of the United States 2 per cent bonds now pledged to secure circulations, the issue of which was made under conditions peculiarly creditable to the Treasury. I do not press any especial plan. Various plans have recently been proposed by expert committees of bankers. Among the plans which are possibly feasible and which certainly should receive your consideration is that repeatedly brought to your attention by the present Secretary of the Treasury, the essential features of which have been approved by many prominent bankers and business men. According to this plan national banks should be permitted to issue a specified proportion of their capital in notes of a given kind, the issue to be taxed at so high a rate as to drive the notes back when not wanted in legitimate trade. This plan would not permit the issue of currency to give banks additional profits, but to meet the emergency presented by times of stringency.
I do not say that this is the right system. I only advance it to emphasize my belief that there is need for the adoption of some system which shall be automatic and open to all sound banks, so as to avoid all possibility of discrimination and favoritism. Such a plan would tend to prevent the spasms of high money and speculation which now obtain in the New York market; for at present there is too much currency at certain seasons of the year, and its accumulation at New York tempts bankers to lend it at low rates for speculative purposes; whereas at other times when the crops are being moved there is urgent need for a large but temporary increase in the currency supply. It must never be forgotten that this question concerns business men generally quite as much as bankers; especially is this true of stockmen, farmers, and business men in the West; for at present at certain seasons of the year the difference in interest rates between the East and the West is from 6 to 10 per cent, whereas in Canada the corresponding difference is but 2 per cent. Any plan must, of course, guard the interests of western and southern bankers as carefully as it guards the interests of New York or Chicago bankers; and must be drawn from the standpoints of the farmer and the merchant no less than from the standpoints of the city banker and the country banker.
The law should be amended so as specifically to provide that the funds derived from customs duties may be treated by the Secretary of the Treasury as he treats funds obtained under the internal-revenue laws. There should be a considerable increase in bills of small denominations. Permission should be given banks, if necessary under settled restrictions, to retire their circulation to a larger amount than three millions a month.
I most earnestly hope that the bill to provide a lower tariff for or else absolute free trade in Philippine products will become a law. No harm will come to any American industry; and while there will be some small but real material benefit to the Filipinos, the main benefit will come by the showing made as to our purpose to do all in our power for their welfare. So far our action in the Philippines has been abundantly justified, not mainly and indeed not primarily because of the added dignity it has given us as a nation by proving that we are capable honorably and efficiently to bear the international burdens which a mighty people should bear, but even more because of the immense benefit that has come to the people of the Philippine Islands. In these islands we are steadily introducing both liberty and order, to a greater degree than their people have ever before known. We have secured justice. We have provided an efficient police force, and have put down ladronism. Only in the islands of Leyte and Samar is the authority of our Government resisted and this by wild mountain tribes under the superstitious inspiration of fakirs and pseudo-religions leaders. We are constantly increasing the measure of liberty accorded the islanders, and next spring, if conditions warrant, we shall take a great stride forward in testing their capacity for self-government by summoning the first Filipino legislative assembly; and the way in which they stand this test will largely determine whether the self-government thus granted will be increased or decreased; for if we have erred at all in the Philippines it has been in proceeding too rapidly in the direction of granting a large measure of self-government. We are building roads. We have, for the immeasurable good of the people, arranged for the building of railroads. Let us also see to it that they are given free access to our markets. This nation owes no more imperative duty to itself and mankind than the duty of managing the affairs of all the islands under the American flag—the Philippines, Porto Rico, and Hawaii—so as to make it evident that it is in every way to their advantage that the flag should fly over them.
American citizenship should be conferred on the citizens of Porto Rico. The harbor of San Juan in Porto Rico should be dredged and improved. The expenses of the federal court of Porto Rico should be met from the Federal Treasury. The administration of the affairs of Porto Rico, together with those of the Philippines, Hawaii, and our other insular possessions, should all be directed under one executive department; by preference the Department of State or the Department of War.
The needs of Hawaii are peculiar; every aid should be given the islands; and our efforts should be unceasing to develop them along the lines of a community of small freeholders, not of great planters with coolie-tilled estates. Situated as this Territory is, in the middle of the Pacific, there are duties imposed upon this small community which do not fall in like degree or manner upon any other American community. This warrants our treating it differently from the way in which we treat Territories contiguous to or surrounded by sister Territories or other States, and justifies the setting aside of a portion of our revenues to be expended for educational and internal improvements therein. Hawaii is now making an effort to secure immigration fit in the end to assume the duties and burdens of full American citizenship, and whenever the leaders in the various industries of those islands finally adopt our ideals and heartily join our administration in endeavoring to develop a middle class of substantial citizens, a way will then be found to deal with the commercial and industrial problems which now appear to them so serious. The best Americanism is that which aims for stability and permanency of prosperous citizenship, rather than immediate returns on large masses of capital.
Alaska’s needs have been partially met, but there must be a complete reorganization of the governmental system, as I have before indicated to you. I ask your especial attention to this. Our fellow-citizens who dwell on the shores of Puget Sound with characteristic energy are arranging to hold in Seattle the Alaska Yukon Pacific Exposition. Its special aims include the upbuilding of Alaska and the development of American commerce on the Pacific Ocean. This exposition, in its purposes and scope, should appeal not only to the people of the Pacific slope, but to the people of the United States at large. Alaska since it was bought has yielded to the Government eleven millions of dollars of revenue, and has produced nearly three hundred millions of dollars in gold, furs, and fish. When properly developed it will become in large degree a land of homes. The countries bordering the Pacific Ocean have a population more numerous than that of all the countries of Europe; their annual foreign commerce amounts to over three billions of dollars, of which the share of the United States is some seven hundred millions of dollars. If this trade were thoroughly understood and pushed by our manufacturers and producers, the industries not only of the Pacific slope, but of all our country, and particularly of our cotton-growing States, would be greatly benefited. Of course, in order to get these benefits, we must treat fairly the countries with which we trade.
It is a mistake, and it betrays a spirit of foolish cynicism, to maintain that all international governmental action is, and must ever be, based upon mere selfishness, and that to advance ethical reasons for such action is always a sign of hypocrisy. This is no more necessarily true of the action of governments than of the action of individuals. It is a sure sign of a base nature always to ascribe base motives for the actions of others. Unquestionably no nation can afford to disregard proper considerations of self-interest, any more than a private individual can so do. But it is equally true that the average private individual in any really decent community does many actions with reference to other men in which he is guided, not by self-interest, but by public spirit, by regard for the rights of others, by a disinterested purpose to do good to others, and to raise the tone of the community as a whole. Similarly, a really great nation must often act, and as a matter of fact often does act, toward other nations in a spirit not in the least of mere self-interest, but paying heed chiefly to ethical reasons; and as the centuries go by this disinterestedness in international action, this tendency of the individuals comprising a nation to require that nation to act with justice toward its neighbors, steadily grows and strengthens. It is neither wise nor right for a nation to disregard its own needs, and it is foolish—and may be wicked—to think that other nations will disregard theirs. But it is wicked for a nation only to regard its own interest, and foolish to believe that such is the sole motive that actuates any other nation. It should be our steady aim to raise the ethical standard of national action just as we strive to raise the ethical standard of individual action.
Not only must we treat all nations fairly, but we must treat with justice and good will all immigrants who come here under the law. Whether they are Catholic or Protestant, Jew or Gentile; whether they come from England or Germany, Russia, Japan, or Italy, matters nothing. All we have a right to question is the man’s conduct. If he is honest and upright in his dealings with his neighbor and with the State, then he is entitled to respect and good treatment. Especially do we need to remember our duty to the stranger within our gates. It is the sure mark of a low civilization, a low morality, to abuse or discriminate against or in any way humiliate such stranger who has come here lawfully and who is conducting himself properly. To remember this is incumbent on every American citizen, and it is of course peculiarly incumbent on every Government official, whether of the nation or of the several States.
I am prompted to say this by the attitude of hostility here and there assumed toward the Japanese in this country. This hostility is sporadic and is limited to a very few places. Nevertheless, it is most discreditable to us as a people, and it may be fraught with the gravest consequences to the nation. The friendship between the United States and Japan has been continuous since the time, over half a century ago, when Commodore Perry, by his expedition to Japan, first opened the islands to western civilization. Since then the growth of Japan has been literally astounding. There is not only nothing to parallel it, but nothing to approach it in the history of civilized mankind. Japan has a glorious and ancient past. Her civilization is older than that of the nations of northern Europe—the nations from whom the people of the United States have chiefly sprung. But fifty years ago Japan’s development was still that of the Middle Ages. During that fifty years the progress of the country in every walk in life has been a marvel to mankind, and she now stands as one of the greatest of civilized nations; great in the arts of war and in the arts of peace; great in military, in industrial, in artistic development and achievement. Japanese soldiers and sailors have shown themselves equal in combat to any of whom history makes note. She has produced great generals and mighty admirals; her fighting men, afloat and ashore, show all the heroic courage, the unquestioning, unfaltering loyalty, the splendid indifference to hardship and death, which marked the Loyal Ronins; and they show also that they possess the highest ideal of patriotism. Japanese artists of every kind see their products eagerly sought for in all lands. The industrial and commercial development of Japan has been phenomenal; greater than that of any other country during the same period. At the same time the advance in science and philosophy is no less marked. The admirable management of the Japanese Red Cross during the late war, the efficiency and humanity of the Japanese officials, nurses, and doctors, won the respectful admiration of all acquainted with the facts. Through the Red Cross the Japanese people sent over $100,000 to the sufferers of San Francisco, and the gift was accepted with gratitude by our people. The courtesy of the Japanese, nationally and individually, has become proverbial. To no other country has there been such an increasing number of visitors from this land as to Japan. In return, Japanese have come here in great numbers. They are welcome, socially and intellectually, in all our colleges and institutions of higher learning, in all our professional and social bodies. The Japanese have won in a single generation the right to stand abreast of the foremost and most enlightened peoples of Europe and America; they have won on their own merits and by their own exertions the right to treatment on a basis of full and frank equality. The overwhelming mass of our people cherish a lively regard and respect for the people of Japan, and in almost every quarter of the Union the stranger from Japan is treated as he deserves; that is, he is treated as the stranger from any part of civilized Europe is and deserves to be treated. But here and there a most unworthy feeling has manifested itself toward the Japanese—the feeling that has been shown in shutting them out from the common schools in San Francisco, and in mutterings against them in one or two other places, because of their efficiency as workers. To shut them out from the public schools is a wicked absurdity, when there are no first-class colleges in the land, including the universities and colleges of California, which do not gladly welcome Japanese students and on which Japanese students do not reflect credit. We have as much to learn from Japan as Japan has to learn from us; and no nation is fit to teach unless it is also willing to learn. Throughout Japan Americans are well treated, and any failure on the part of Americans at home to treat the Japanese with a like courtesy and consideration is by just so much a confession of inferiority in our civilization.
Our nation fronts on the Pacific, just as it fronts on the Atlantic. We hope to play a constantly growing part in the great ocean of the Orient. We wish, as we ought to wish, for a great commercial development in our dealings with Asia; and it is out of the question that we should permanently have such development unless we freely and gladly extend to other nations the same measure of justice and good treatment which we expect to receive in return. It is only a very small body of our citizens that act badly. Where the Federal Government has power it will deal summarily with any such. Where the several States have power I earnestly ask that they also deal wisely and promptly with such conduct, or else this small body of wrongdoers may bring shame upon the great mass of their innocent and right-thinking fellows—that is, upon our nation as a whole. Good manners should be an international no less than an individual attribute. I ask fair treatment for the Japanese as I would ask fair treatment for Germans or Englishmen, Frenchmen, Russians, or Italians. I ask it as due to humanity and civilization. I ask it as due to ourselves because we must act uprightly toward all men.
I recommend to the Congress that an act be passed specifically providing for the naturalization of Japanese who come here intending to become American citizens. One of the great embarrassments attending the performance of our international obligations is the fact that the Statutes of the United States are entirely inadequate. They fail to give to the National Government sufficiently ample power, through United States courts and by the use of the Army and Navy, to protect aliens in the rights secured to them under solemn treaties which are the law of the land. I therefore earnestly recommend that the criminal and civil statutes of the United States be so amended and added to as to enable the President, acting for the United States Government, which is responsible in our international relations, to enforce the rights of aliens under treaties. Even as the law now is something can be done by the Federal Government toward this end, and in the matter now before me affecting the Japanese everything that it is in my power to do will be done, and all of the forces, military and civil, of the United States which I may lawfully employ will be so employed. There should, however, be no particle of doubt as to the power of the National Government completely to perform and enforce its own obligations to other nations. The mob of a single city may at any time perform acts of lawless violence against some class of foreigners which would plunge us into war. That city by itself would be powerless to make defense against the foreign power thus assaulted, and if independent of this Government it would never venture to perform or permit the performance of the acts complained of. The entire power and the whole duty to protect the offending city or the offending community lies in the hands of the United States Government. It is unthinkable that we should continue a policy under which a given locality may be allowed to commit a crime against a friendly nation, and the United States Government limited, not to preventing the commission of the crime, but, in the last resort, to defending the people who have committed it against the consequences of their own wrongdoing.
Last August an insurrection broke out in Cuba which it speedily grew evident that the existing Cuban Government was powerless to quell. This Government was repeatedly asked by the then Cuban Government to intervene, and finally was notified by the President of Cuba that he intended to resign; that his decision was irrevocable; that none of the other constitutional officers would consent to carry on the Government, and that he was powerless to maintain order. It was evident that chaos was impending, and there was every probability that if steps were not immediately taken by this Government to try to restore order the representatives of various European nations in the island would apply to their respective governments for armed intervention in order to protect the lives and property of their citizens. Thanks to the preparedness of our Navy, I was able immediately to send enough ships to Cuba to prevent the situation from becoming hopeless; and I furthermore dispatched to Cuba the Secretary of War and the Assistant Secretary of State, in order that they might grapple with the situation on the ground. All efforts to secure an agreement between the contending factions, by which they should themselves come to an amicable understanding and settle upon some modus vivendi—some provisional government of their own—failed. Finally the President of the Republic resigned. The quorum of Congress assembled failed by deliberate purpose of its members, so that there was no power to act on his resignation, and the Government came to a halt. In accordance with the so-called Platt amendment, which was embodied in the constitution of Cuba, I thereupon proclaimed a provisional government for the island, the Secretary of War acting as provisional governor until he could be replaced by Mr. Magoon, the late minister to Panama and governor of the Canal Zone on the Isthmus; troops were sent to support them and to relieve the Navy, the expedition being handled with most satisfactory speed and efficiency. The insurgent chiefs immediately agreed that their troops should lay down their arms and disband; and the agreement was carried out. The provisional government has left the personnel of the old government and the old laws, so far as might be, unchanged, and will thus administer the island for a few months until tranquillity can be restored, a new election properly held, and a new government inaugurated. Peace has come in the island; and the harvesting of the sugar-cane crop, the great crop of the island, is about to proceed.
When the election has been held and the new government inaugurated in peaceful and orderly fashion the provisional government will come to an end. I take this opportunity of expressing upon behalf of the American people, with all possible solemnity, our most earnest hope that the people of Cuba will realize the imperative need of preserving justice and keeping order in the Island. The United States wishes nothing of Cuba except that it shall prosper morally and materially, and wishes nothing of the Cubans save that they shall be able to preserve order among themselves and therefore to preserve their independence. If the elections become a farce, and if the insurrectionary habit becomes confirmed in the Island, it is absolutely out of the question that the Island should continue independent; and the United States, which has assumed the sponsorship before the civilized world for Cuba’s career as a nation, would again have to intervene and to see that the government was managed in such orderly fashion as to secure the safety of life and property. The path to be trodden by those who exercise self-government is always hard, and we should have every charity and patience with the Cubans as they tread this difficult path. I have the utmost sympathy with, and regard for, them; but I most earnestly adjure them solemnly to weigh their responsibilities and to see that when their new government is started it shall run smoothly, and with freedom from flagrant denial of right on the one hand, and from insurrectionary disturbances on the other.
The Second International Conference of American Republics, held in Mexico in the years 1901-2, provided for the holding of the third conference within five years, and committed the fixing of the time and place and the arrangements for the conference to the governing board of the Bureau of American Republics, composed of the representatives of all the American nations in Washington. That board discharged the duty imposed upon it with marked fidelity and painstaking care, and upon the courteous invitation of the United States of Brazil the conference was held at Rio de Janeiro, continuing from the 23d of July to the 29th of August last. Many subjects of common interest to all the American nations were discust by the conference, and the conclusions reached, embodied in a series of resolutions and proposed conventions, will be laid before you upon the coming in of the final report of the American delegates. They contain many matters of importance relating to the extension of trade, the increase of communication, the smoothing away of barriers to free intercourse, and the promotion of a better knowledge and good understanding between the different countries represented. The meetings of the conference were harmonious and the conclusions were reached with substantial unanimity. It is interesting to observe that in the successive conferences which have been held the representatives of the different American nations have been learning to work together effectively, for, while the First Conference in Washington in 1889, and the Second Conference in Mexico in 1901-2, occupied many months, with much time wasted in an unregulated and fruitless discussion, the Third Conference at Rio exhibited much of the facility in the practical dispatch of business which characterizes permanent deliberative bodies, and completed its labors within the period of six weeks originally allotted for its sessions.
Quite apart from the specific value of the conclusions reached by the conference, the example of the representatives of all the American nations engaging in harmonious and kindly consideration and discussion of subjects of common interest is itself of great and substantial value for the promotion of reasonable and considerate treatment of all international questions. The thanks of this country are due to the Government of Brazil and to the people of Rio de Janeiro for the generous hospitality with which our delegates, in common with the others, were received, entertained, and facilitated in their work.
Incidentally to the meeting of the conference, the Secretary of State visited the city of Rio de Janeiro and was cordially received by the conference, of which he was made an honorary president. The announcement of his intention to make this visit was followed by most courteous and urgent invitations from nearly all the countries of South America to visit them as the guest of their Governments. It was deemed that by the acceptance of these invitations we might appropriately express the real respect and friendship in which we hold our sister Republics of the southern continent, and the Secretary, accordingly, visited Brazil, Uruguay, Argentina, Chile, Peru, Panama, and Colombia. He refrained from visiting Paraguay, Bolivia, and Ecuador only because the distance of their capitals from the seaboard made it impracticable with the time at his disposal. He carried with him a message of peace and friendship, and of strong desire for good understanding and mutual helpfulness; and he was everywhere received in the spirit of his message. The members of government, the press, the learned professions, the men of business, and the great masses of the people united everywhere in emphatic response to his friendly expressions and in doing honor to the country and cause which he represented.
In many parts of South America there has been much misunderstanding of the attitude and purposes of the United States towards the other American Republics. An idea had become prevalent that our assertion of the Monroe Doctrine implied, or carried with it, an assumption of superiority, and of a right to exercise some kind of protectorate over the countries to whose territory that doctrine applies. Nothing could be farther from the truth. Yet that impression continued to be a serious barrier to good understanding, to friendly intercourse, to the introduction of American capital and the extension of American trade. The impression was so widespread that apparently it could not be reached by any ordinary means.
It was part of Secretary Root’s mission to dispel this unfounded impression, and there is just cause to believe that he has succeeded. In an address to the Third Conference at Rio on the 31st of July—an address of such note that I send it in, together with this message—he said:
"We wish for no victories but those of peace; for no territory except our own; for no sovereignty except the sovereignty over ourselves. We deem the independence and equal rights of the smallest and weakest member of the family of nations entitled to as much respect as those of the greatest empire, and we deem the observance of that respect the chief guaranty of the weak against the oppression of the strong. We neither claim nor desire any rights or privileges or powers that we do not freely concede to every American Republic. We wish to increase our prosperity, to extend our trade, to grow in wealth, in wisdom, and in spirit, but our conception of the true way to accomplish this is not to pull down others and profit by their ruin, but to help all friends to a common prosperity and a common growth, that we may all become greater and stronger together. Within a few months for the first time the recognized possessors of every foot of soil upon the American continents can be and I hope will be represented with the acknowledged rights of equal sovereign states in the great World Congress at The Hague. This will be the world’s formal and final acceptance of the declaration that no part of the American continents is to be deemed subject to colonization. Let us pledge ourselves to aid each other in the full performance of the duty to humanity which that accepted declaration implies, so that in time the weakest and most unfortunate of our Republics may come to march with equal step by the side of the stronger and more fortunate. Let us help each other to show that for all the races of men the liberty for which we have fought and labored is the twin sister of justice and peace. Let us unite in creating and maintaining and making effective an all-American public opinion, whose power shall influence international conduct and prevent international wrong, and narrow the causes of war, and forever preserve our free lands from the burden of such armaments as are massed behind the frontiers of Europe, and bring us ever nearer to the perfection of ordered liberty. So shall come security and prosperity, production and trade, wealth, learning, the arts, and happiness for us all."
These words appear to have been received with acclaim in every part of South America. They have my hearty approval, as I am sure they will have yours, and I can not be wrong in the conviction that they correctly represent the sentiments of the whole American people. I can not better characterize the true attitude of the United States in its assertion of the Monroe Doctrine than in the words of the distinguished former minister of foreign affairs of Argentina, Doctor Drago, in his speech welcoming Mr. Root at Buenos Ayres. He spoke of—
"The traditional policy of the United States (which) without accentuating superiority or seeking preponderance, condemned the oppression of the nations of this part of the world and the control of their destinies by the great Powers of Europe."
It is gratifying to know that in the great city of Buenos Ayres, upon the arches which spanned the streets, entwined with Argentine and American flags for the reception of our representative, there were emblazoned not’ only the names of Washington and Jefferson and Marshall, but also, in appreciative recognition of their services to the cause of South American independence, the names of James Monroe, John Quincy Adams, Henry Clay, and Richard Rush. We take especial pleasure in the graceful courtesy of the Government of Brazil, which has given to the beautiful and stately building first used for the meeting of the conference the name of "Palacio Monroe." Our grateful acknowledgments are due to the Governments and the people of all the countries visited by the Secretary of State for the courtesy, the friendship, and the honor shown to our country in their generous hospitality to him.
In my message to you on the 5th of December, 1905, I called your attention to the embarrassment that might be caused to this Government by the assertion by foreign nations of the right to collect by force of arms contract debts due by American republics to citizens of the collecting nation, and to the danger that the process of compulsory collection might result in the occupation of territory tending to become permanent. I then said:
"Our own Government has always refused to enforce such contractual obligations on behalf of its citizens by an appeal to arms. It is much to be wisht that all foreign governments would take the same view."
This subject was one of the topics of consideration at the conference at Rio and a resolution was adopted by that conference recommending to the respective governments represented "to consider the advisability of asking the Second Peace Conference at The Hague to examine the question of the compulsory collection of public debts, and, in general, means tending to diminish among nations conflicts of purely pecuniary origin."
This resolution was supported by the representatives of the United States in accordance with the following instructions:
"It has long been the established policy of the United States not to use its armed forces for the collection of ordinary contract debts due to its citizens by other governments. We have not considered the use of force for such a purpose consistent with that respect for the independent sovereignty of other members of the family of nations which is the most important principle of international law and the chief protection of weak nations against the oppression of the strong. It seems to us that the practise is injurious in its general effect upon the relations of nations and upon the welfare of weak and disordered states, whose development ought to be encouraged in the interests of civilization; that it offers frequent temptation to bullying and oppression and to unnecessary and unjustifiable warfare. We regret that other powers, whose opinions and sense of justice we esteem highly, have at times taken a different view and have permitted themselves, though we believe with reluctance, to collect such debts by force. It is doubtless true that the non-payment of public debts may be accompanied by such circumstances of fraud and wrongdoing or violation of treaties as to justify the use of force. This Government would be glad to see an international consideration of the subject which shall discriminate between such cases and the simple nonperformance of a contract with a private person, and a resolution in favor of reliance upon peaceful means in cases of the latter class.
"It is not felt, however, that the conference at Rio should undertake to make such a discrimination or to resolve upon such a rule. Most of the American countries are still debtor nations, while the countries of Europe are the creditors. If the Rio conference, therefore, were to take such action it would have the appearance of a meeting of debtors resolving how their creditors should act, and this would not inspire respect. The true course is indicated by the terms of the program, which proposes to request the Second Hague Conference, where both creditors and debtors will be assembled, to consider the subject."
Last June trouble which had existed for some time between the Republics of Salvador, Guatemala, and Honduras culminated in war—a war which threatened to be ruinous to the countries involved and very destructive to the commercial interests of Americans, Mexicans, and other foreigners who are taking an important part in the development of these countries. The thoroughly good understanding which exists between the United States and Mexico enabled this Government and that of Mexico to unite in effective mediation between the warring Republics; which mediation resulted, not without long-continued and patient effort, in bringing about a meeting of the representatives of the hostile powers on board a United States warship as neutral territory, and peace was there concluded; a peace which resulted in the saving of thousands of lives and in the prevention of an incalculable amount of misery and the destruction of property and of the means of livelihood. The Rio Conference past the following resolution in reference to this action:
"That the Third International American Conference shall address to the Presidents of the United States of America and of the United States of Mexico a note in which the conference which is being held at Rio expresses its satisfaction at the happy results of their mediation for the celebration of peace between the Republics of Guatemala, Honduras, and Salvador."
This affords an excellent example of one way in which the influence of the United States can properly be exercised for the benefit of the peoples of the Western Hemisphere; that is, by action taken in concert with other American republics and therefore free from those suspicions and prejudices which might attach if the action were taken by one alone. In this way it is possible to exercise a powerful influence toward the substitution of considerate action in the spirit of justice for the insurrectionary or international violence which has hitherto been so great a hindrance to the development of many of our neighbors. Repeated examples of united action by several or many American republics in favor of peace, by urging cool and reasonable, instead of excited and belligerent, treatment of international controversies, can not fail to promote the growth of a general public opinion among the American nations which will elevate the standards of international action, strengthen the sense of international duty among governments, and tell in favor of the peace of mankind.
I have just returned from a trip to Panama and shall report to you at length later on the whole subject of the Panama Canal.
The Algeciras Convention, which was signed by the United States as well as by most of the powers of Europe, supersedes the previous convention of 1880, which was also signed both by the United States and a majority of the European powers. This treaty confers upon us equal commercial rights with all European countries and does not entail a single obligation of any kind upon us, and I earnestly hope it may be speedily ratified. To refuse to ratify it would merely mean that we forfeited our commercial rights in Morocco and would not achieve another object of any kind. In the event of such refusal we would be left for the first time in a hundred and twenty years without any commercial treaty with Morocco; and this at a time when we are everywhere seeking new markets and outlets for trade.
The destruction of the Pribilof Islands fur seals by pelagic sealing still continues. The herd which, according to the surveys made in 1874 by direction of the Congress, numbered 4,700,000, and which, according to the survey of both American and Canadian commissioners in 1891, amounted to 1,000,000, has now been reduced to about 180,000. This result has been brought about by Canadian and some other sealing vessels killing the female seals while in the water during their annual pilgrimage to and from the south, or in search of food. As a rule the female seal when killed is pregnant, and also has an unweaned pup on land, so that, for each skin taken by pelagic sealing, as a rule, three lives are destroyed—the mother, the unborn offspring, and the nursing pup, which is left to starve to death. No damage whatever is done to the herd by the carefully regulated killing on land; the custom of pelagic sealing is solely responsible for all of the present evil, and is alike indefensible from the economic standpoint and from the standpoint of humanity.
In 1896 over 16,000 young seals were found dead from starvation on the Pribilof Islands. In 1897 it was estimated that since pelagic sealing began upward of 400,000 adult female seals had been killed at sea, and over 300,000 young seals had died of starvation as the result. The revolting barbarity of such a practise, as well as the wasteful destruction which it involves, needs no demonstration and is its own condemnation. The Bering Sea Tribunal, which sat in Paris in 1893, and which decided against the claims of the United States to exclusive jurisdiction in the waters of Bering Sea and to a property right in the fur seals when outside of the three-mile limit, determined also upon certain regulations which the Tribunal considered sufficient for the proper protection and preservation of the fur seal in, or habitually resorting to, the Bering Sea. The Tribunal by its regulations established a close season, from the 1st of May to the 31st of July, and excluded all killing in the waters within 60 miles around the Pribilof Islands. They also provided that the regulations which they had determined upon, with a view to the protection and preservation of the seals, should be submitted every five years to new examination, so as to enable both interested Governments to consider whether, in the light of past experience, there was occasion for any modification thereof.
The regulations have proved plainly inadequate to accomplish the object of protection and preservation of the fur seals, and for a long time this Government has been trying in vain to secure from Great Britain such revision and modification of the regulations as were contemplated and provided for by the award of the Tribunal of Paris.
The process of destruction has been accelerated during recent years by the appearance of a number of Japanese vessels engaged in pelagic sealing. As these vessels have not been bound even by the inadequate limitations prescribed by the Tribunal of Paris, they have paid no attention either to the close season or to the sixty-mile limit imposed upon the Canadians, and have prosecuted their work up to the very islands themselves. On July 16 and 17 the crews from several Japanese vessels made raids upon the island of St. Paul, and before they were beaten off by the very meager and insufficiently armed guard, they succeeded in killing several hundred seals and carrying off the skins of most of them. Nearly all the seals killed were females and the work was done with frightful barbarity. Many of the seals appear to have been skinned alive and many were found half skinned and still alive. The raids were repelled only by the use of firearms, and five of the raiders were killed, two were wounded, and twelve captured, including the two wounded. Those captured have since been tried and sentenced to imprisonment. An attack of this kind had been wholly unlookt for, but such provision of vessels, arms, and ammunition will now be made that its repetition will not be found profitable.
Suitable representations regarding the incident have been made to the Government of Japan, and we are assured that all practicable measures will be taken by that country to prevent any recurrence of the outrage. On our part, the guard on the island will be increased and better equipped and organized, and a better revenue-cutter patrol service about the islands will be established; next season a United States war vessel will also be sent there.
We have not relaxed our efforts to secure an agreement with Great Britain for adequate protection of the seal herd, and negotiations with Japan for the same purpose are in progress.
The laws for the protection of the seals within the jurisdiction of the United States need revision and amendment. Only the islands of St. Paul and St. George are now, in terms, included in the Government reservation, and the other islands are also to be included. The landing of aliens as well as citizens upon the islands, without a permit from the Department of Commerce and Labor, for any purpose except in case of stress of weather or for water, should be prohibited under adequate penalties. The approach of vessels for the excepted purposes should be regulated. The authority of the Government agents on the islands should be enlarged, and the chief agent should have the powers of a committing magistrate. The entrance of a vessel into the territorial waters surrounding the islands with intent to take seals should be made a criminal offense and cause of forfeiture. Authority for seizures in such cases should be given and the presence on any such vessel of seals or sealskins, or the paraphernalia for taking them, should be made prima facie evidence of such intent. I recommend what legislation is needed to accomplish these ends; and I commend to your attention the report of Mr. Sims, of the Department of Commerce and Labor, on this subject.
In case we are compelled to abandon the hope of making arrangements with other governments to put an end to the hideous cruelty now incident to pelagic sealing, it will be a question for your serious consideration how far we should continue to protect and maintain the seal herd on land with the result of continuing such a practise, and whether it is not better to end the practice by exterminating the herd ourselves in the most humane way possible.
In my last message I advised you that the Emperor of Russia had taken the initiative in bringing about a second peace conference at The Hague. Under the guidance of Russia the arrangement of the preliminaries for such a conference has been progressing during the past year. Progress has necessarily been slow, owing to the great number of countries to be consulted upon every question that has arisen. It is a matter of satisfaction that all of the American Republics have now, for the first time, been invited to join in the proposed conference.
The close connection between the subjects to be taken up by the Red Cross Conference held at Geneva last summer and the subjects which naturally would come before The Hague Conference made it apparent that it was desirable to have the work of the Red Cross Conference completed and considered by the different powers before the meeting at The Hague. The Red Cross Conference ended its labors on the 6th day of July, and the revised and amended convention, which was signed by the American delegates, will be promptly laid before the Senate.
By the special and highly appreciated courtesy of the Governments of Russia and the Netherlands, a proposal to call The Hague Conference together at a time which would conflict with the Conference of the American Republics at Rio de Janeiro in August was laid aside. No other date has yet been suggested. A tentative program for the conference has been proposed by the Government of Russia, and the subjects which it enumerates are undergoing careful examination and consideration in preparation for the conference.
It must ever be kept in mind that war is not merely justifiable, but imperative, upon honorable men, upon an honorable nation, where peace can only be obtained by the sacrifice of conscientious conviction or of national welfare. Peace is normally a great good, and normally it coincides with righteousness; but it is righteousness and not peace which should bind the conscience of a nation as it should bind the conscience of an individual; and neither a nation nor an individual can surrender conscience to another’s keeping. Neither can a nation, which is an entity, and which does not die as individuals die, refrain from taking thought for the interest of the generations that are to come, no less than for the interest of the generation of to-day; and no public men have a right, whether from shortsightedness, from selfish indifference, or from sentimentality, to sacrifice national interests which are vital in character. A just war is in the long run far better for a nation’s soul than the most prosperous peace obtained by acquiescence in wrong or injustice. Moreover, though it is criminal for a nation not to prepare for war, so that it may escape the dreadful consequences of being defeated in war, yet it must always be remembered that even to be defeated in war may be far better than not to have fought at all. As has been well and finely said, a beaten nation is not necessarily a disgraced nation; but the nation or man is disgraced if the obligation to defend right is shirked.
We should as a nation do everything in our power for the cause of honorable peace. It is morally as indefensible for a nation to commit a wrong upon another nation, strong or weak, as for an individual thus to wrong his fellows. We should do all in our power to hasten the day when there shall be peace among the nations—a peace based upon justice and not upon cowardly submission to wrong. We can accomplish a good deal in this direction, but we can not accomplish everything, and the penalty of attempting to do too much would almost inevitably be to do worse than nothing; for it must be remembered that fantastic extremists are not in reality leaders of the causes which they espouse, but are ordinarily those who do most to hamper the real leaders of the cause and to damage the cause itself. As yet there is no likelihood of establishing any kind of international power, of whatever sort, which can effectively check wrongdoing, and in these circumstances it would be both a foolish and an evil thing for a great and free nation to deprive itself of the power to protect its own rights and even in exceptional cases to stand up for the rights of others. Nothing would more promote iniquity, nothing would further defer the reign upon earth of peace and righteousness, than for the free and enlightened peoples which, though with much stumbling and many shortcomings, nevertheless strive toward justice, deliberately to render themselves powerless while leaving every despotism and barbarism armed and able to work their wicked will. The chance for the settlement of disputes peacefully, by arbitration, now depends mainly upon the possession by the nations that mean to do right of sufficient armed strength to make their purpose effective.
The United States Navy is the surest guarantor of peace which this country possesses. It is earnestly to be wisht that we would profit by the teachings of history in this matter. A strong and wise people will study its own failures no less than its triumphs, for there is wisdom to be learned from the study of both, of the mistake as well as of the success. For this purpose nothing could be more instructive than a rational study of the war of 1812, as it is told, for instance, by Captain Mahan. There was only one way in which that war could have been avoided. If during the preceding twelve years a navy relatively as strong as that which this country now has had been built up, and an army provided relatively as good as that which the country now has, there never would have been the slightest necessity of fighting the war; and if the necessity had arisen the war would under such circumstances have ended with our speedy and overwhelming triumph. But our people during those twelve years refused to make any preparations whatever, regarding either the Army or the Navy. They saved a million or two of dollars by so doing; and in mere money paid a hundredfold for each million they thus saved during the three years of war which followed—a war which brought untold suffering upon our people, which at one time threatened the gravest national disaster, and which, in spite of the necessity of waging it, resulted merely in what was in effect a drawn battle, while the balance of defeat and triumph was almost even.
I do not ask that we continue to increase our Navy. I ask merely that it be maintained at its present strength; and this can be done only if we replace the obsolete and outworn ships by new and good ones, the equals of any afloat in any navy. To stop building ships for one year means that for that year the Navy goes back instead of forward. The old battle ship Texas, for instance, would now be of little service in a stand-up fight with a powerful adversary. The old double-turret monitors have outworn their usefulness, while it was a waste of money to build the modern single-turret monitors. All these ships should be replaced by others; and this can be done by a well-settled program of providing for the building each year of at least one first-class battle ship equal in size and speed to any that any nation is at the same time building; the armament presumably to consist of as large a number as possible of very heavy guns of one caliber, together with smaller guns to repel torpedo attack; while there should be heavy armor, turbine engines, and in short, every modern device. Of course, from time to time, cruisers, colliers, torpedo-boat destroyers or torpedo boats, Will have to be built also. All this, be it remembered, would not increase our Navy, but would merely keep it at its present strength. Equally of course, the ships will be absolutely useless if the men aboard them are not so trained that they can get the best possible service out of the formidable but delicate and complicated mechanisms intrusted to their care. The marksmanship of our men has so improved during the last five years that I deem it within bounds to say that the Navy is more than twice as efficient, ship for ship, as half a decade ago. The Navy can only attain proper efficiency if enough officers and men are provided, and if these officers and men are given the chance (and required to take advantage of it) to stay continually at sea and to exercise the fleets singly and above all in squadron, the exercise to be of every kind and to include unceasing practise at the guns, conducted under conditions that will test marksmanship in time of war.
In both the Army and the Navy there is urgent need that everything possible should be done to maintain the highest standard for the personnel, alike as regards the officers and the enlisted men. I do not believe that in any service there is a finer body of enlisted men and of junior officer than we have in both the Army and the Navy, including the Marine Corps. All possible encouragement to the enlisted men should be given, in pay and otherwise, and everything practicable done to render the service attractive to men of the right type. They should be held to the strictest discharge of their duty, and in them a spirit should be encouraged which demands not the mere performance of duty, but the performance of far more than duty, if it conduces to the honor and the interest of the American nation; and in return the amplest consideration should be theirs.
West Point and Annapolis already turn out excellent officers. We do not need to have these schools made more scholastic. On the contrary we should never lose sight of the fact that the aim of each school is to turn out a man who shall be above everything else a fighting man. In the Army in particular it is not necessary that either the cavalry or infantry officer should have special mathematical ability. Probably in both schools the best part of the education is the high standard of character and of professional morale which it confers.
But in both services there is urgent need for the establishment of a principle of selection which will eliminate men after a certain age if they can not be promoted from the subordinate ranks, and which will bring into the higher ranks fewer men, and these at an earlier age. This principle of selection will be objected to by good men of mediocre capacity, who are fitted to do well while young in the lower positions, but who are not fitted to do well when at an advanced age they come into positions of command and of great responsibility. But the desire of these men to be promoted to positions which they are not competent to fill should not weigh against the interest of the Navy and the country. At present our men, especially in the Navy, are kept far too long in the junior grades, and then, at much too advanced an age, are put quickly through the senior grades, often not attaining to these senior grades until they are too old to be of real use in them; and if they are of real use, being put through them so quickly that little benefit to the Navy comes from their having been in them at all.
The Navy has one great advantage over the Army in the fact that the officers of high rank are actually trained in the continual performance of their duties; that is, in the management of the battle ships and armored cruisers gathered into fleets. This is not true of the army officers, who rarely have corresponding chances to exercise command over troops under service conditions. The conduct of the Spanish war showed the lamentable loss of life, the useless extravagance, and the inefficiency certain to result, if during peace the high officials of the War and Navy Departments are praised and rewarded only if they save money at no matter what cost to the efficiency of the service, and if the higher officers are given no chance whatever to exercise and practise command. For years prior to the Spanish war the Secretaries of War were praised chiefly if they practised economy; which economy, especially in connection with the quartermaster, commissary, and medical departments, was directly responsible for most of the mismanagement that occurred in the war itself—and parenthetically be it observed that the very people who clamored for the misdirected economy in the first place were foremost to denounce the mismanagement, loss, and suffering which were primarily due to this same misdirected economy and to the lack of preparation it involved. There should soon be an increase in the number of men for our coast defenses; these men should be of the right type and properly trained; and there should therefore be an increase of pay for certain skilled grades, especially in the coast artillery. Money should be appropriated to permit troops to be massed in body and exercised in maneuvers, particularly in marching. Such exercise during the summer just past has been of incalculable benefit to the Army and should under no circumstances be discontinued. If on these practise marches and in these maneuvers elderly officers prove unable to bear the strain, they should be retired at once, for the fact is conclusive as to their unfitness for war; that is, for the only purpose because of which they should be allowed to stay in the service. It is a real misfortune to have scores of small company or regimental posts scattered throughout the country; the Army should be gathered in a few brigade or division posts; and the generals should be practised in handling the men in masses. Neglect to provide for all of this means to incur the risk of future disaster and disgrace.
The readiness and efficiency of both the Army and Navy in dealing with the recent sudden crisis in Cuba illustrate afresh their value to the Nation. This readiness and efficiency would have been very much less had it not been for the existence of the General Staff in the Army and the General Board in the Navy; both are essential to the proper development and use of our military forces afloat and ashore. The troops that were sent to Cuba were handled flawlessly. It was the swiftest mobilization and dispatch of troops over sea ever accomplished by our Government. The expedition landed completely equipped and ready for immediate service, several of its organizations hardly remaining in Havana over night before splitting up into detachments and going to their several posts, It was a fine demonstration of the value and efficiency of the General Staff. Similarly, it was owing in large part to the General Board that the Navy was able at the outset to meet the Cuban crisis with such instant efficiency; ship after ship appearing on the shortest notice at any threatened point, while the Marine Corps in particular performed indispensable service. The Army and Navy War Colleges are of incalculable value to the two services, and they cooperate with constantly increasing efficiency and importance.
The Congress has most wisely provided for a National Board for the promotion of rifle practise. Excellent results have already come from this law, but it does not go far enough. Our Regular Army is so small that in any great war we should have to trust mainly to volunteers; and in such event these volunteers should already know how to shoot; for if a soldier has the fighting edge, and ability to take care of himself in the open, his efficiency on the line of battle is almost directly Proportionate to excellence in marksmanship. We should establish shooting galleries in all the large public and military schools, should maintain national target ranges in different parts of the country, and should in every way encourage the formation of rifle clubs throughout all parts of the land. The little Republic of Switzerland offers us an excellent example in all matters connected with building up an efficient citizen soldiery.

Conversation-based seminars for collegial PD, one-day and multi-day seminars, graduate credit seminars (MA degree), online and in-person.