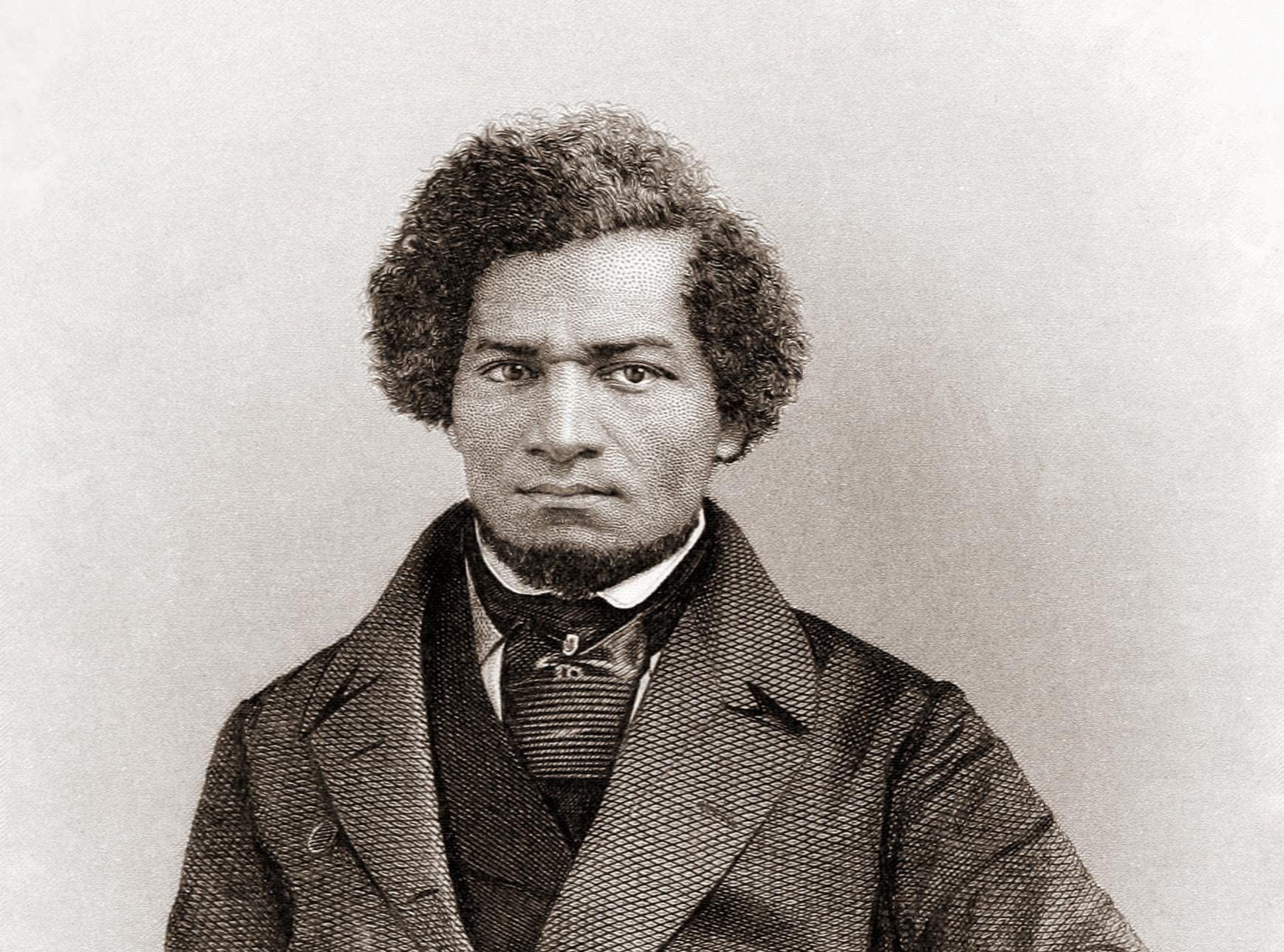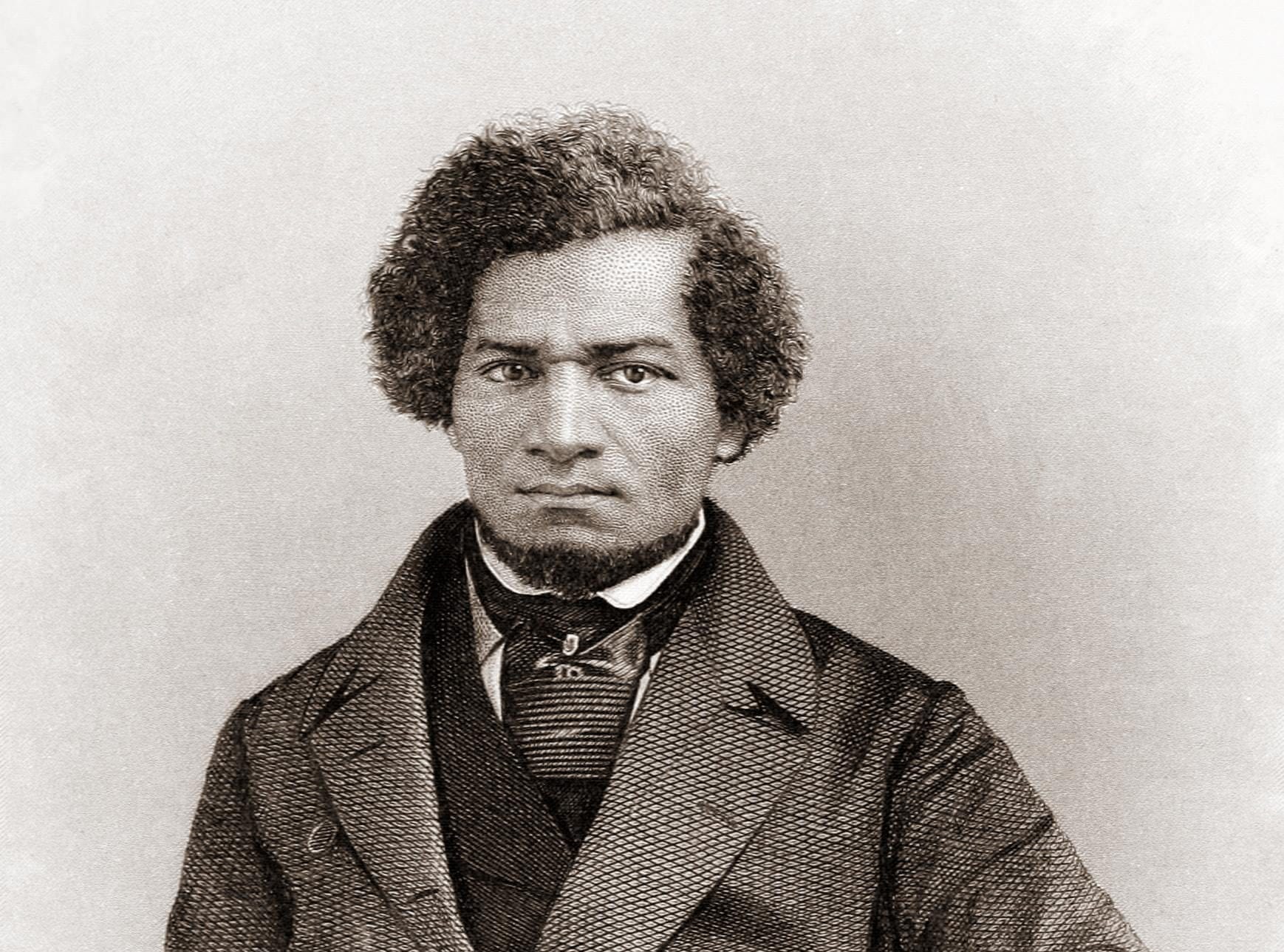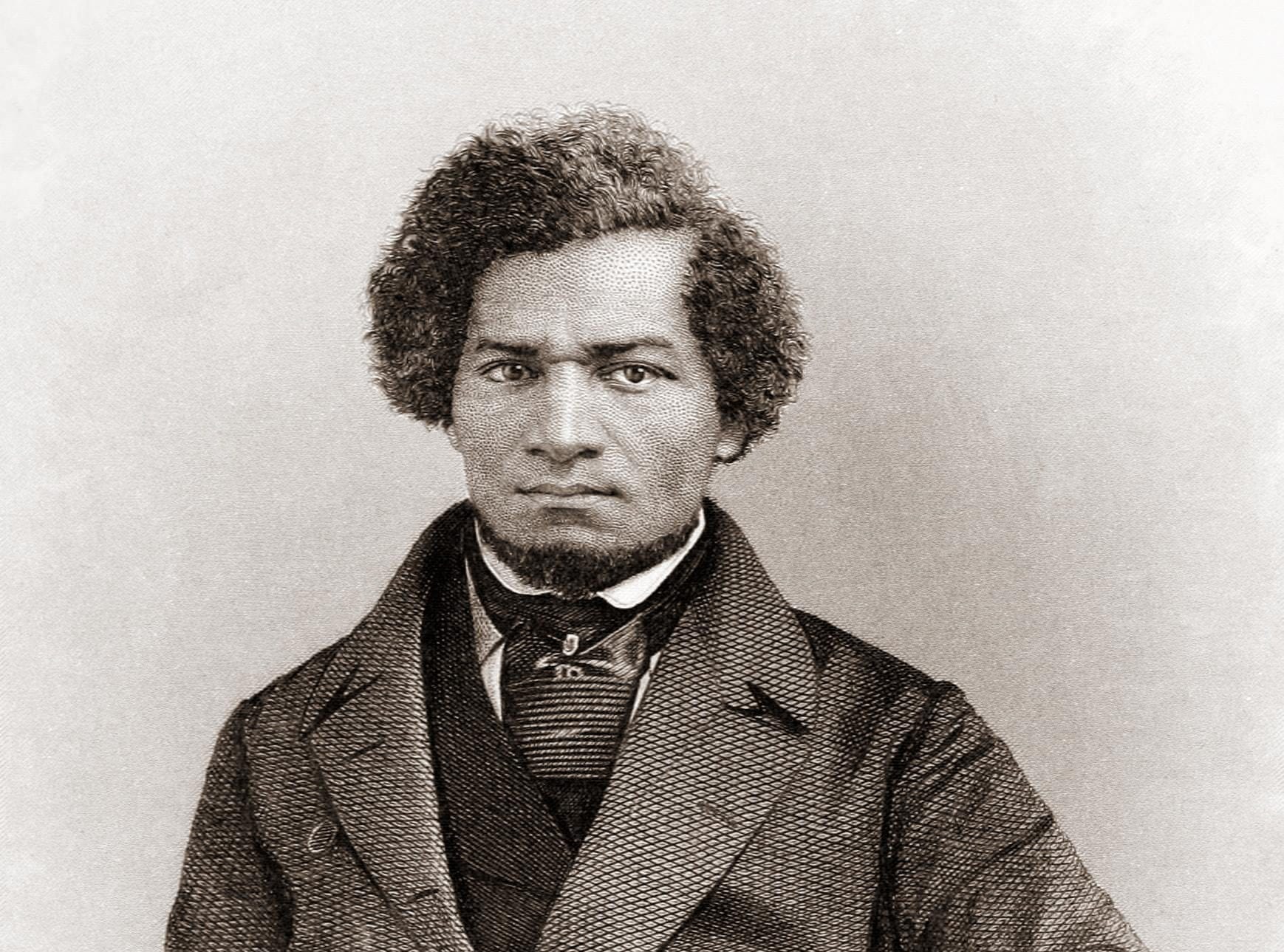No related resources
Introduction
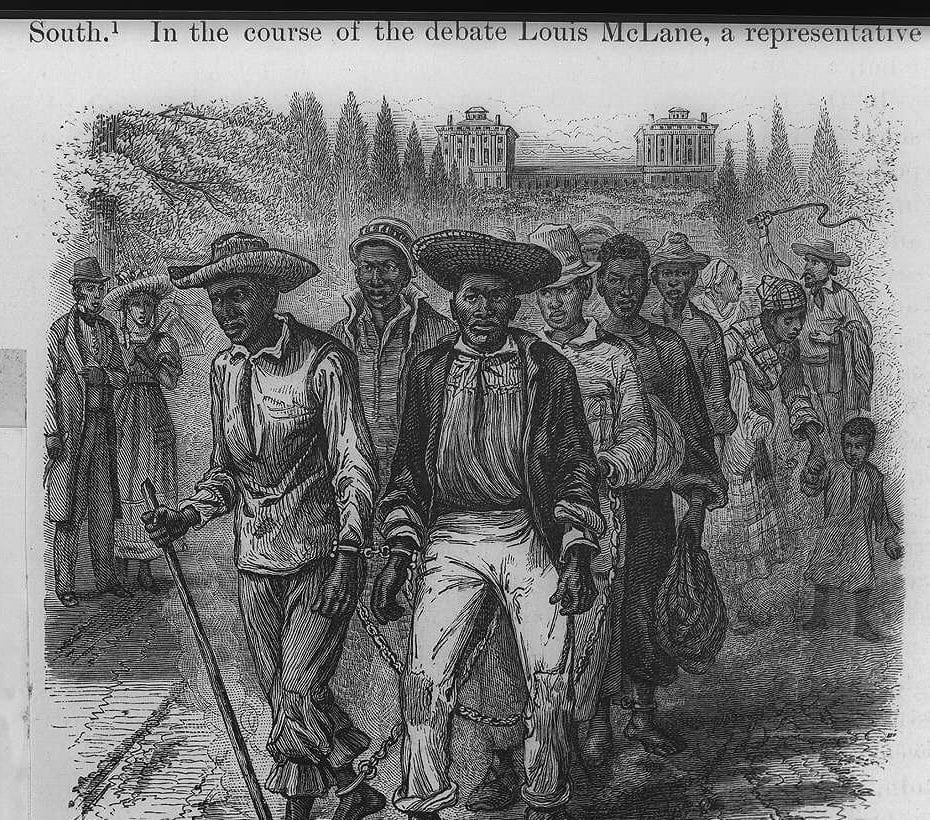
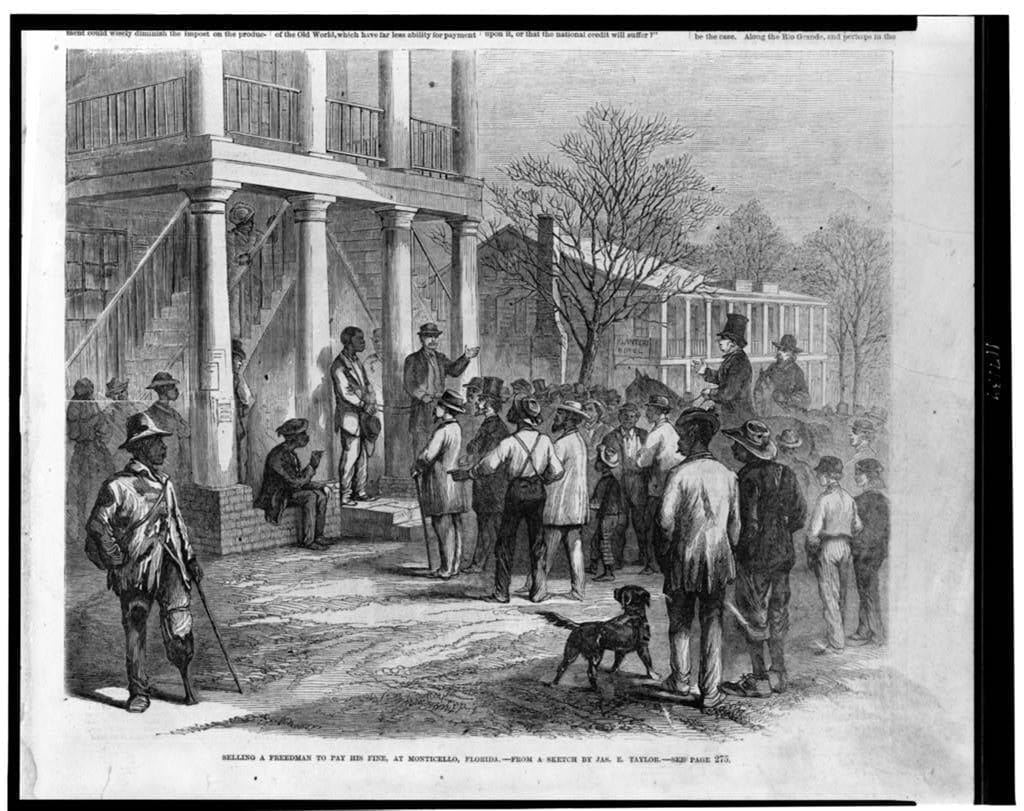
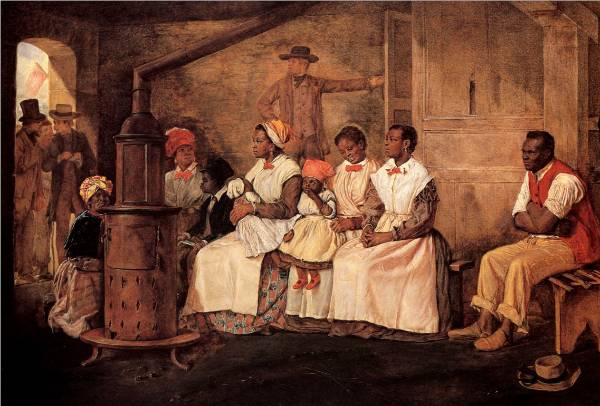
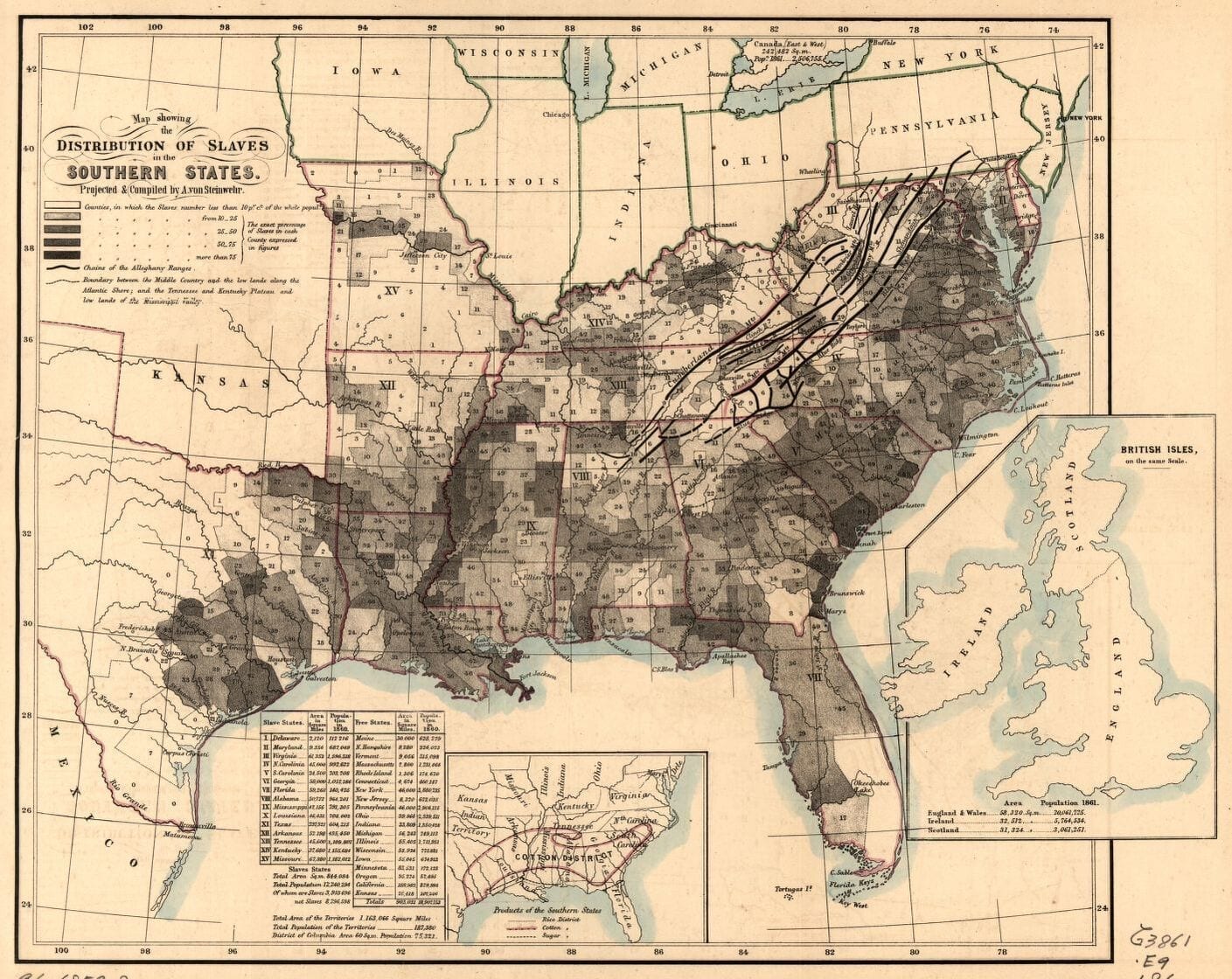
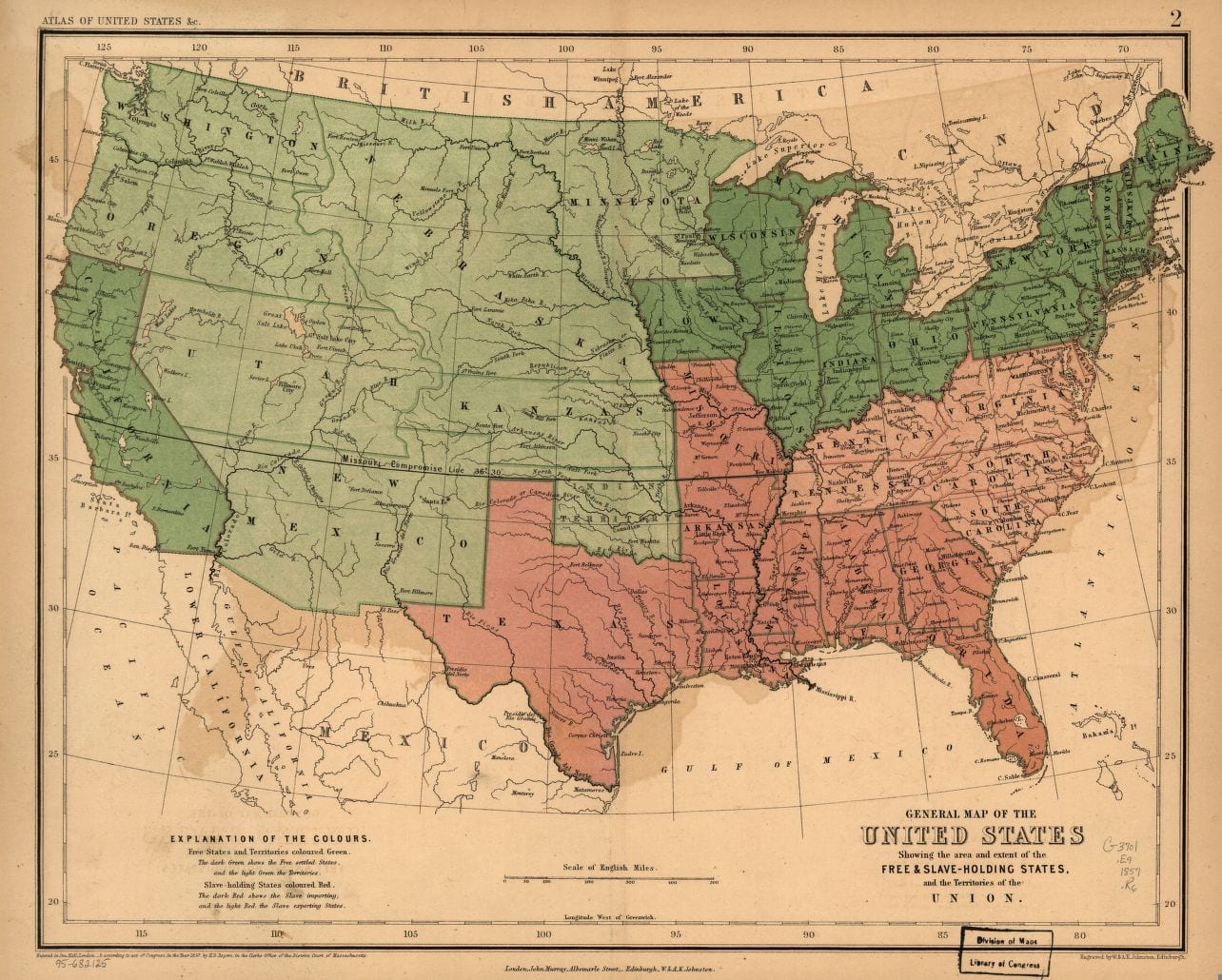
By 1830, slavery had become very much a regional, as opposed to a national institution (see Number of Slaves in the Territory Enumerated, 1790 to 1850). The New England and Middle States had, through a combination of gradual abolition and immediate emancipation measures, dramatically decreased the number of slaves in their territories, while the Southern states had increased their reliance upon slave labor in the production of various cash crops, chief among them “King Cotton.” Nevertheless, there were individuals in both sections of the country who recognized the need for continued prudential reform. In December 1833, dozens of Northern activists met in Philadelphia to found the American Anti-Slavery Society. Although the group called for the immediate and uncompensated emancipation of all enslaved persons, they also denounced the use of violent resistance – an important concession to Southern slaveholders fearful of additional armed uprisings like Nat Turner’s Rebellion (1831). Southern activist Angelina Grimke addressed similar fears in her Appeal to the Christian Women of the South. Grimke urged Southern women to speak out against slavery as an unjust and oppressive system, but also counseled them to encourage patience and submission on the part of their slaves until freedom was obtained.
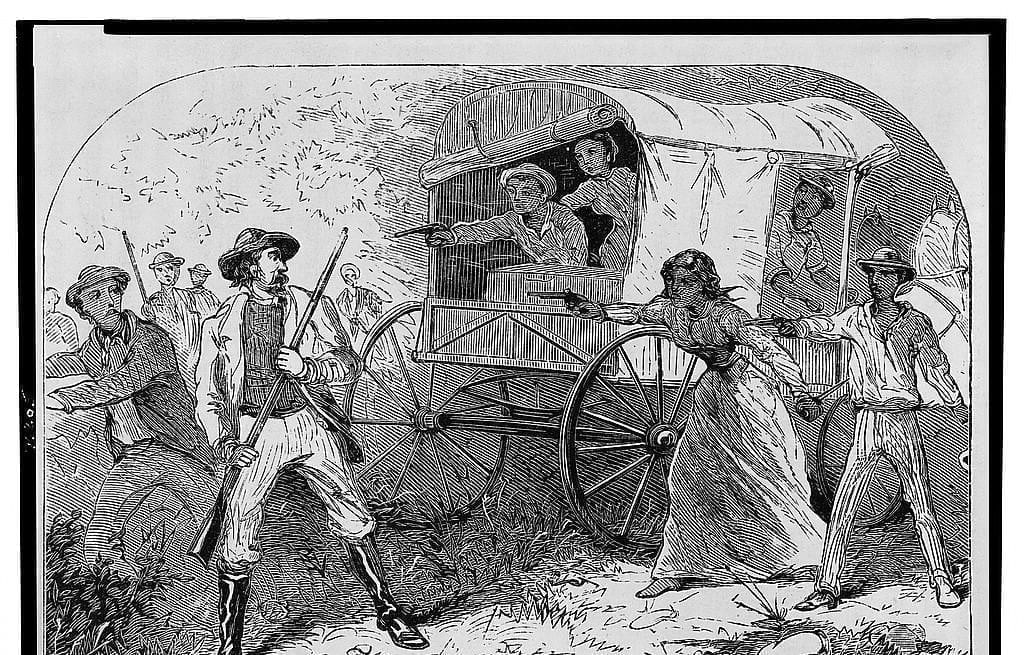
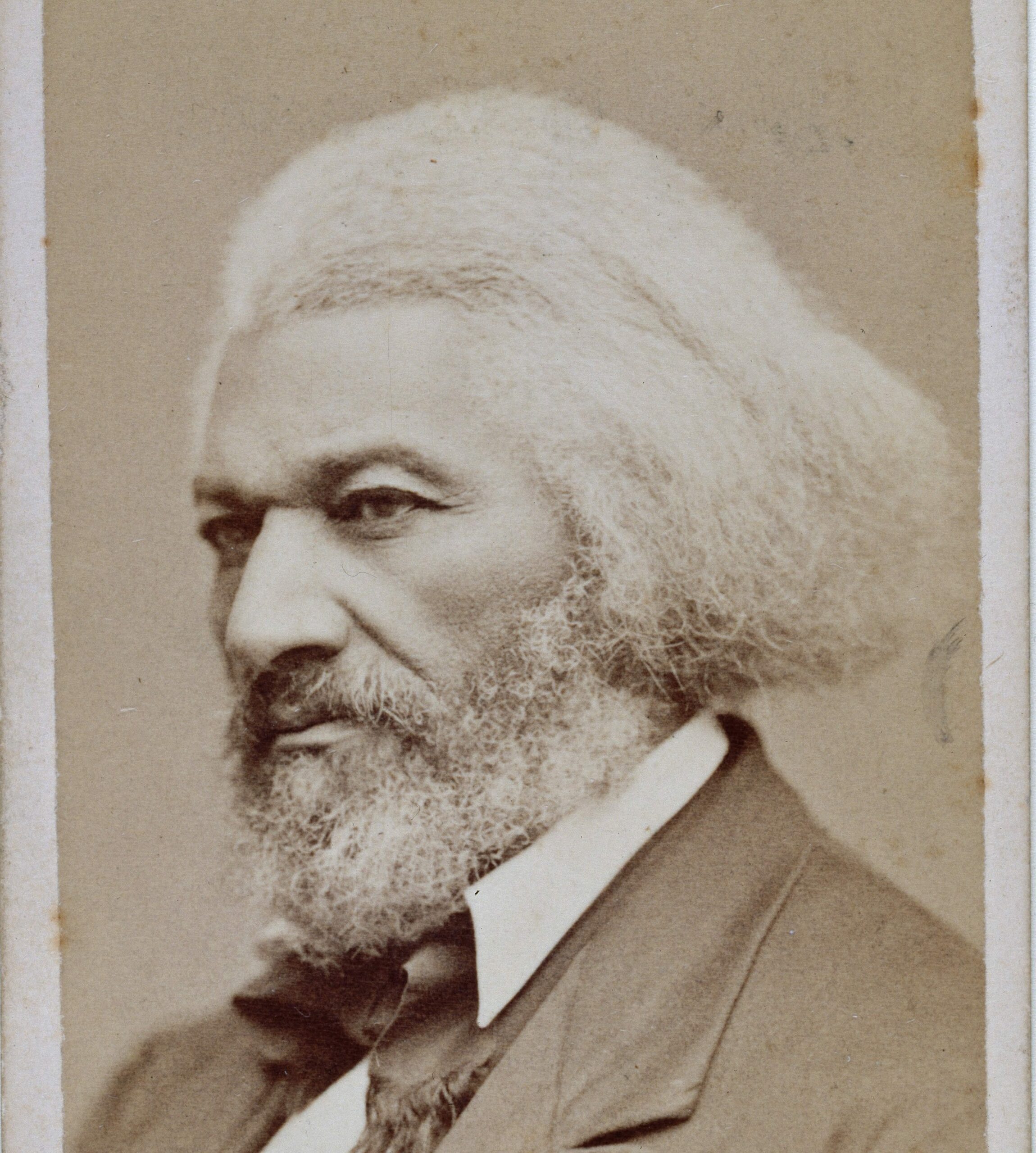
As the decade wore on, such moderate positions were eclipsed by a hardening of views and greater entrenchment on both sides. Southern newspapers carried advertisements for runaway slaves that described them in horrific, brutalizing terms, which Northern publishers delighted in reprinting to highlight the inhumanity of slaveholders. In 1849, Frederick Douglass – a self-emancipated former slave – emphatically denounced all plans related to abolition that did not also aim at ending racial prejudice and lead towards the formal equality of blacks and whites. Yet five years later, Southern sociologist George Fitzhugh was still defending race-based slavery as positive good, arguing that it benefited the slave as well as the owner.
Declaration of Sentiments of the American Anti-Slavery Convention, Selections from the Writings of W. L. Garrison (Boston:1852), 66–71.
The Convention assembled in the city of Philadelphia, to organize a National Anti-Slavery Society, promptly seize the opportunity to promulgate the following Declaration of Sentiments, as cherished by them in relation to the enslavement of one-sixth portion of the American people.
More than fifty-seven years have elapsed, since a band of patriots convened in this place, to devise measures for the deliverance of this country from a foreign yoke. The corner-stone upon which they founded the Temple of Freedom was broadly this – “‘that all men are created equal; that they are endowed by their Creator with certain inalienable rights; that among these are life, LIBERTY, and the pursuit of happiness.” At the sound of their trumpet-call, three millions of people rose up as from the sleep of death, and rushed to the strife of blood; deeming it more glorious to die instantly as freemen, than desirable to live one hour as slaves. They were few in number – poor in resources; but the honest conviction that Truth, Justice and Right were on their side, made them invincible.
We have met together for the achievement of an enterprise, without which that of our fathers is incomplete; and which, for its magnitude, solemnity, and probable results upon the destiny of the world, as far transcends theirs as moral truth does physical force.
In purity of motive, in earnestness of zeal, in decision of purpose, in intrepidity of action, in steadfastness of faith, in sincerity of spirit, we would not be inferior to them.
Their principles led them to wage war against their oppressors, and to spill human blood like water, in order to be free.
Ours forbid the doing of evil that good may come, and lead us to reject, and to entreat the oppressed to reject, the use of all carnal weapons for deliverance from bondage; relying solely upon those which are spiritual, and mighty through God to the pulling down of strong holds. Their measures were physical resistance – the marshalling in arms – the hostile array – the mortal encounter. Ours shall be such only as the opposition of moral purity to moral corruption – the destruction of error by the potency of truth – the overthrow of prejudice by the power of love – and the abolition of slavery by the spirit of repentance.
Their grievances, great as they were, were trifling in comparison with the wrongs and sufferings of those for whom we plead. Our fathers were never slaves – never bought and sold like cattle – never shut out from the light of knowledge and religion – never subjected to the lash of brutal taskmasters.
But those, for whose emancipation we are striving – constituting at the present time at least one-sixth part of our countrymen – are recognized by law, and treated by their fellow-beings, as marketable commodities, as goods and chattels, as brute beasts; are plundered daily of the fruits of their toil without redress; really enjoy no constitutional nor legal protection from licentious and murderous outrages upon their persons; and are ruthlessly torn asunder – the tender babe from the arms of its frantic mother – the heart-broken wife from her weeping husband – at the caprice or pleasure of irresponsible tyrants. For the crime of having a dark complexion, they suffer the pangs of hunger, the infliction of stripes, the ignominy of brutal servitude. They are kept in heathenish darkness by laws expressly enacted to make their instruction a criminal offence.
These are the prominent circumstances in the condition of more than two millions of our people, the proof of which may be found in thousands of indisputable facts, and in the laws of the slaveholding States.
Hence we maintain – that, in view of the civil and religious privileges of this nation, the guilt of its oppression is unequalled by any other on the face of the earth; and, therefore, that it is bound to repent instantly, to undo the heavy burdens, and to let the oppressed go free.
We further maintain – that no man has a right to enslave or imbrute his brother – to hold or acknowledge him, for one moment, as a piece of merchandise – to keep back his hire by fraud – or to brutalize his mind, by denying him the means of intellectual, social and moral improvement.
The right to enjoy liberty is inalienable. To invade it is to usurp the prerogative of Jehovah. Every man has a right to his own body – to the products of his own labor – to the protection of law – and to the common advantages of society. It is piracy to buy or steal a native African, and subject him to servitude. Surely, the sin is as great to enslave an American as an African.
Therefore we believe and affirm – that there is no difference, in principle, between the African slave trade and American slavery:
That every American citizen, who detains a human being in involuntary bondage as his property, is, according to Scripture, (Ex. xxi. 16,) a man-stealer:
That the slaves ought instantly to be set free, and brought under the protection of law:
That if they had lived from the time of Pharaoh down to the present period, and had been entailed through successive generations, their right to be free could never have been alienated, but their claims would have constantly risen in solemnity:
That all those laws which are now in force, admitting the right of slavery, are therefore, before God, utterly null and void; being an audacious usurpation of the Divine prerogative, a daring infringement on the law of nature, a base over-throw of the very foundations of the social compact, a complete extinction of all the relations, endearments and obligations of mankind, and a presumptuous transgression of all the holy commandments; and that therefore they ought instantly to be abrogated.
We further believe and affirm – that all persons of color, who possess the qualifications which are demanded of others, ought to be admitted forthwith to the enjoyment of the same privileges, and the exercise of the same prerogatives, as others; and that the paths of preferment, of wealth, and of intelligence, should be opened as widely to them as to persons of a white complexion.
We maintain that no compensation should be given to the planters emancipating their slaves:
Because it would be a surrender of the great fundamental principle, that man cannot hold property in man:
Because slavery is a crime, and therefore is not an article to be sold:
Because the holders of slaves are not the just proprietors of what they claim; freeing the slave is not depriving them of property, but restoring it to its rightful owner; it is not wronging the master, but righting the slave – restoring him to himself:
Because immediate and general emancipation would only destroy nominal, not real property; it would not amputate a limb or break a bone of the slaves, but by infusing motives into their breasts, would make them doubly valuable to the masters as free laborers; and
Because, if compensation is to be given at all, it should be given to the outraged and guiltless slaves, and not to those who have plundered and abused them.
We regard as delusive, cruel and dangerous, any scheme of expatriation which pretends to aid, either directly or indirectly, in the emancipation of the slaves, or to be a substitute for the immediate and total abolition of slavery.
We fully and unanimously recognize the sovereignty of each State, to legislate exclusively on the subject of the slavery which is tolerated within its limits; we concede that Congress, under the present national compact, has no right to interfere with any of the slave States, in relation to this momentous subject:
But we maintain that Congress has a right, and is solemnly bound, to suppress the domestic slave trade between the several States, and to abolish slavery in those portions of our territory which the Constitution has placed under its exclusive jurisdiction.
We also maintain that there are, at the present time, the highest obligations resting upon the people of the free States to remove slavery by moral and political action, as prescribed in the Constitution of the United States. They are now living under a pledge of their tremendous physical force, to fasten the galling fetters of tyranny upon the limbs of millions in the Southern States; they are liable to be called at any moment to suppress a general insurrection of the slaves; they authorize the slave owner to vote for three-fifths of his slaves as property, and thus enable him to perpetuate his oppression; they support a standing army at the South for its protection and they seize the slave, who has escaped into their territories, and send him back to be tortured by an enraged master or a brutal driver. This relation to slavery is criminal, and full of danger: IT MUST BE BROKEN UP.
These are our views and principles – these our designs and measures. With entire confidence in the overruling justice of God, we plant ourselves upon the Declaration of our Independence and the truths of Divine Revelation, as upon the Everlasting Rock.
We shall organize Anti-Slavery Societies, if possible, in every city, town and village in our land.
We shall send forth agents to lift up the voice of remonstrance, of warning, of entreaty, and of rebuke.
We shall circulate, unsparingly and extensively, anti-slavery tracts and periodicals.
We shall enlist the pulpit and the press in the cause of the suffering and the dumb.
We shalt aim at a purification of the churches from all participation in the guilt of slavery.
We shall encourage the labor of freemen rather than that of slaves, by giving a preference to their productions: and
We shall spare no exertions nor means to bring the whole nation to speedy repentance.
Our trust for victory is solely in God. We may be personally defeated, but our principles never. Truth, Justice, Reason, Humanity, must and will gloriously triumph. Already a host is coming up to the help of the Lord against the mighty, and the prospect before us is full of encouragement.
Submitting this Declaration to the candid examination of the people of this country, and of the friends of liberty throughout the world, we hereby affix our signatures to it; pledging ourselves that, under the guidance and by the help of Almighty God, we will do all that in us lies, consistently with this Declaration of our principles, to overthrow the most execrable system of slavery that has ever been witnessed upon earth; to deliver our land from its deadliest curse; to wipe out the foulest stain which rests upon our national escutcheon; and to secure to the colored population of the United States, all the rights and privileges which belong to them as men, and as Americans – come what may to our persons, our interests, or our reputation – whether we live to witness the triumph of Liberty, Justice and Humanity, or perish untimely as martyrs in this great, benevolent, and holy cause.
Speeches on the Removal Power
March 07, 1834
Conversation-based seminars for collegial PD, one-day and multi-day seminars, graduate credit seminars (MA degree), online and in-person.