No related resources
Introduction
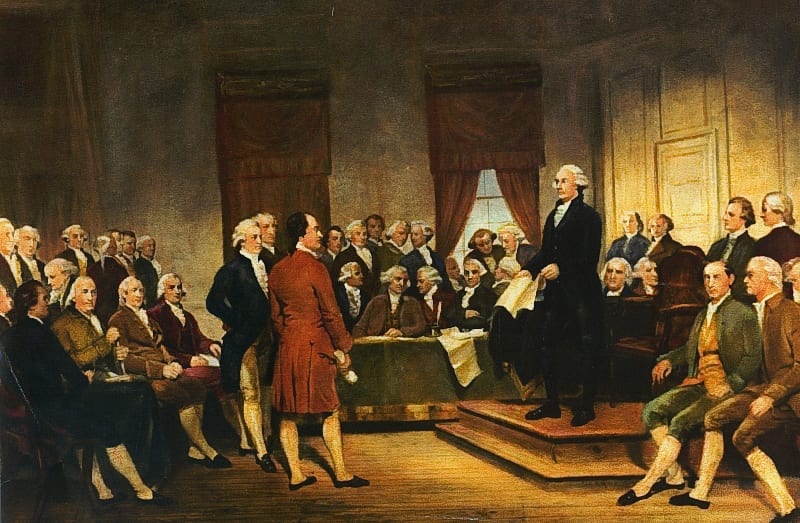
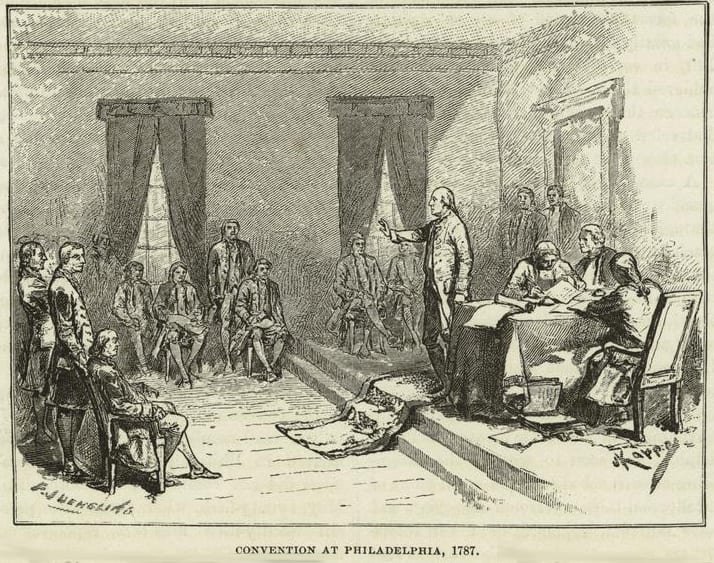
The American Revolution and the Declaration of Independence did much to weaken the institution of slavery in the United States (See Commonwealth v. Nathaniel Jennison), but it still existed when the delegates met in Philadelphia to draft a new constitution. The meeting had come about because of a sense among many people that the new nation needed a stronger union among the states if Americans were to achieve the lofty goals of the Revolution. There was general agreement among the delegates that slavery contradicted those goals. Even some southerners spoke of the evils of slavery. But slavery existed, and southern delegates, especially those from South Carolina and Georgia, made clear that there would be no union at all unless the new constitution accommodated slavery.
Slavery came up in the deliberations of the delegates in several ways. One of those was during the discussion of representation. The discussion turned on two questions. First, should representation be proportional to population in both houses, or should the Senate represent not population but the states? Second, which persons resident in the United States should be counted in deciding representation in the House of Representatives? The excerpts presented below focus on the second question. The excerpts show the delegates presenting arguments for and against a variety of options. Early in the discussion, representatives from the lower South (North Carolina, South Carolina, and Georgia) raised the issue of counting slaves for purposes of representation, arguing that property ownership, and not population, should determine the number of representatives each state sent to the House. The proposal made clear that for these southern delegates, protecting slavery was a condition for remaining in the government the delegates were devising. A number of the other delegates objected to counting enslaved inhabitants. As the southern delegates continued to press the issue, the delegates considered the idea of counting free inhabitants and “three fifths of all other persons” as a compromise basis for representation.
In considering this compromise and the arguments raised for and against it, we should keep two things in mind. At certain points in the discussion, delegates considered counting only white inhabitants fully and counting three fifths of all others, including both free and enslaved African Americans. The delegates did not choose that course. As adopted, the Constitution read “representatives. . . shall be apportioned among the several states . . . according to their respective numbers which shall be determined by adding the whole number of free persons, including those bound to service for a term of years, and excluding Indians not taxed, three fifths of all other persons.” It would thus be inaccurate to say that the three-fifths clause meant that the delegates considered every African American to be only three fifths of a white person, since free African Americans were counted as whole persons. Second, since southern delegates proposed counting slaves the same as free inhabitants, the three-fifths compromise was less than the slaveholders asked for, and to that extent was a limitation on the slave states’ power in national politics.
Even after the compromise was approved by the majority of state delegations, it continued to grate on a number of delegates. We include in these excerpts a later discussion of representation that contains comments by various delegates on the implications of the compromise.
During the time that the delegates discussed the three-fifths clause, the Northwest Ordinance passed in Congress (July 13, 1787). Article 6 of the Ordinance declared that “there shall be neither slavery nor involuntary servitude in the said territory, otherwise than in the punishment of crimes whereof the party shall have been duly convicted.”
Source: Debates in the Federal Convention of 1787 by James Madison, a Member, ed. Gordon Lloyd (Ashland, OH: Ashbrook Center, 2014), 66, 69–70, 79–81, 209, 210, 215–216, 217–221, 224–226, 330–333
June 11
… Mr. SHERMAN1 proposed that the proportion of suffrage in the first branch2 should be according to the respective numbers of free inhabitants; and that in the second branch, or Senate, each state should have one vote and no more. He said, as the states would remain possessed of certain individual rights, each state ought to be able to protect itself; otherwise, a few large states will rule the rest. The House of Lords in England, he observed, had certain particular rights under the constitution, and hence they have an equal vote with the House of Commons, that they may be able to defend their rights.
Mr. RUTLEDGE3 proposed that the proportion of suffrage in the first branch should be according to the quotas of contribution. The justice of this rule, he said, could not be contested. Mr. BUTLER4 urged the same idea; adding, that money was power; and that the states ought to have weight in the government in proportion to their wealth.
Mr. KING5 and Mr. WILSON6 moved “that the right of suffrage in the first branch of the national legislature ought not to be according to the rule established in the Articles of Confederation,7 but according to some equitable ratio of representation.” The clause, so far as it related to suffrage in the first branch, was postponed in order to consider this motion.
Mr. DICKINSON8 contended for the actual contributions of the states, as the rule of their representation and suffrage in the first branch. By thus connecting the interests of the states with their duty, the latter would be sure to be performed.
Mr. KING remarked that it was uncertain what mode might be used in levying a national revenue; but that it was probable, imposts would be one source of it. If the actual contributions were to be the rule, the nonimporting states, as Connecticut and New Jersey, would be in a bad situation, indeed. It might so happen that they would have no representation. . . .
It was then moved by Mr. RUTLEDGE, seconded by Mr. BUTLER, to add to the words “equitable ratio of representation,” at the end of the motion just agreed to, the words “according to the quotas of contribution.”
On motion of Mr. WILSON, seconded by Mr. PINCKNEY,9 this was postponed, in order to add, after the words “equitable ratio of representation” the words following: “in proportion to the whole number of white and other free citizens and inhabitants of every age, sex, and condition, including those bound to servitude for a term of years, and three fifths of all other persons not comprehended in the foregoing description, except Indians not paying taxes, in each state”—this being the rule in the act of Congress, agreed to by eleven states, for apportioning quotas of revenue on the states, and requiring a census only every five, seven, or ten years.10
Mr. GERRY11 thought property not the rule of representation. Why, then, should the blacks, who were property in the South, be in the rule of representation more than the cattle and horses of the North? . . .
Mr. SHERMAN moved that a question be taken, whether each state shall have one vote in the second branch. Everything, he said, depended on this. The smaller states would never agree to the plan on any other principle than an equality of suffrage in this branch. Mr. ELLSWORTH12 seconded the motion. . . .
… Mr. GORHAM13 made a report, which was postponed till tomorrow, to give an opportunity for other plans to be proposed—the report was in the words following:. . .
- Resolved, that the rights of suffrage in the first branch of the national legislature, ought not to be according to the rule established in the Articles of Confederation, but according to some equitable ratio of representation, namely, in proportion to the whole number of white and other free citizens and inhabitants, of every age, sex, and condition, including those bound to servitude for a term of years, and three-fifths of all other persons, not comprehended in the foregoing description, except Indians not paying taxes, in each state.
- Resolved, that the right of suffrage in the second branch of the national legislature ought to be according to the rule established for the first. . . .
July 11
Mr. WILLIAMSON14. . .moved . . .“that in order to ascertain the alterations that may happen in the population and wealth of the several states, a census shall be taken of the free white inhabitants, and three fifths of those of other descriptions on the first year after this government shall have been adopted, and every __ year thereafter; and that the representation be regulated accordingly.”
. . . Mr. BUTLER and General PINCKNEY15 insisted that blacks be included in the rule of representation equally with the whites; and for that purpose moved that the words “three fifths” be struck out.
Mr. GERRY thought that three fifths of them was, to say the least, the full proportion that could be admitted.
Mr. GORHAM. This ratio was fixed by Congress as a rule of taxation. Then it was urged, by the delegates representing the states having slaves, that the blacks were still more inferior to freemen. At present, when the ratio of representation is to be established, we are assured that they are equal to freemen. The arguments on the former occasion had convinced him that three fifths was pretty near the just proportion, and he should vote according to the same opinion now.
Mr. BUTLER insisted that the labor of a slave in South Carolina was as productive and valuable as that of a freeman in Massachusetts; that as wealth was the great means of defense and utility to the nation, they were equally valuable to it with freemen; and that consequently an equal representation ought to be allowed for them in a government which was instituted principally, for the protection of property, and was itself to be supported by property. . . .
. . . Mr. WILLIAMSON reminded Mr. GORHAM that if the southern states contended for the inferiority of blacks to whites when taxation was in view, the eastern states, on the same occasion, contended for their equality. He did not, however, either then or now, concur in either extreme, but approved of the ratio of three fifths.
On Mr. BUTLER’S motion, for considering blacks as equal to whites in the apportionment of representation: Delaware, South Carolina, Georgia, aye—3; Massachusetts, Connecticut, New Jersey, Pennsylvania, Maryland, Virginia, North Carolina, no—7; New York, not on the floor. . . .
Mr. KING, being much opposed to fixing numbers as the rule of representation, was particularly so on account of the blacks. He thought the admission of them along with whites at all, would excite great discontents among the states having no slaves. He had never said, as to any particular point, that he would in no event acquiesce in and support it; but he would say that if in any case such a declaration was to be made by him, it would be in this. He remarked that in the temporary allotment of representatives made by the committee, the southern states had received more than the number of their white and three fifths of their black inhabitants entitled them to. . . .
Mr. GORHAM . . .recollected that when the proposition of Congress for changing the eighth article of the Confederation was before the legislature of Massachusetts, the only difficulty then was, to satisfy them that the negroes ought not to have been counted equally with the whites, instead of being counted in the ratio of three fifths only.
Mr. WILSON did not well see on what principle the admission of blacks in the proportion of three fifths could be explained. Are they admitted as citizens—then why are they not admitted on an equality with white citizens? Are they admitted as property—then why is not other property admitted into the computation? These were difficulties, however, which he thought must be overruled by the necessity of compromise. He had some apprehensions also, from the tendency of the blending of the blacks with the whites, to give disgust to the people of Pennsylvania. . . .
Mr. GOUVERNEUR MORRIS16 was compelled to declare himself reduced to the dilemma of doing injustice to the southern states or to human nature; and he must therefore do it to the former. For he could never agree to give such encouragement to the slave trade, as would be given by allowing them a representation for their negroes; and he did not believe those states would ever confederate on terms that would deprive them of that trade. On the question for agreeing to include three fifths of the blacks: Connecticut, Virginia, North Carolina, Georgia, aye—4; Massachusetts, New Jersey, Pennsylvania, Delaware, Maryland, South Carolina, no—6. . . .
July 12
Mr. GOUVERNEUR MORRIS moved to add to the clause empowering the legislature to vary the representation according to the principles of wealth and numbers of inhabitants, a proviso “that taxation shall be in proportion to representation.”
Mr. BUTLER contended again, that representation should be according to the full number of inhabitants including all the blacks.
Mr. MASON17 also admitted the justice of the principle, but was afraid embarrassments might be occasioned to the legislature by it. . . .
Mr. GOUVERNEUR MORRIS admitted that some objections lay against his motion, but supposed they would be removed by restraining the rule to direct taxation. . . .
General PINCKNEY liked the idea. . . . He was alarmed at what was said yesterday, concerning the negroes. . . .
… Mr. DAVIE18 said it was high time now to speak out. He saw that it was meant by some gentlemen to deprive the southern states of any share of representation for their blacks. He was sure that North Carolina would never confederate on any terms that did not rate them at least as three fifths. If the eastern states meant, therefore, to exclude them altogether, the business was at an end. . . .
Mr. GOUVERNEUR MORRIS. It had been said that it is high time to speak out. As one member, he would candidly do so. He came here to form a compact for the good of America. He was ready to do so with all the states. He hoped and believed that all would enter into such a compact. If they would not, he was ready to join with any states that would. But as the compact was to be voluntary, it is in vain for the eastern states to insist on what the southern states will never agree to. It is equally vain for the latter to require what the other states can never admit; and he verily believed the people of Pennsylvania will never agree to a representation of negroes. What can be desired by these states more than has been already proposed—that the legislature shall from time to time regulate representation according to population and wealth?
General PINCKNEY desired that the rule of wealth should be ascertained, and not left to the pleasure of the legislature; and that property in slaves should not be exposed to danger, under a government instituted for the protection of property.
. . . Mr. ELLSWORTH. . .moved to add to the last clause adopted by the House the words following, “and that the rule of contribution by direct taxation, for the support of the government of the United States, shall be the number of white inhabitants and three fifths of every other description in the several states, until some other rule that shall more accurately ascertain the wealth of the several states can be devised and adopted by the legislature.”
Mr. BUTLER seconded the motion, in order that it might be committed.
Mr. RANDOLPH was not satisfied with the motion. . . . He proposed, in lieu of Mr. ELLSWORTH’s motion, “that in order to ascertain the alterations in representation that may be required, from time to time, by changes in the relative circumstances of the states, a census shall be taken within two years from the first meeting of the General Legislature of the United States, and once within the term of every _ years afterward, of all the inhabitants, in the manner and according to the ratio recommended by Congress in their Resolution of the eighteenth day of April, 1783 (rating the blacks at three fifths of their number); and that the legislature of the United States shall arrange the representation accordingly.” He urged strenuously that express security ought to be provided for including slaves in the ratio of representation. He lamented that such a species of property existed. But as it did exist, the holders of it would require this security. It was perceived that the design was entertained by some of excluding slaves altogether; the legislature therefore ought not to be left at liberty.
Mr. ELLSWORTH withdraws his motion, and seconds that of Mr. RANDOLPH.
Mr. WILSON observed that less umbrage would perhaps be taken against an admission of the slaves into the rule of representation, if it should be so expressed as to make them indirectly only an ingredient in the rule, by saying that they should enter into the rule of taxation; and as representation was to be according to taxation, the end would be equally attained. He accordingly moved, and was seconded, so to alter the last clause adopted by the House that, together with the amendment proposed, the whole should read as follows: “provided always that the representation ought to be proportioned according to direct taxation; and in order to ascertain the alterations in the direct taxation which may be required from time to time by the changes in the relative circumstances of the states, resolved, that a census be taken within two years from the first meeting of the legislature of the United States, and once within the term of every _ years afterward, of all the inhabitants of the United States, in the manner and according to the ratio recommended by Congress in their resolution of the eighteenth day of April 1783; and that the legislature of the United States shall proportion the direct taxation accordingly.”
Mr. KING. Although this amendment varies the aspect somewhat, he had still two powerful objections against tying down the legislature to the rule of numbers—first, they were at this time an uncertain index of the relative wealth of the states; secondly, if they were a just index at this time, it cannot be supposed always to continue so. He was far from wishing to retain any unjust advantage whatever in one part of the Republic. If justice was not the basis of the connection, it could not be of long duration. He must be short-sighted indeed who does not foresee, that, whenever the southern states shall be more numerous than the northern, they can and will hold a language that will awe them into justice. If they threaten to separate now in case injury shall be done them, will their threats be less urgent or effectual when force shall back their demands? Even in the intervening period there will be no point of time at which they will not be able to say, do us justice or we will separate. He urged the necessity of placing confidence, to a certain degree in every government, and did not conceive that the proposed confidence, as to a periodical readjustment of the representation, exceeded that degree.
Mr. PINCKNEY moved to amend Mr. RANDOLPH’S motion, so as to make “blacks equal to the whites in the ratio of representation.” This, he urged, was nothing more than justice. The blacks are the laborers, the peasants, of the southern states. They are as productive of pecuniary resources as those of the northern states. They add equally to the wealth, and, considering money as the sinew of war, to the strength, of the nation. It will also be politic with regard to the northern states, as taxation is to keep pace with representation.
. . . On Mr. PINCKNEY’S motion, for rating blacks as equal to whites, instead of as three fifths: South Carolina, Georgia, aye—2; Massachusetts, Connecticut (Doctor JOHNSON, aye), New Jersey, Pennsylvania (three against two), Delaware, Maryland, Virginia, North Carolina, no—8. . . .
On the question on the whole proposition, as proportioning representation to direct taxation, and both to the white and three fifths of the black inhabitants, and requiring a census within six years, and within every ten years afterward: Connecticut, Pennsylvania, Maryland, Virginia, North Carolina, Georgia, aye—6; New Jersey, Delaware, no—2; Massachusetts, South Carolina, divided.
July 13
. . .On the motion of Mr. RANDOLPH, the vote of Monday last, authorizing the legislature to adjust, from time to time, the representation upon the principles of wealth and numbers of inhabitants, was reconsidered by common consent, in order to strike out wealth and adjust the resolution to that requiring periodical revisions according to the number of whites and three fifths of the blacks.
The motion was in the words following: “But as the present situation of the states may probably alter in the number of their inhabitants, that the legislature of the United States be authorized, from time to time, to apportion the number of representatives; and in case any of the states shall hereafter be divided, or any two or more states united, or new states created within the limits of the United States, the legislature of the United States shall possess authority to regulate the number of representatives in any of the foregoing cases, upon the principle of their number of inhabitants, according to the provisions hereafter mentioned.”
Mr. GOUVERNEUR MORRIS opposed the alteration, as leaving still an incoherence. If negroes were to be viewed as inhabitants, and the revision was to proceed on the principle of numbers of inhabitants, they ought to be added in their entire number, and not in the proportion of three fifths. If as property, the word “wealth” was right; and striking it out would produce the very inconsistency which it was meant to get rid of. The train of business, and the late turn which it had taken, had led him, he said, into deep meditation on it, and he would candidly state the result. A distinction had been set up, and urged, between the northern and southern states. He had hitherto considered this doctrine as heretical. He still thought the distinction groundless. He sees, however, that it is persisted in; and the southern gentlemen will not be satisfied unless they see the way open to their gaining a majority in the public councils. The consequence of such a transfer of power from the maritime to the interior and landed interest will, he foresees, be such an oppression to commerce, that he shall be obliged to vote for the vicious principle of equality in the second branch, in order to provide some defense for the northern states against it. But, to come more to the point, either this distinction is fictitious or real; if fictitious, let it be dismissed, and let us proceed with due confidence. If it be real, instead of attempting to blend incompatible things, let us at once take a friendly leave of each other. . . .
Mr. BUTLER. The security the southern states want is that their negroes may not be taken from them, which some gentlemen within or without doors have a very good mind to do. . . .
On the question to strike out “wealth,” and to make the change as moved by Mr. RANDOLPH, it passed in the affirmative: Massachusetts, Connecticut, New Jersey, Pennsylvania, Maryland, Virginia, North Carolina, South Carolina, Georgia, aye—9; Delaware, divided. . . .
August 8
. . .Article 4, sect. 4, was then taken up.19
Mr. WILLIAMSON moved to strike out “according to the provisions hereinafter made,” and to insert the words “according to the rule hereafter to be provided for direct taxation.” See Art. 7, sect. 3. On the question for agreeing to Mr. WILLIAMSON’S amendment: New Hampshire, Massachusetts, Connecticut, Pennsylvania, Maryland, Virginia, North Carolina, South Carolina, Georgia, aye—9; New Jersey, Delaware, no—2.
Mr. KING wished to know what influence the vote just passed was meant to have on the succeeding part of the report, concerning the admission of slaves into the rule of representation. He could not reconcile his mind to the article if it was to prevent objections to the latter part. The admission of slaves was a most grating circumstance to his mind, and he believed would be so to a great part of the people of America. He had not made a strenuous opposition to it heretofore, because he had hoped that this concession would have produced a readiness, which had not been manifested, to strengthen the general government, and to mark a full confidence in it. The report under consideration had, by the tenor of it, put an end to all those hopes. In two great points the hands of the legislature were absolutely tied. The importation of slaves could not be prohibited.20 Exports could not be taxed. Is this reasonable? What are the great objects of the general system? First, defense against foreign invasion; secondly, against internal sedition. Shall all the states, then, be bound to defend each, and shall each be at liberty to introduce a weakness which will render defense more difficult? Shall one part of the United States be bound to defend another part, and that other part be at liberty not only to increase its own danger, but to withhold the compensation for the burden? If slaves are to be imported, shall not the exports produced by their labor supply a revenue the better to enable the general government to defend their masters? There was so much inequality and unreasonableness in all this, that the people of the northern states could never be reconciled to it. No candid man could undertake to justify it to them. He had hoped that some accommodation would have taken place on this subject; that at least a time would have been limited for the importation of slaves. He never could agree to let them be imported without limitation, and then be represented in the national legislature. Indeed, he could so little persuade himself of the rectitude of such a practice that he was not sure he could assent to it under any circumstances. At all events, either slaves should not be represented, or exports should be taxable.
Mr. SHERMAN regarded the slave trade as iniquitous; but the point of representation having been settled, after much difficulty and deliberation, he did not think himself bound to make opposition; especially as the present article, as amended, did not preclude any arrangement whatever on that point, in another place of the report.
Mr. MADISON21 objected to one for every forty thousand inhabitants as a perpetual rule. The future increase of population, if the Union should be permanent, will render the number of representatives excessive.
Mr. GORHAM. It is not to be supposed that the government will last so long as to produce this effect. Can it be supposed that this vast country, including the western territory, will, one hundred and fifty years hence, remain one nation?
Mr. ELLSWORTH. If the government should continue so long, alterations may be made in the Constitution in the manner proposed in a subsequent article.
Mr. SHERMAN and Mr. MADISON moved to insert the words “not exceeding” before the words “one for every forty thousand”; which was agreed to, nem. con.22
Mr. GOUVERNEUR MORRIS moved to insert “free” before the word “inhabitants.” Much, he said, would depend on this point. He never would concur in upholding domestic slavery. It was a nefarious institution. It was the curse of Heaven on the states where it prevailed. Compare the free regions of the middle states, where a rich and noble cultivation marks the prosperity and happiness of the people, with the misery and poverty which overspread the barren wastes of Virginia, Maryland, and the other states having slaves. Travel through the whole continent, and you behold the prospect continually varying with the appearance and disappearance of slavery. The moment you leave the eastern states and enter New York, the effects of the institution become visible. Passing through the Jerseys and entering Pennsylvania, every criterion of superior improvement witnesses the change. Proceed southwardly, and every step you take, through the great regions of slaves, presents a desert increasing with the increasing proportion of these wretched beings. Upon what principle is it that the slaves shall be computed in the representation? Are they men? Then make them citizens and let them vote. Are they property? Why, then, is no other property included? The houses in this city (Philadelphia) are worth more than all the wretched slaves who cover the rice swamps of South Carolina. The admission of slaves into the representation, when fairly explained, comes to this—that the inhabitant of Georgia and South Carolina who goes to the coast of Africa and, in defiance of the most sacred laws of humanity, tears away his fellow creatures from their dearest connections, and damns them to the most cruel bondage, shall have more votes in a government instituted for protection of the rights of mankind than the citizen of Pennsylvania or New Jersey, who views with a laudable horror so nefarious a practice. He would add that domestic slavery is the most prominent feature in the aristocratic countenance of the proposed constitution. The vassalage of the poor has ever been the favorite offspring of aristocracy. And what is the proposed compensation to the northern states for a sacrifice of every principle of right, of every impulse of humanity? They are to bind themselves to march their militia for the defense of the southern states, for their defense against those very slaves of whom they complain. They must supply vessels and seamen in case of foreign attack. The legislature will have indefinite power to tax them by excises, and duties on imports; both of which will fall heavier on them than on the southern inhabitants; for the Bohea tea23 used by a northern freeman will pay more tax than the whole consumption of the miserable slave, which consists of nothing more than his physical subsistence and the rag that covers his nakedness. On the other side, the southern states are not to be restrained from importing fresh supplies of wretched Africans, at once to increase the danger of attack and the difficulty of defense; nay, they are to be encouraged to it, by an assurance of having their votes in the national government increased in proportion: and are, at the same time, to have their exports and their slaves exempt from all contributions for the public service. Let it not be said that direct taxation is to be proportioned to representation. It is idle to suppose that the general government can stretch its hand directly into the pockets of the people, scattered over so vast a country. They can only do it through the medium of exports, imports, and excises. For what, then, are all the sacrifices to be made? He would sooner submit himself to a tax for paying for all the negroes in the United States than saddle posterity with such a Constitution.
Mr. DAYTON24 seconded the motion. He did it, he said, that his sentiments on the subject might appear, whatever might be the fate of the amendment.
Mr. SHERMAN did not regard the admission of the negroes into the ratio of representation as liable to such insuperable objections. It was the freemen of the southern states who were, in fact, to be represented according to the taxes paid by them, and the negroes are only included in the estimate of the taxes. This was his idea of the matter.
Mr. PINCKNEY considered the fisheries and the western frontier as more burdensome to the United States than the slaves. He thought this could be demonstrated, if the occasion were a proper one. . . .
- 1. Roger Sherman, Connecticut.
- 2. What became the House of Representatives.
- 3. John Rutledge, South Carolina.
- 4. Pierce Butler, South Carolina.
- 5. Rufus King, Massachusetts.
- 6. James Wilson, Pennsylvania.
- 7. In the Articles of Confederation, each state had one vote.
- 8. John Dickinson, Delaware.
- 9. Charles Pinckney, South Carolina.
- 10. Wilson (Pennsylvania), seconded by Pinckney (South Carolina) introduced the three-fifths clause into the debate. As Wilson’s remark indicates, the idea of proportioning representation in part by counting slaves as three fifths of free inhabitants had its roots in the way the Confederation Congress had apportioned financial support of the general government. Under the Articles of Confederation, representation was not the issue in counting slaves as three fifths of free inhabitants, because each state had one vote. The issue was a revenue formula. As Richard Beeman remarked, “the fraction ‘three-fifths’ was intended as a rough approximation of the measure of wealth that an individual slave contributed to the economy of his or her state” (Plain, Honest Men: The Making of the American Constitution [New York: Random House, 2009], 154). At the Constitutional Convention, in order to prompt resolution of one of the issues involved in representation, Wilson applied in a new context a concept the delegates were familiar with.
- 11. Elbridge Gerry, Massachusetts.
- 12. Oliver Ellsworth, Connecticut.
- 13. Nathaniel Gorham, Massachusetts.
- 14. Hugh Williamson, North Carolina.
- 15. Charles Cotesworth Pinckney, South Carolina.
- 16. Gouverneur Morris, Pennsylvania.
- 17. George Mason, Virginia.
- 18. William Davie, North Carolina.
- 19. Article IV, section 4 of the Committee of Detail Report, an early draft of the Constitution. Section 4 read: As the proportions of numbers in different states will alter from time to time; as some of the states may hereafter be divided: as others may be enlarged by addition of territory; as two or more states may be united; as new states will be erected within the limits of the United States, the legislature shall, in each of these cases, regulate the number of representatives by the number of inhabitants, according to the provisions hereinafter made, at the rate of one for every forty thousand.
- 20. In the Constitution as finally adopted and ratified, the importation of slave could not be prohibited for twenty years.
- 21. James Madison, Virginia.
- 22. nem. con is an abbreviation for nemine contradicente, which means no one disagreeing.
- 23. The most commonly consumed tea in America.
- 24. Jonathan Dayton, New Jersey.
The Gerry Committee Report
July 05, 1787
Conversation-based seminars for collegial PD, one-day and multi-day seminars, graduate credit seminars (MA degree), online and in-person.




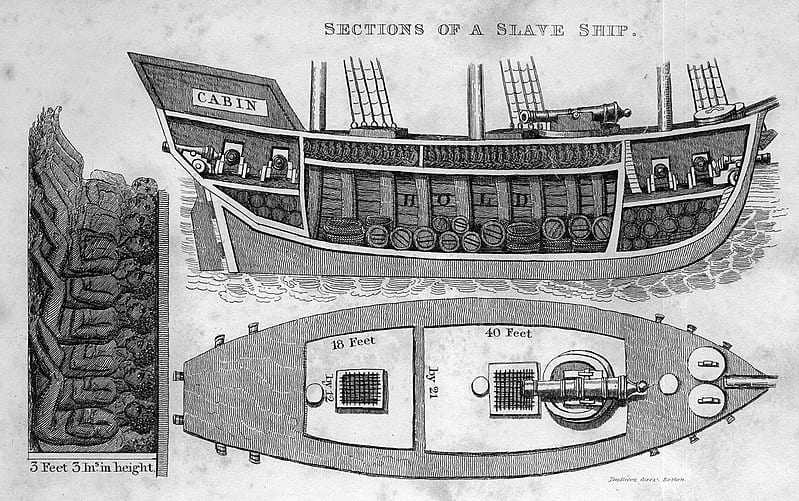






























































































































































![Finley, A. (1829) Pennsylvania. Philada. [Map] Retrieved from the Library of Congress, https://www.loc.gov/item/98688548/.](/content/uploads/2024/02/Map-of-PA--273x190.jpg)