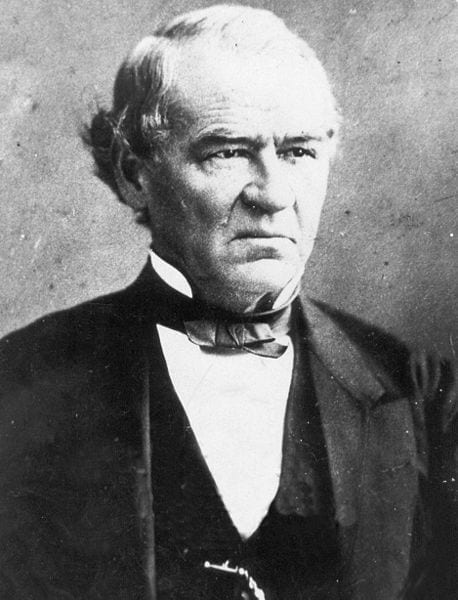No related resources
Introduction
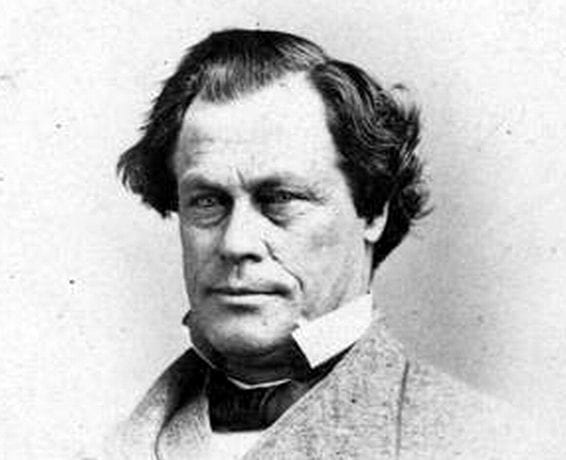
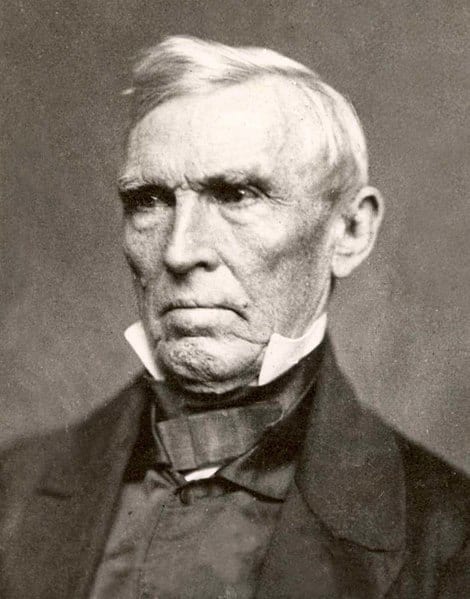
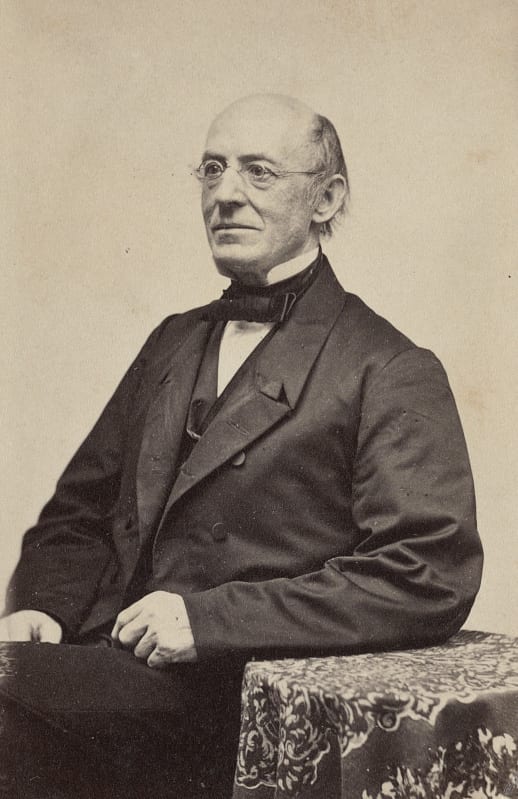
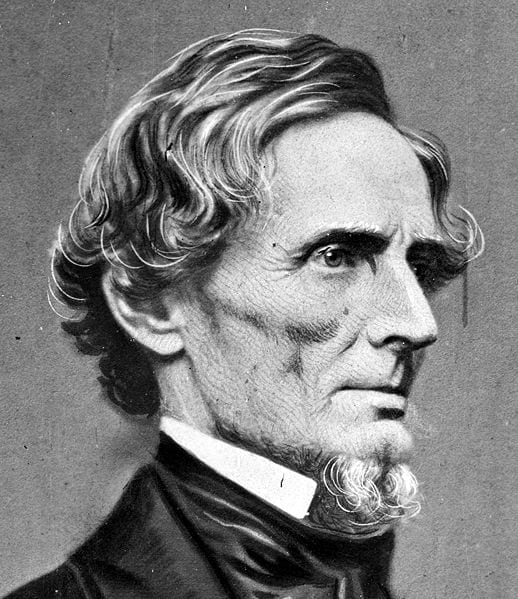
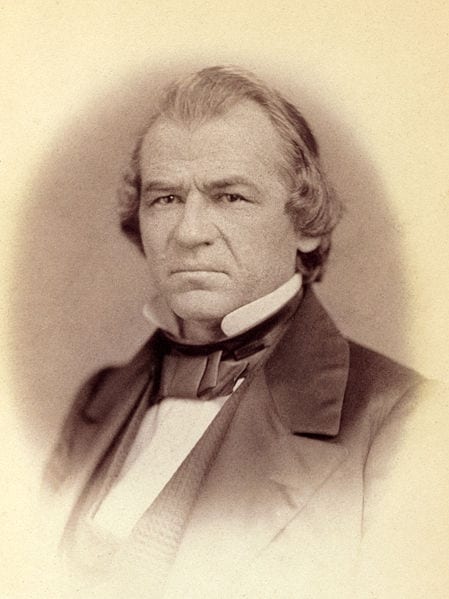
Alexander Stephens (1812–1883) served in various offices in the Georgia state government and also in the House of Representatives in Washington, DC. For most of his career Stephens was a Whig, the party to which Abraham Lincoln belonged, and the two served together in the same Congress. While he was a congressman, Lincoln praised a speech that Stephens gave against the war with Mexico. But the two men disagreed strongly on the issue of slavery. Stephens, like Lincoln, was a Unionist, but he was also a supporter of slavery. When forced to choose between the Union and slavery, Stephens went over to the secession movement and became the vice president of the Confederate States of America.
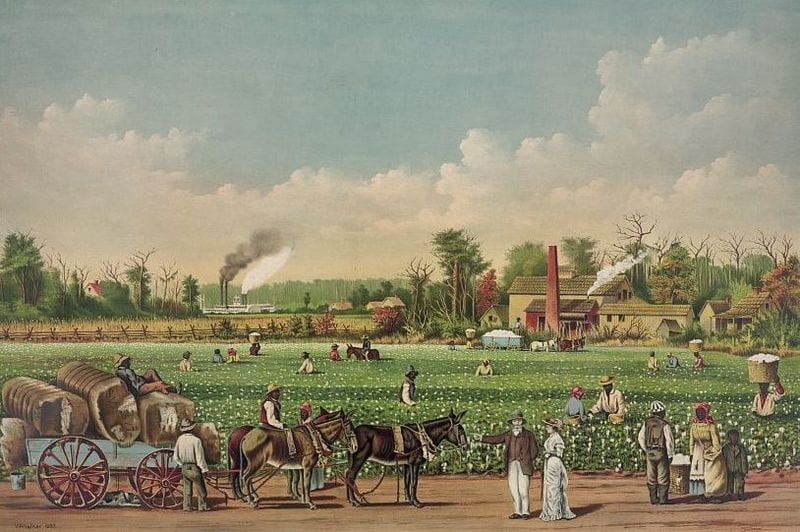
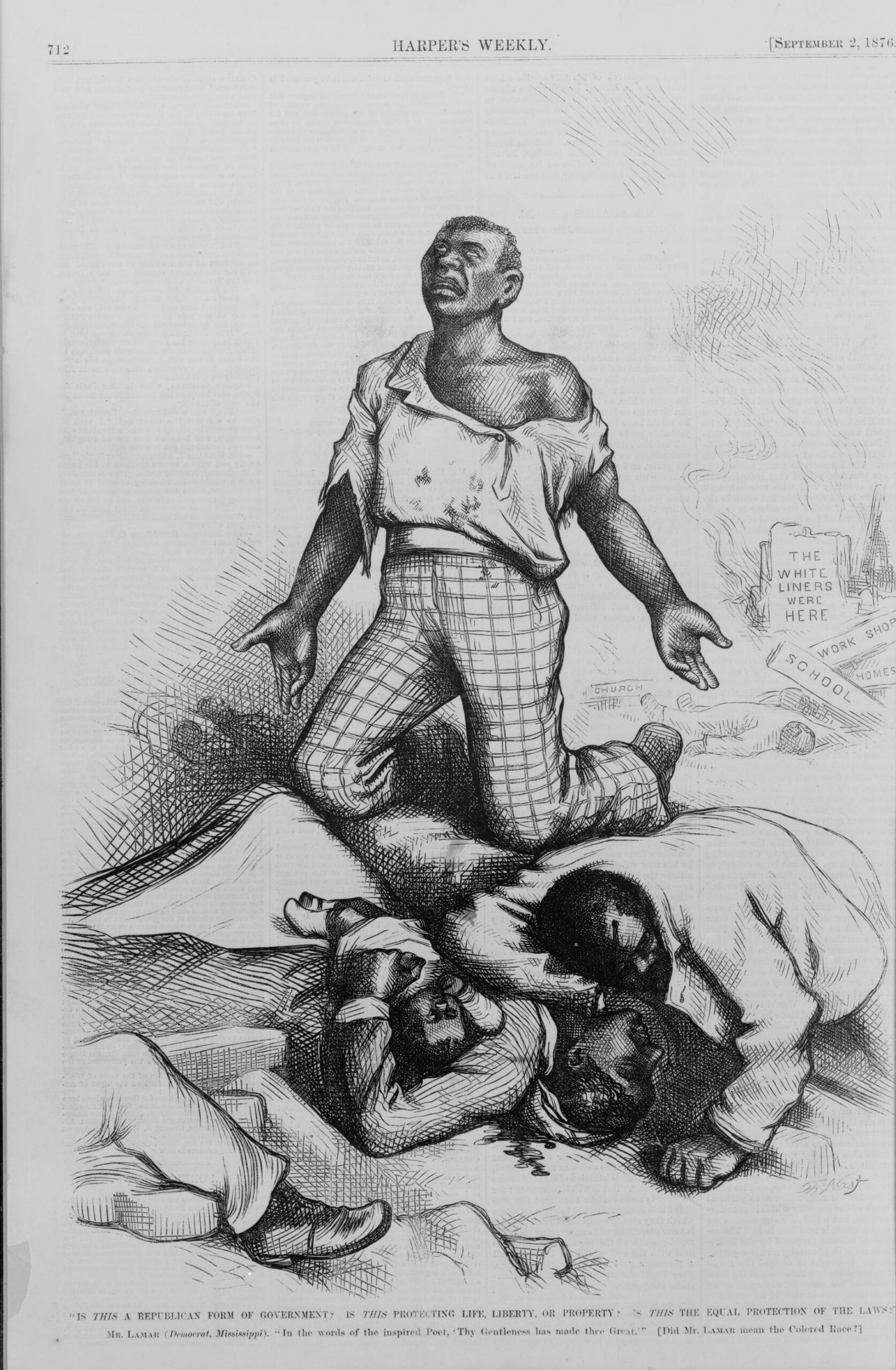
Speaking before a raucous crowd in Savannah, Georgia, a few weeks after Lincoln’s inauguration, Stephens passionately declared that the Confederacy was explicitly founded on slavery and white supremacy, thereby forever undercutting the view still espoused by many southerners, and some northerners, that the Civil War was fought to preserve not slavery but states’ rights, and to oppose northern tyranny. Stephens’ speech is noteworthy for two other reasons. First, he acknowledged that Thomas Jefferson and the other Founders believed that all men, including Africans, were equal, but argued that that they had been mistaken. Second, the Founders were wrong because inequality was in accord not just with the Bible and God’s providence, but with the scientific understanding of the world. The Confederacy, Stephens claimed, was the first government based on this “physical, philosophical, and moral truth.” Jefferson, in his final letter (1826), declared that “the light of science has already laid open to every view the palpable truth, that the mass of mankind has not been born with saddles on their backs, nor a favored few booted and spurred, ready to ride them legitimately, by the grace of God.” In making his contrary claim, Stephens was apparently swayed by the studies of race that gained influence in the years after Jefferson’s death. This scientific racism remained influential in the United States and the world well into the twentieth century.
The text of the speech reprinted here is from a newspaper reporter’s account and opens and closes with the reporter’s comments.
Source: Alexander H. Stephens, in Public and Private, with Letters and Speeches, before, during and since the War, ed. Henry Cleveland (Philadelphia: National Publishing Company, 1866), 717–728, available at https://archive.org/details/alexanderhstephe6114clev/page/n9/mode/2up.
At half past seven o’clock on Thursday evening, the largest audience ever assembled at the Athenaeum was in the house, waiting most impatiently for the appearance of the orator of the evening, Hon. A. H. Stephens, Vice President of the Confederate States of America. The committee, with invited guests, were seated on the stage when, at the appointed hour, the Hon. C. C. Jones, Mayor, and the speaker entered, and were greeted by the immense assemblage with deafening rounds of applause. . . .
. . .[W]e are passing through one of the greatest revolutions in the annals of the world. Seven states have within the last three months thrown off an old government and formed a new. This revolution has been signally marked, up to this time, by the fact of its having been accomplished without the loss of a single drop of blood.
This new constitution, or form of government, constitutes the subject to which your attention will be partly invited. In reference to it, I make this first general remark: it amply secures all our ancient rights, franchises, and liberties. All the great principles of Magna Charta are retained in it. No citizen is deprived of life, liberty, or property, but by the judgment of his peers under the laws of the land. The great principle of religious liberty, which was the honor and pride of the old Constitution, is still maintained and secured. All the essentials of the old Constitution, which have endeared it to the hearts of the American people, have been preserved and perpetuated. Some changes have been made. Some of these I should have preferred not to have seen made; but other important changes do meet my cordial approbation. They form great improvements upon the old Constitution. So, taking the whole new constitution, I have no hesitancy in giving it as my judgment that it is decidedly better than the old.
Allow me briefly to allude to some of these improvements . . .
But not to be tedious in enumerating the numerous changes for the better, allow me to allude to one other though last, not least. The new constitution has put at rest, forever, all the agitating questions relating to our peculiar institution—African slavery as it exists amongst us—the proper status of the negro in our form of civilization. This was the immediate cause of the late rupture and present revolution. Jefferson in his forecast, had anticipated this, as the “rock upon which the old Union would split.”1 He was right. What was conjecture with him, is now a realized fact. But whether he fully comprehended the great truth upon which that rock stood and stands, may be doubted. The prevailing ideas entertained by him and most of the leading statesmen at the time of the formation of the old Constitution, were that the enslavement of the African was in violation of the laws of nature; that it was wrong in principle, socially, morally, and politically. It was an evil they knew not well how to deal with, but the general opinion of the men of that day was that, somehow or other in the order of Providence, the institution would be evanescent and pass away. This idea, though not incorporated in the Constitution, was the prevailing idea at that time. The Constitution, it is true, secured every essential guarantee to the institution while it should last, and hence no argument can be justly urged against the constitutional guarantees thus secured, because of the common sentiment of the day. Those ideas, however, were fundamentally wrong. They rested upon the assumption of the equality of races. This was an error. It was a sandy foundation, and the government built upon it fell when the “storm came and the wind blew.”2
Our new government is founded upon exactly the opposite idea; its foundations are laid, its corner-stone rests, upon the great truth that the negro is not equal to the white man; that slavery, subordination to the superior race, is his natural and normal condition. This, our new government, is the first, in the history of the world, based upon this great physical, philosophical, and moral truth. This truth has been slow in the process of its development, like all other truths in the various departments of science. It has been so even amongst us. Many who hear me, perhaps, can recollect well that this truth was not generally admitted, even within their day. The errors of the past generation still clung to many as late as twenty years ago. Those at the North, who still cling to these errors, with a zeal above knowledge, we justly denominate fanatics. All fanaticism springs from an aberration of the mind from a defect in reasoning. It is a species of insanity. One of the most striking characteristics of insanity, in many instances, is forming correct conclusions from fancied or erroneous premises; so with the antislavery fanatics. Their conclusions are right if their premises were. They assume that the negro is equal, and hence conclude that he is entitled to equal privileges and rights with the white man. If their premises were correct, their conclusions would be logical and just, but their premise being wrong, their whole argument fails. I recollect once of having heard a gentleman from one of the northern states, of great power and ability, announce in the House of Representatives, with imposing effect, that we of the South would be compelled, ultimately, to yield upon this subject of slavery, that it was as impossible to war successfully against a principle in politics, as it was in physics or mechanics. That the principle would ultimately prevail. That we, in maintaining slavery as it exists with us, were warring against a principle, a principle founded in nature, the principle of the equality of men. The reply I made to him was, that upon his own grounds, we should, ultimately, succeed, and that he and his associates, in this crusade against our institutions, would ultimately fail. The truth announced, that it was as impossible to war successfully against a principle in politics as it was in physics and mechanics, I admitted; but told him that it was he, and those acting with him, who were warring against a principle. They were attempting to make things equal which the Creator had made unequal.
In the conflict thus far, success has been on our side, complete throughout the length and breadth of the Confederate states. It is upon this, as I have stated, our social fabric is firmly planted; and I cannot permit myself to doubt the ultimate success of a full recognition of this principle throughout the civilized and enlightened world.
As I have stated, the truth of this principle may be slow in development, as all truths are and ever have been, in the various branches of science. It was so with the principles announced by Galileo [and] it was so with Adam Smith and his principles of political economy. It was so with Harvey, and his theory of the circulation of the blood. It is stated that not a single one of the medical profession, living at the time of the announcement of the truths made by him, admitted them. Now, they are universally acknowledged. May we not, therefore, look with confidence to the ultimate universal acknowledgment of the truths upon which our system rests? It is the first government ever instituted upon the principles in strict conformity to nature, and the ordination of Providence, in furnishing the materials of human society. Many governments have been founded upon the principle of the subordination and serfdom of certain classes of the same race; such were and are in violation of the laws of nature. Our system commits no such violation of nature’s laws. With us, all of the white race, however high or low, rich or poor, are equal in the eye of the law. Not so with the negro. Subordination is his place. He, by nature, or by the curse against Canaan,3 is fitted for that condition which he occupies in our system. The architect, in the construction of buildings, lays the foundation with the proper material—the granite; then comes the brick or the marble. The substratum of our society is made of the material fitted by nature for it, and by experience we know that it is best, not only for the superior, but for the inferior race, that it should be so. It is, indeed, in conformity with the ordinance of the Creator. It is not for us to inquire into the wisdom of His ordinances, or to question them. For His own purposes, He has made one race to differ from another, as He has made “one star to differ from another star in glory.”4 The great objects of humanity are best attained when there is conformity to His laws and decrees, in the formation of governments as well as in all things else. Our confederacy is founded upon principles in strict conformity with these laws. This stone which was rejected by the first builders “is become the chief of the corner”5 the real “corner-stone” in our new edifice. I have been asked, what of the future? It has been apprehended by some that we would have arrayed against us the civilized world. I care not who or how many they may be against us, when we stand upon the eternal principles of truth, if we are true to ourselves and the principles for which we contend, we are obliged to, and must triumph.
Thousands of people who begin to understand these truths are not yet completely out of the shell; they do not see them in their length and breadth. We hear much of the civilization and Christianization of the barbarous tribes of Africa. In my judgment, those ends will never be attained, but by first teaching them the lesson taught to Adam, that “in the sweat of his brow he should eat his bread,”6 and teaching them to work, and feed, and clothe themselves. . . .
Reporter’s Note.—Your reporter begs to state that the above is not a perfect report, but only such a sketch of the address of Mr. Stephens as embraces, in his judgment, the most important points presented by the orator.—G.
- 1. This does not appear to be a direct quote from Jefferson.
- 2. Stephens was alluding to Matthew 7:27. He built his speech on the images in Matthew 7:24–27: “Therefore everyone who hears these words of mine and puts them into practice is like a wise man who built his house on the rock. The rain came down, the streams rose, and the winds blew and beat against that house; yet it did not fall, because it had its foundation on the rock. But everyone who hears these words of mine and does not put them into practice is like a foolish man who built his house on sand. The rain came down, the streams rose, and the winds blew and beat against that house, and it fell with a great crash."
- 3. Genesis 9:20–27. Noah cursed Ham’s son Canaan to be a servant because Ham saw Noah naked when Noah was drunk. This was taken by some Christians to justify the enslavement of Africans, although the Bible does not mention skin color.
- 4. 1 Corinthians 15:41.
- 5. Psalm 118:22.
- 6. Genesis 3:19.

Conversation-based seminars for collegial PD, one-day and multi-day seminars, graduate credit seminars (MA degree), online and in-person.