No related resources
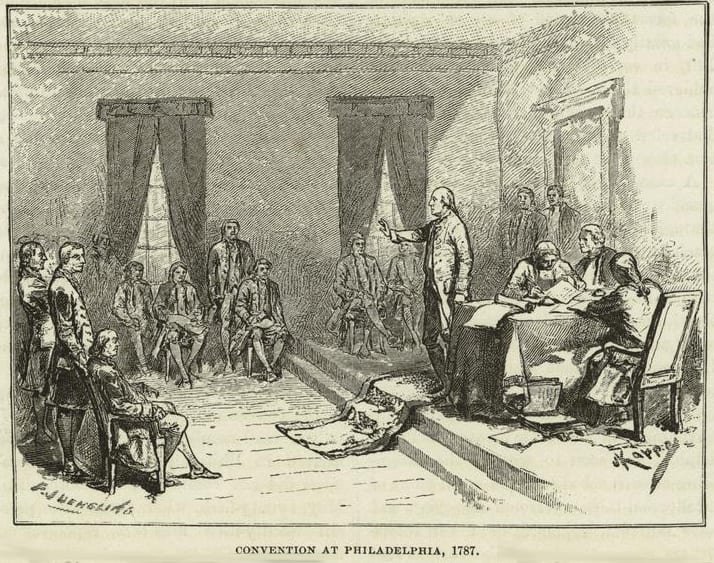
Introduction
On June 13, the delegates completed their second discussion of the Virginia Plan. The 19 resolutions of the amended Virginia Plan preserved the new institutional structure proposed by the original plan. On June 15, however, William Patterson presented the alternative New Jersey Plan. It restored the structure of the Articles of Confederation but also increased the powers of Congress. Why, after two weeks of negotiation concerning the representation of people, states, and wealth, would the New Jersey coalition be willing to start all over again? Madison provided an answer in the footnote (reproduced below) he added to his account of the debate on June 15. For different reasons, a coalition of states had formed opposed to a national government as proposed in the Virginia Plan.
Source: Gordon Lloyd, ed., Debates in the Federal Convention of 1787 by James Madison, a Member (Ashland, OH: Ashbrook Center, 2014), 77–86.
The Revised Virginia Plan
June 13
. . . Mr. GORHAM[1] made a report, which was postponed till to-morrow, to give an opportunity for other plans to be proposed – the Report was in the words following:
- Resolved, that it is the opinion of this Committee, that a national Government ought to be established, consisting of a supreme Legislative, Executive and Judiciary.
- Resolved, that the National Legislature ought to consist of two branches.
- Resolved, that the members of the first branch of the National Legislature ought to be elected by the people of the several States for the term of three years; to receive fixed stipends by which they may be compensated for the devotion of their time to the public service, to be paid out of the National Treasury; to be ineligible to any office established by a particular State, or under the authority of the United States (except those peculiarly belonging to the functions of the first branch) during the term of service, and under the national Government for the space of one year after its expiration.
- Resolved, that the members of the second branch of the National Legislature ought to be chosen by the individual Legislatures; to be of the age of thirty years at least; to hold their offices for a term sufficient to insure their independence, namely, seven years; to receive fixed stipends by which they may be compensated for the devotion of their time to the public service, to be paid out of the National Treasury; to be ineligible to any office established by a particular State, or under the authority of the United States (except those peculiarly belonging to the functions of the second branch) during the term of service, and under the national Government, for the space of one year after its expiration.
- Resolved, that each branch ought to possess the right of originating acts.
- Resolved, that the National Legislature ought to be empowered to enjoy the legislative rights vested in Congress by the Confederation; and moreover to legislate in all cases to which the separate States are incompetent, or in which the harmony of the United States may be interrupted by the exercise of individual legislation; to negative all laws passed by the several States contravening, in the opinion of the National Legislature, the Articles of Union, or any treaties subsisting under the authority of the Union.
- Resolved, that the rights of suffrage in the first branch of the National Legislature, ought not to be according to the rule established in the Articles of Confederation, but according to some equitable ratio of representation, namely, in proportion to the whole number of white and other free citizens and inhabitants, of every age, sex and condition, including those bound to servitude for a term of years, and three-fifths of all other persons, not comprehended in the foregoing description, except Indians not paying taxes, in each State.
- Resolved, that the right of suffrage in the second branch of the National Legislature, ought to be according to the rule established for the first.
- Resolved, that a National Executive be instituted, to consist of a single person; to be chosen by the National Legislature, for the term of seven years; with power to carry into execution the national laws; to appoint to offices in cases not otherwise provided for; to be ineligible a second time; and to be removable on impeachment and conviction of malpractices or neglect of duty; to receive a fixed stipend by which he may be compensated for the devotion of his time to the public service, to be paid out of the National Treasury.
- Resolved, that the national Executive shall have a right to negative any legislative act which shall not be afterwards passed by two-thirds of each branch of the national Legislature.
- Resolved, that a national Judiciary be established, to consist of one supreme tribunal, the Judges of which shall be appointed by the second branch of the national Legislature, to hold their offices during good behavior, and to receive punctually, at stated times, a fixed compensation for their services, in which no increase or diminution shall be made, so as to affect the persons actually in office at the time of such increase or diminution.
- Resolved, that the national Legislature be empowered to appoint inferior tribunals.
- Resolved, that the jurisdiction of the national Judiciary shall extend to all cases which respect the collection of the national revenue, impeachments of any national officers, and questions which involve the national peace and harmony.
- Resolved, that provision ought to be made for the admission of States lawfully arising within the limits of the United States, whether from a voluntary junction of government and territory, or otherwise, with the consent of a number of voices in the national Legislature less than the whole.
- Resolved, that provision ought to be made for the continuance of Congress and their authorities and privileges, until a given day, after the reform of the Articles of Union shall be adopted, and for the completion of all their engagements.
- Resolved, that a republican constitution, and its existing laws, ought to be guaranteed to each State, by the United States.
- Resolved, that provision ought to be made for the amendment of the Articles of Union, whensoever it shall seem necessary.
- Resolved, that the Legislative, Executive and Judiciary powers within the several States, ought to be bound by oath to support the Articles of Union.
- Resolved, that the amendments which shall be offered to the Confederation by the Convention ought, at a proper time or times after the approbation of Congress, to be submitted to an assembly or assemblies recommended by the several Legislatures, to be expressly chosen by the people to consider and decide thereon.
The New Jersey Plan
June 15
In Convention, – Mr. PATTERSON[2] laid before the Convention the plan which he said several of the Deputations wished to be substituted in place of that proposed by Mr. RANDOLPH[3] [the Virginia Plan]. After some little discussion of the most proper mode of giving it a fair deliberation, it was agreed, that it should be referred to a Committee of the Whole; and that, in order to place the two plans in due comparison, the other should be recommitted. At the earnest request of Mr. LANSING[4] and some other gentleman, it was also agreed that the Convention should not go into Committee of the Whole on the subject till to-morrow; by which delay the friends of the plan proposed by Mr. PATTERSON would be better prepared to explain and support it, and all would have an opportunity of taking copies.*
The propositions from New Jersey, moved by Mr. PATTERSON, were in the words following:
- Resolved, that the Articles of Confederation ought to be so revised, corrected, and enlarged, as to render the Federal Constitution adequate to the exigencies of government, and the preservation of the Union.
- Resolved, that, in addition to the powers vested in the United States in Congress, by the present existing Articles of Confederation, they be authorized to pass acts for raising a revenue, by levying a duty or duties on all goods or merchandizes of foreign growth or manufacture, imported into any part of the United States; by stamps on paper, vellum or parchment; and by a postage on all letters or packages passing through the general post-office; to be applied to such Federal purposes as they shall deem proper and expedient; to make rules and regulations for the collection thereof; and the same, from time to time, to alter and amend in such manner as they shall think proper; to pass acts for the regulation of trade and commerce, as well with foreign nations as with each other; provided that all punishments, fines, forfeitures and penalties, to be incurred for contravening such acts, rules and regulations, shall be adjudged by the common law Judiciaries of the State in which any offence contrary to the true intent and meaning of such acts, rules, and regulations, shall have been committed or perpetrated, with liberty of commencing in the first instance all suits and prosecutions for that purpose in the Superior common law Judiciary in such State; subject, nevertheless, for the correction of all errors, both in law and fact, in rendering judgment, to an appeal to the Judiciary of the United States.
- Resolved, that whenever requisitions shall be necessary, instead of the rule for making requisitions mentioned in the Articles of Confederation, the United States in Congress be authorized to make such requisitions in proportion to the whole number of white and other free citizens and inhabitants, of every age, sex, and condition, including those bound to servitude for a term of years, and three-fifths of all other persons not comprehended in the foregoing description, except Indians not paying taxes; that, if such requisitions be not complied with, in the time specified therein, to direct the collection thereof in the non-complying States; and for that purpose to devise and pass acts directing and authorizing the same; provided, that none of the powers hereby vested in the United States in Congress, shall be exercised without the consent of at least – States; and in that proportion, if the number of confederated States should hereafter be increased or diminished.
- Resolved, that the United States in Congress be authorized to elect a Federal Executive, to consist of —— persons, to continue in office for the term of – years; to receive punctually, at stated times, a fixed compensation for their services, in which no increase nor diminution shall be made so as to affect the persons composing the Executive at the time of such increase or diminution; to be paid out of the Federal treasury; to be incapable of holding any other office or appointment during their time of service, and for —— years thereafter: to be ineligible a second time, and removable by Congress, on application by a majority of the Executives of the several States; that the Executive, besides their general authority to execute the Federal acts, ought to appoint all Federal officers not otherwise provided for, and to direct all military operations; provided, that none of the persons composing the Federal Executive shall, on any occasion, take command of any troops, so as personally to conduct any military enterprise, as General, or in any other capacity.
- Resolved, that a Federal Judiciary be established, to consist of a supreme tribunal, the Judges of which to be appointed by the Executive, and to hold their offices during good behavior; to receive punctually, at stated times, a fixed compensation for their services, in which no increase nor diminution shall be made so as to affect the persons actually in office at the time of such increase or diminution. That the Judiciary so established shall have authority to hear and determine, in the first instance, on all impeachments of Federal officers; and, by way of appeal, in the dernier resort, in all cases touching the rights of ambassadors; in all cases of captures from an enemy; in all cases of piracies and felonies on the high seas; in all cases in which foreigners may be interested; in the construction of any treaty or treaties, or which may arise on any of the acts for the regulation of trade, or the collection of the Federal revenue: that none of the Judiciary shall, during the time they remain in office, be capable of receiving or holding any other office or appointment during their term of service, or for – thereafter.
- Resolved, that all acts of the United States in Congress, made by virtue and in pursuance of the powers hereby, and by the Articles of Confederation, vested in them, and all treaties made and ratified under the authority of the United States, shall be the supreme law of the respective States, so far forth as those acts or treaties shall relate to the said States or their citizens; and that the Judiciary of the several States shall be bound thereby in their decisions, any thing in the respective laws of the individual States to the contrary notwithstanding: and that if any State, or any body of men in any State, shall oppose or prevent the carrying into execution such acts or treaties, the Federal Executive shall be authorized to call forth the power of the confederated States, or so much thereof as may be necessary, to enforce and compel an obedience to such acts, or an observance of such treaties.
- Resolved, that provision be made for the admission of new States into the Union.
- Resolved, that the rule for naturalization ought to be the same in every State.
- Resolved, that a citizen of one State committing an offence in another State of the Union, shall be deemed guilty of the same offence as if it had been committed by a citizen of the State in which the offence was committed.
* [Madison’s footnote]
This plan had been concerted among the Deputations, or members thereof, from Connecticut, New York, New Jersey, Delaware, and perhaps Mr. Martin, from Maryland, who made with them a common cause, though on different principles. Connecticut and New York were against a departure from the principle of the Confederation, wishing rather to add a few new powers to Congress than to substitute a National Government. The States of New Jersey and Delaware were opposed to a National Government, because its patrons considered a proportional representation of the States as the basis of it. The eagerness displayed by the members opposed to a National Government, from these different motives, began now to produce serious anxiety for the result of the Convention. Mr. Dickinson said to Mr. Madison, “You see the consequence of pushing things too far. Some of the members from the small States wish for two branches in the General Legislature, and are friends to a good National Government; but we would sooner submit to a foreign power, than submit to be deprived, in both branches of the legislature, of an equality of suffrage, and thereby be thrown under the domination of the larger States.”

Conversation-based seminars for collegial PD, one-day and multi-day seminars, graduate credit seminars (MA degree), online and in-person.



































































































































































![Finley, A. (1829) Pennsylvania. Philada. [Map] Retrieved from the Library of Congress, https://www.loc.gov/item/98688548/.](/content/uploads/2024/02/Map-of-PA--273x190.jpg)