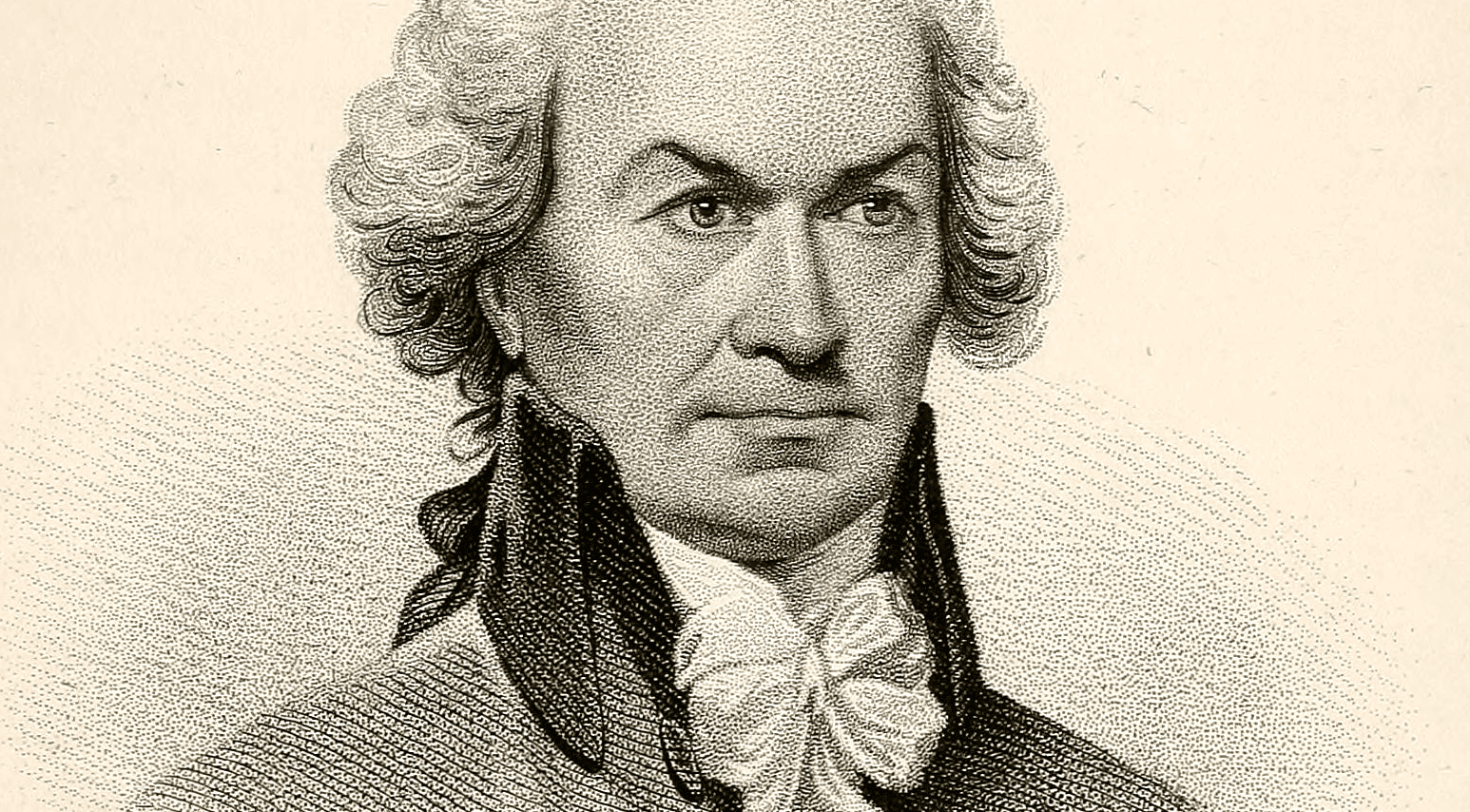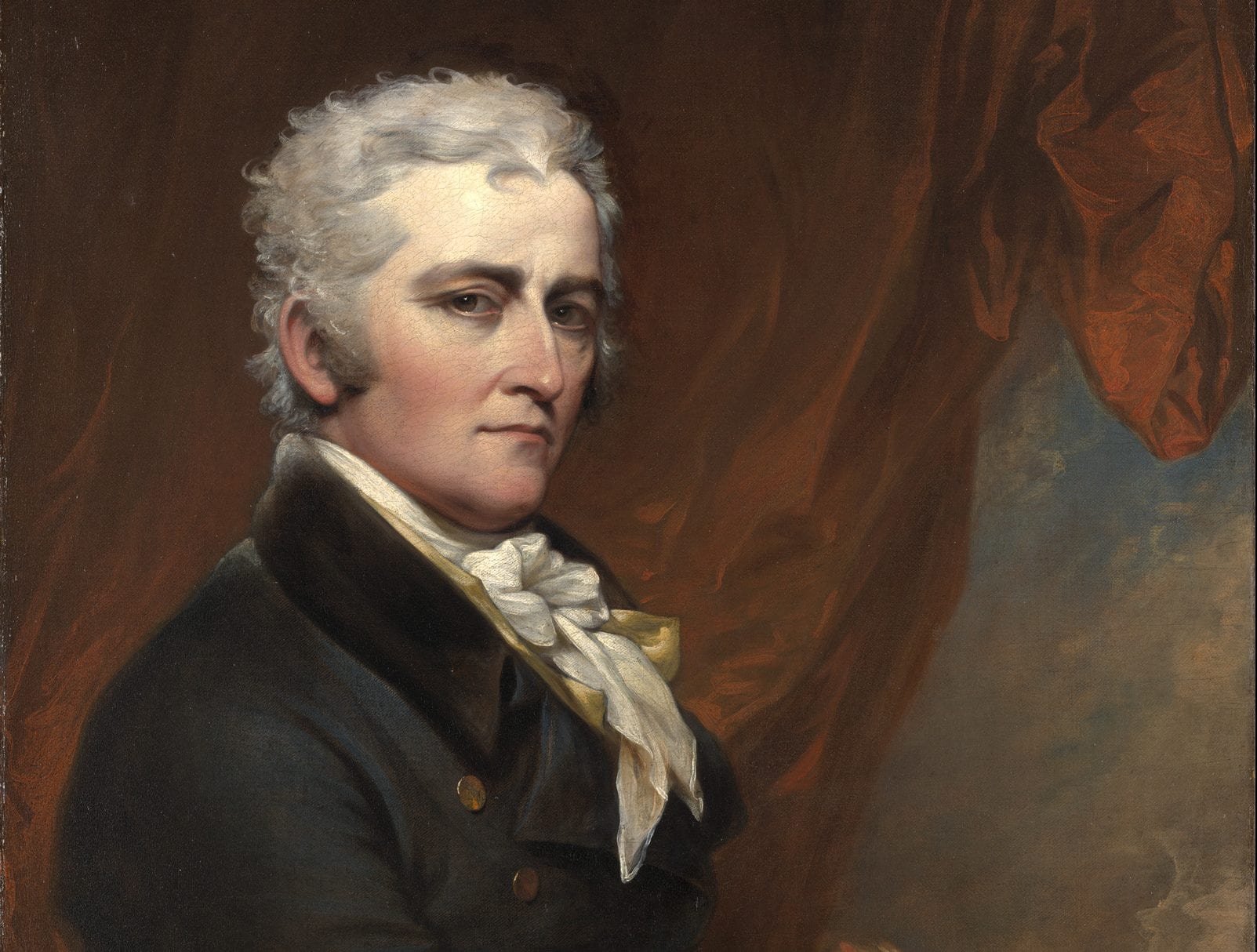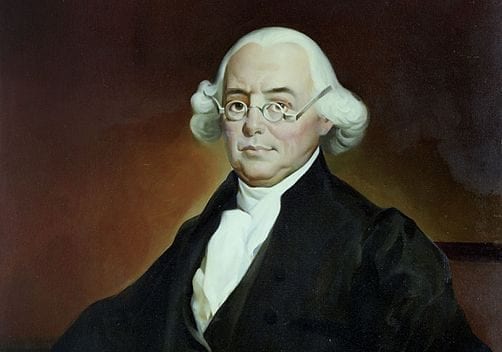No related resources
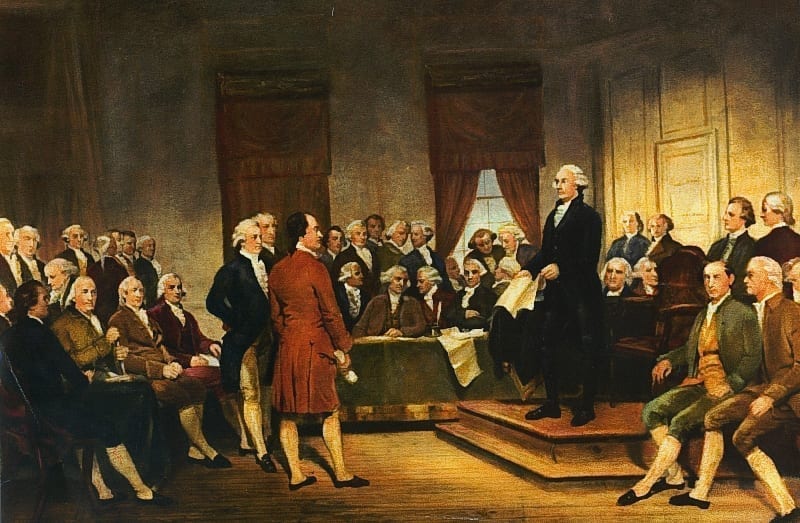
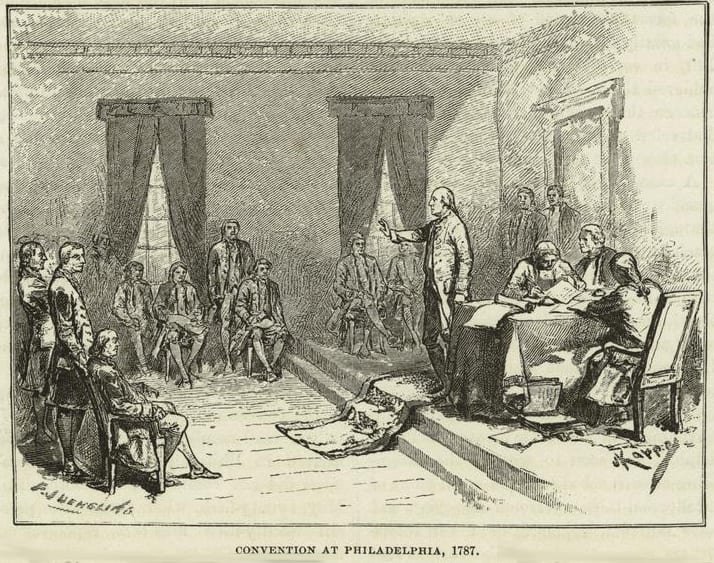
Introduction
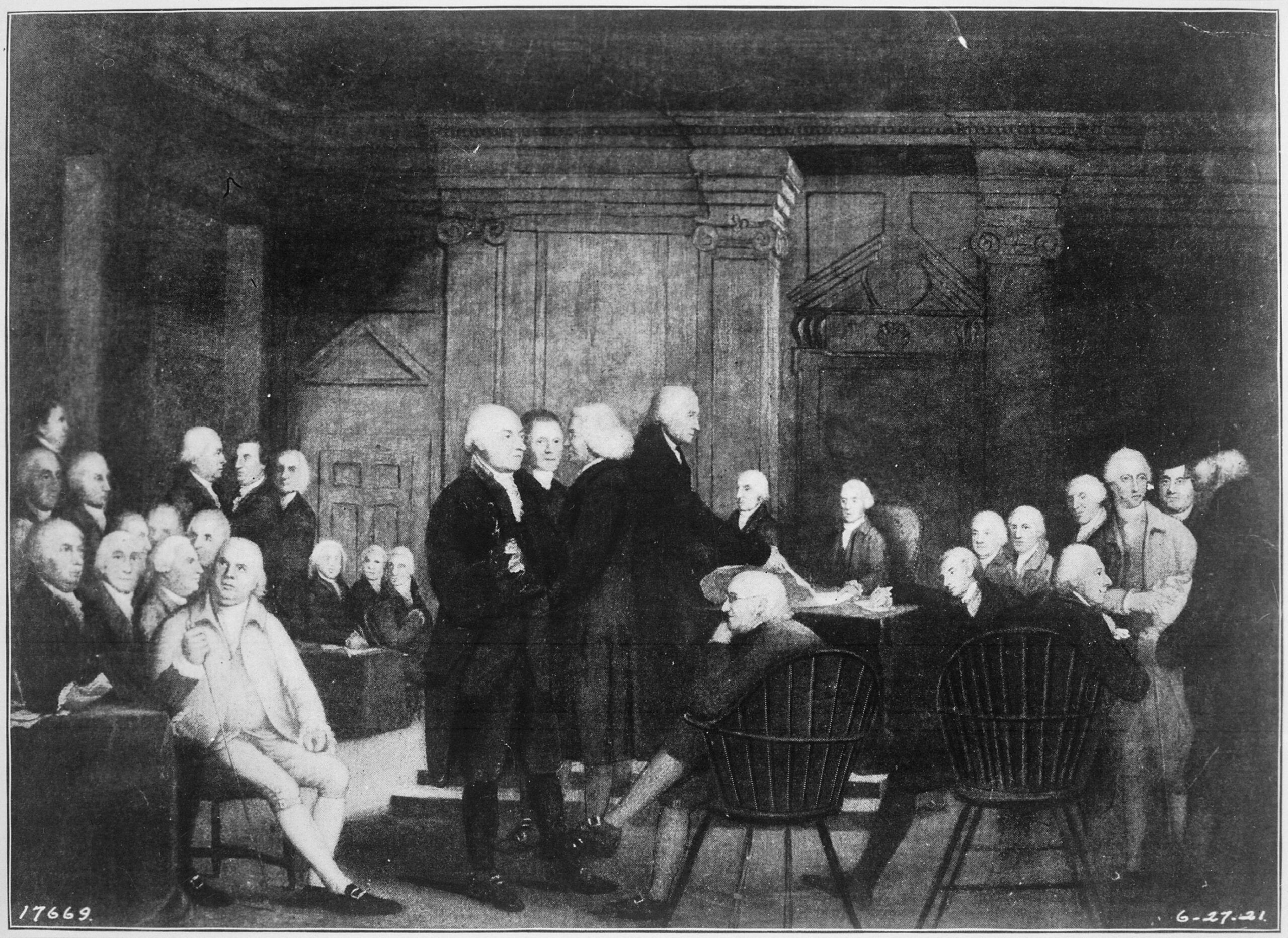
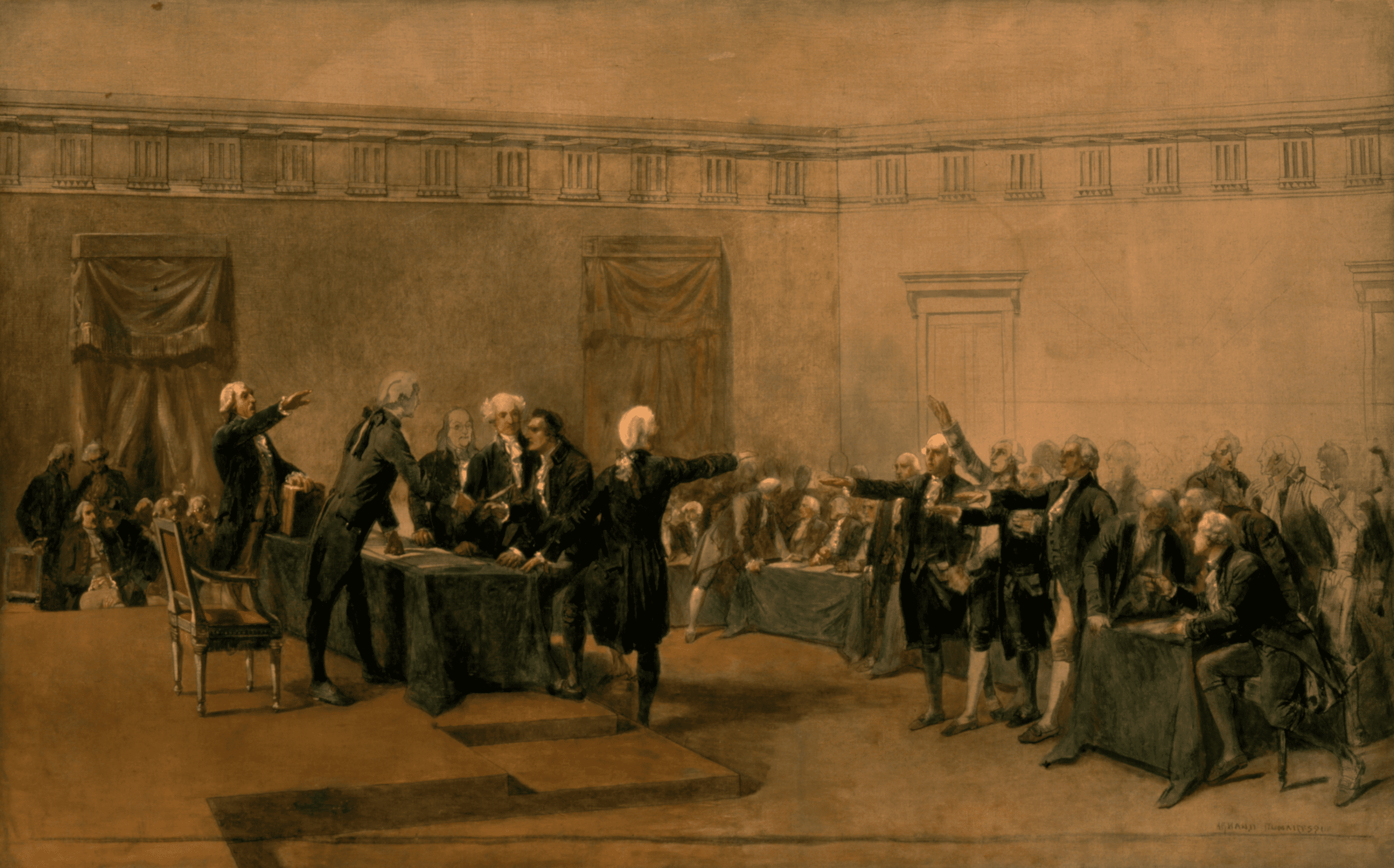
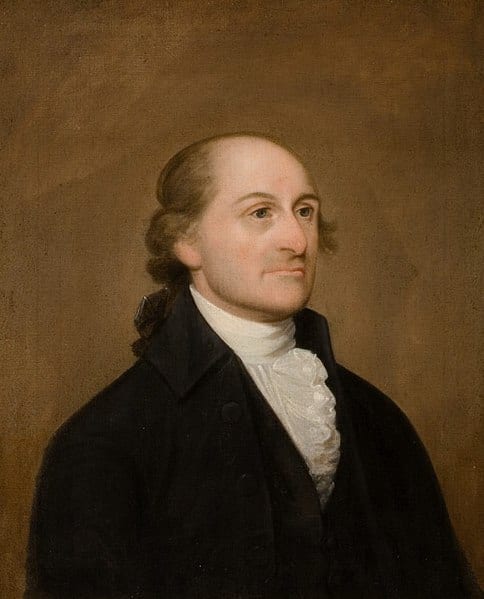
The delegates debated the merits and demerits of the revised Virginia Plan and the New Jersey Plan. John Lansing of New York defended the New Jersey Plan as consistent with the authorization of the Constitutional Convention by the Confederation Congress and the sentiments of the people. He relied on a strict or narrow interpretation of the Confederation mandate. Edmund Randolph, who had introduced the original Virginia Plan, in effect invoked the authority of the Annapolis Convention, as well as a vision of a new republic. Lansing’s remarks explain why New York joined in the coalition opposed to a national government.
Source: Gordon Lloyd, ed., Debates in the Federal Convention of 1787 by James Madison, a Member (Ashland, OH: Ashbrook Center, 2014), 86–92.
In Committee of the Whole, on the Resolutions proposed by Mr. PATTERSON[1] and Mr. RANDOLPH.[2] Mr. LANSING[3] called for the reading of the first Resolution of each plan, which he considered as involving principles directly in contrast. That of Mr. PATTERSON [the New Jersey Plan], says he, sustains the sovereignty of the respective States, that of Mr. RANDOLPH destroys it. The latter requires a negative on all the laws of the particular States, the former only certain general power for the general good. The plan of Mr. RANDOLPH in short absorbs all power, except what may be exercised in the little local matters of the States which are not objects worthy of the supreme cognizance. He grounded his preference of Mr. PATTERSON’S plan, chiefly, on two objections to that of Mr. RANDOLPH, – first, want of power in the Convention to discuss and propose it; secondly, the improbability of its being adopted.
- He was decidedly of opinion that the power of the Convention was restrained to amendments of a Federal nature, and having for their basis the Confederacy in being. The acts of Congress, the tenor of the acts of the States, the commissions produced by the several Deputations, all proved this. And this limitation of the power to an amendment of the Confederacy marked the opinion of the States, that it was unnecessary and improper to go farther. He was sure that this was the case with his State. New York would never have concurred in sending Deputies to the Convention, if she had supposed the deliberations were to turn on a consolidation of the States, and a National Government.
- Was it probable that the States would adopt and ratify a scheme which they had never authorized us to propose, and which so far exceeded what they regarded as sufficient? We see by their several acts, particularly in relation to the plan of revenue proposed by Congress in 1783, not authorized by the Articles of Confederation, what were the ideas they then entertained. Can so great a change be supposed to have already taken place? To rely on any change which is hereafter to take place in the sentiments of the people, would be trusting to too great an uncertainty. We know only what their present sentiments are. And it is in vain to propose what will not accord with these. The States will never feel a sufficient confidence in a General Government, to give it a negative on their laws. The scheme is itself totally novel. There is no parallel to it to be found. The authority of Congress is familiar to the people, and an augmentation of the powers of Congress will be readily approved by them.
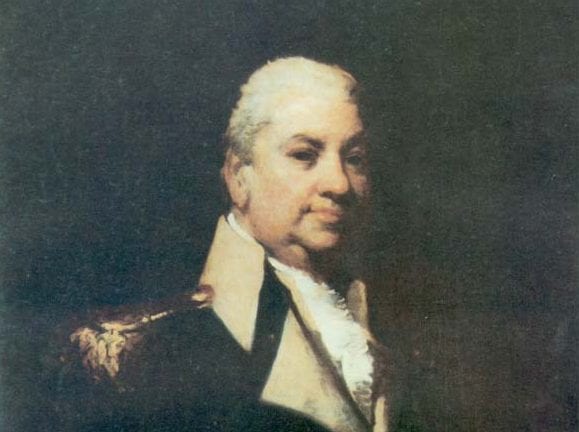
Mr. PATTERSON said, as he had on a former occasion given his sentiments on the plan proposed by Mr. RANDOLPH, he would now, avoiding repetition as much as possible, give his reasons in favor of that proposed by himself. He preferred it because it accorded, – first, with the powers of the Convention; secondly, with the sentiments of the people.
If the Confederacy was radically wrong, let us return to our States, and obtain larger powers, not assume them ourselves. I came here not to speak my own sentiments, but the sentiments of those who sent me. Our object is not such a government as may be best in itself, but such a one as our constituents have authorized us to prepare, and as they will approve. If we argue the matter on the supposition that no confederacy at present exists, it cannot be denied that all the States stand on the footing of equal sovereignty. All, therefore, must concur before any can be bound. If a proportional representation[4] be right, why do we not vote so here? If we argue on the fact that a Federal compact actually exists, and consult the articles of it, we still find an equal sovereignty to be the basis of it.
He reads the fifth Article of the Confederation, giving each State a vote; and the thirteenth, declaring that no alteration shall be made without unanimous consent. This is the nature of all treaties. What is unanimously done, must be unanimously undone. It was observed (by Mr. WILSON[5]) that the larger States gave up the point, not because it was right, but because the circumstances of the moment urged the concession. Be it so. Are they for that reason at liberty to take it back? Can the donor resume his gift without the consent of the donee? This doctrine may be convenient, but it is a doctrine that will sacrifice the lesser States. The larger States acceded readily to the Confederacy. It was the small ones that came in reluctantly and slowly. New Jersey and Maryland were the two last;[6] the former objecting to the want of power in Congress over trade; both of them to the want of power to appropriate the vacant territory to the benefit of the whole.
If the sovereignty of the States is to be maintained, the representatives must be drawn immediately from the States, not from the people; and we have no power to vary the idea of equal sovereignty. The only expedient that will cure the difficulty is that of throwing the States into hotchpot.[7]
To say that this is impracticable, will not make it so. Let it be tried, and we shall see whether the citizens of Massachusetts, Pennsylvania, and Virginia accede to it. It will be objected, that coercion will be impracticable. But will it be more so in one plan than the other? Its efficacy will depend on the quantum of power collected, not on its being drawn from the States, or from the individuals; and according to his plan it may be exerted on individuals as well as according to that of Mr. RANDOLPH.
A distinct Executive and Judiciary also were equally provided by his plan. It is urged, that two branches in the Legislature are necessary. Why? For the purpose of a check. But the reason for the precaution is not applicable to this case. Within a particular State, where party heats prevail, such a check may be necessary. In such a body as Congress, it is less necessary; and, besides, the Delegations of the different States are checks on each other.
Do the people at large complain of Congress? No. What they wish is, that Congress may have more power. If the power now proposed be not enough, the people hereafter will make additions to it. With proper powers Congress will act with more energy and wisdom than the proposed National Legislature; being fewer in number, and more secreted and refined by the mode of election.
The plan of Mr. RANDOLPH will also be enormously expensive. Allowing Georgia and Delaware two representatives each in the popular branch, the aggregate number of that branch will be one hundred and eighty. Add to it half as many for the other branch, and you have two hundred and seventy members, coming once at least a year, from the most distant as well as the most central parts of the Republic. In the present deranged state of our finances, can so expensive a system be seriously thought of? By enlarging the powers of Congress, the greatest part of this expense will be saved, and all purposes will be answered. At least a trial ought to be made.
Mr. WILSON entered into a contrast of the principal points of the two plans, so far, he said, as there had been time to examine the one last proposed. These points were:
- In the Virginia plan there are two, and in some degree three, branches in the Legislature; in the plan from New Jersey there is to be a single Legislature only.
- Representation of the people at large is the basis of one; the State Legislatures the pillars of the other.
- Proportional representation prevails in one, equality of suffrage in the other.
- A single Executive Magistrate is at the head of the one; a plurality is held out in the other.
- In the one, a majority of the people of the United States must prevail; in the other, a minority may prevail.
- The National Legislature is to make laws in all cases to which the separate States are incompetent, etc.; in place of this, Congress are to have additional power in a few cases only.
- A negative on the laws of the States; in place of this, coercion to be substituted.
- The Executive to be removable on impeachment and conviction, in one plan; in the other, to be removable at the instance of a majority of the Executives of the States.
- Revision of the laws provided for, in one; no such check in the other.
- Inferior national tribunals, in one; none such in the other.
- In the one, jurisdiction of national tribunals to extend, etc.; an appellate jurisdiction only allowed in the other.
- Here, the jurisdiction is to extend to all cases affecting the national peace and harmony; there, a few cases only are marked out.
- Finally, the ratification is, in this, to be by the people themselves; in that, by the legislative authorities, according to the thirteenth Article of the Confederation.
With regard to the power of the Convention, he conceived himself authorized to conclude nothing, but to be at liberty to propose any thing. In this particular, he felt himself perfectly indifferent to the two plans.
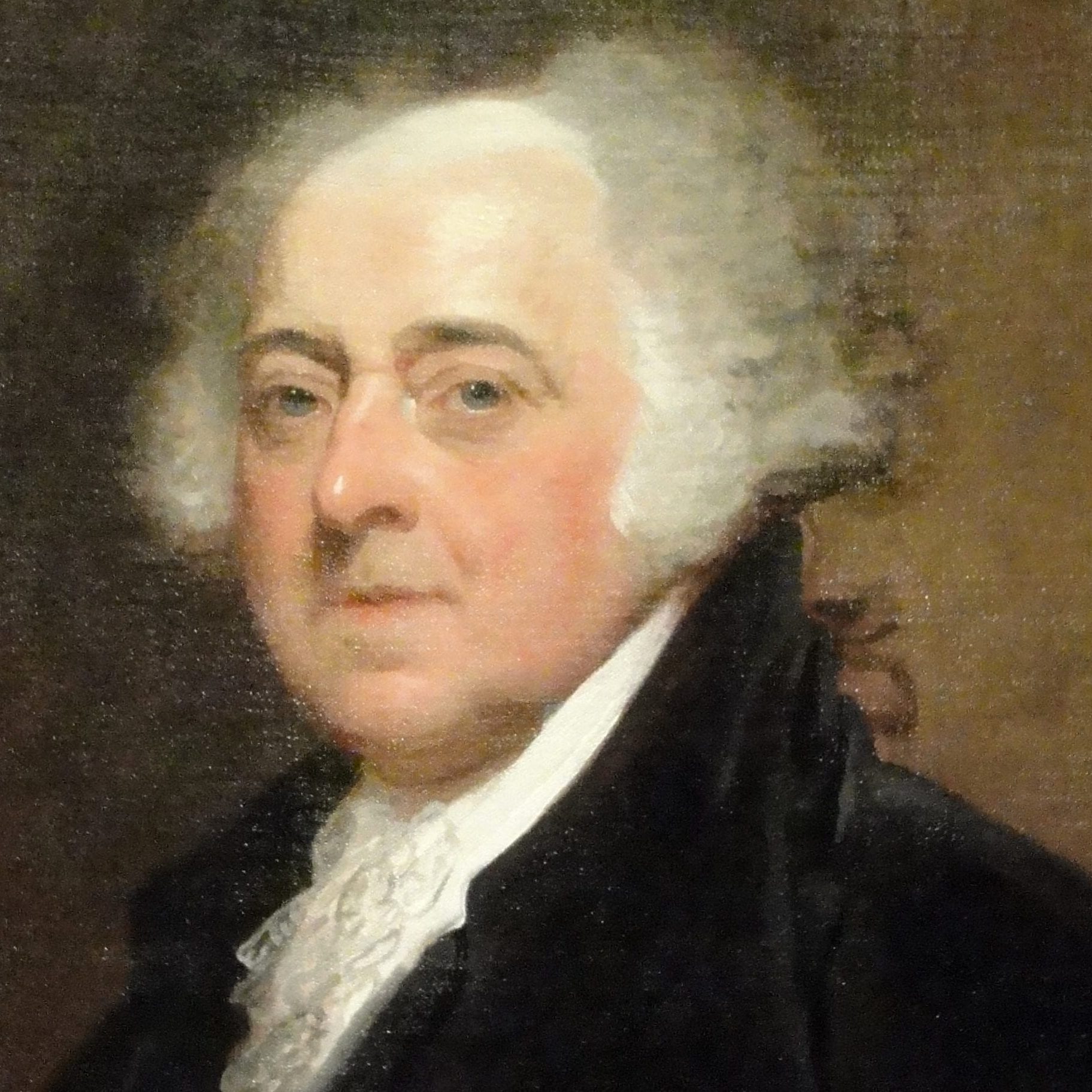
With regard to the sentiments of the people, he conceived it difficult to know precisely what they are. Those of the particular circle in which one moved were commonly mistaken for the general voice. He could not persuade himself that the State Governments and sovereignties were so much the idols of the people, nor a National Government so obnoxious to them, as some supposed. Why should a National Government be unpopular? Has it less dignity? Will each citizen enjoy under it less liberty or protection? Will a citizen of Delaware be degraded by becoming a citizen of the United States? Where do the people look at present for relief from the evils of which they complain? Is it from an internal reform of their governments? No, sir. It is from the national councils that relief is expected. For these reasons, he did not fear that the people would not follow us into a National Government; and it will be a further recommendation of Mr. RANDOLPH’S plan, that it is to be submitted to them, and not to the Legislatures, for ratification.
Proceeding now to the first point on which he had contrasted the two plans, he observed, that, anxious as he was for some augmentation of the Federal powers, it would be with extreme reluctance, indeed, that he could ever consent to give powers to Congress. He had two reasons, either of which was sufficient, – first, Congress, as a legislative body, does not stand on the people; secondly, it is a single body.
- He would not repeat the remarks he had formerly made on the principles of representation. He would only say, that an inequality in it has ever been a poison contaminating every branch of government. In Great Britain, where this poison has had a full operation, the security of private rights is owing entirely to the purity of her tribunals of justice, the judges of which are neither appointed nor paid by a venal parliament. The political liberty of that nation, owing to the inequality of representation, is at the mercy of its rulers. He means not to insinuate that there is any parallel between the situation of that country and ours, at present. . . .
- Congress is a single Legislature. Despotism comes on mankind in different shapes, sometimes in an Executive, sometimes in a military one. Is there no danger of a Legislative despotism? Theory and practice both proclaim it. If the Legislative authority be not restrained, there can be neither liberty nor stability; and it can only be restrained by dividing it within itself, into distinct and independent branches. In a single House there is no check, but the inadequate one, of the virtue and good sense of those who compose it.
On another great point, the contrast was equally favorable to the plan reported by the Committee of the Whole. It vested the Executive powers in a single magistrate. The plan of New Jersey, vested them in a plurality. In order to control the Legislative authority, you must divide it. In order to control the Executive you must unite it. One man will be more responsible than three. Three will contend among themselves, till one becomes the master of his colleague. . . .
Mr. PINCKNEY.[8] The whole comes to this, as he conceived. Give New Jersey an equal vote, and she will dismiss her scruples, and concur in the National system. He thought the Convention authorized to go any length, in recommending, which they found necessary to remedy the evils which produced this Convention.
Mr. ELLSWORTH[9] proposed, as a more distinctive form of collecting the mind of the Committee on the subject, “that the Legislative power of the United States should remain in Congress.” This was not seconded, though it seemed better calculated for the purpose than the first proposition of Mr. PATTERSON, in place of which Mr. ELLSWORTH wished to substitute it.
Mr. RANDOLPH was not scrupulous on the point of power. When the salvation of the Republic was at stake, it would be treason to our trust, not to propose what we found necessary. He painted in strong colors the imbecility of the existing Confederacy, and the danger of delaying a substantial reform.
In answer to the objection drawn from the sense of our constituents, as denoted by their acts relating to the Convention and the objects of their deliberation, he observed, that, as each State acted separately in the case, it would have been indecent for it to have charged the existing Constitution, with all the vices which it might have perceived in it. The first State that set on foot this experiment would not have been justified in going so far, ignorant as it was of the opinion of others, and sensible as it must have been of the uncertainty of a successful issue to the experiment. There are reasons certainly of a peculiar nature, where the ordinary cautions must be dispensed with; and this is certainly one of them. He would not, as far as depended on him, leave any thing that seemed necessary, undone. The present moment is favorable, and is probably the last that will offer.
The true question is, whether we shall adhere to the Federal plan, or introduce the National plan. The insufficiency of the former has been fully displayed by the trial already made. There are but two modes by which the end of a General Government can be attained: the first, by coercion, as proposed by Mr. PATTERSON’S plan; the second, by real legislation, as proposed by the other plan.
Coercion he pronounced to be impracticable, expensive, cruel to individuals. It tended, also, to habituate the instruments of it to shed the blood, and riot in the spoils of their fellow citizens, and consequently train them up for the service of ambition. We must resort therefore to a national legislation over individuals; for which Congress are unfit. To vest such power in them would be blending the Legislative with the Executive, contrary to the received maxim on this subject. If the union of these powers, heretofore, in Congress has been safe, it has been owing to the general impotency of that body. Congress are, moreover, not elected by the people, but by the Legislatures, who retain even a power of recall. They have therefore no will of their own; they are a mere diplomatic body, and are always obsequious to the views of the States, who are always encroaching on the authority of the United States. A provision for harmony among the States, as in trade, naturalization, etc.; for crushing rebellion, whenever it may rear its crest, and for certain other general benefits, must be made.
The powers for these purposes can never be given to a body inadequate as Congress are in point of representation, elected in the mode in which they are, and possessing no more confidence than they do: for, notwithstanding what has been said to the contrary, his own experience satisfied him that a rooted distrust of Congress pretty generally prevailed. A National Government alone, properly constituted, will answer the purpose; and he begged it to be considered that the present is the last moment for establishing one. After this select experiment, the people will yield to despair.
The Committee rose and the House adjourned.
- 1. William Patterson, New Jersey
- 2. Edmund J. Randolph, Virginia
- 3. John Lansing Jr., New York
- 4. The aim of “proportional representation” is that the numerical size of each political district should be roughly equal or “proportional” to the number of residents. Although representation of the people did take place in England, it was more in the form of “rotten boroughs” where there were huge disparities in the number of people contained in each district.
- 5. James Wilson, Pennsylvania
- 6. These two states and Delaware and Connecticut, all small states, joined with New York in opposing the Virginia Plan. See Madison’s note in The Three-Fifths Clause and Fedeal Representation.
- 7. legal term referring to the process of combining the property of different individuals so it can be divided equally
- 8. Charles Pinckney, South Carolina
- 9. Oliver Ellsworth, Connecticut

Conversation-based seminars for collegial PD, one-day and multi-day seminars, graduate credit seminars (MA degree), online and in-person.



































































































































































![Finley, A. (1829) Pennsylvania. Philada. [Map] Retrieved from the Library of Congress, https://www.loc.gov/item/98688548/.](/content/uploads/2024/02/Map-of-PA--273x190.jpg)